It’s always a little unsettling when your pet—or any animal, really—stares off into space for what seems like forever. They’re focused on something invisible, and it’s easy to wonder, “What’s going on in their minds?” While some animal behaviors have clear explanations, others, like staring at nothing, remain a mystery. These odd moments can leave us scratching our heads, trying to figure out if there’s a deeper meaning behind them.
In this article, we’ll look at 28 animal behaviors that still puzzle scientists, including the strange habit of staring into thin air. From cats to birds, animals seem to have a knack for doing things that make us question what they’re really seeing or feeling. Some of these unexplained behaviors might even reveal more about how animals experience the world around them than we ever imagined.
Hearing High-Frequency Sounds
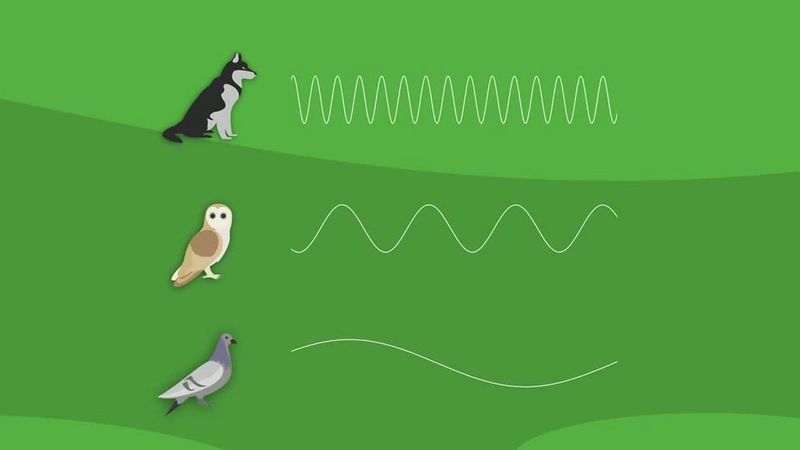

Dogs and cats have a remarkable ability to hear sounds at frequencies far beyond our human range. This acute sense of hearing enables them to pick up on sounds imperceptible to us, such as the faint buzzing of electrical appliances or distant noises from outside.
When an animal suddenly stares at what seems like nothing, they might be tuning into these high-frequency sounds. This natural behavior can often lead them to appear as if they’re engaged with an unseen entity. It’s a fascinating glimpse into how their senses interpret the world around them.
Invisible Insects

Ever notice your cat or dog staring intently at a corner? It might be that they’re observing tiny insects that are invisible to the naked eye. Animals have sharper eyesight when it comes to detecting small movements, which could explain their curious gazes.
This ability to spot minuscule creatures can make it seem like they’re staring at nothing. For animals, these moments are full of intrigue and excitement, offering them a tiny world of wonder that we often overlook in our daily lives.
Reflective Surfaces

Reflective surfaces can captivate animals, leading them to stare or interact with their own reflections. Birds, for example, may peck at windows, mistaking their reflection for another bird.
This behavior is not limited to birds; cats and dogs can also be drawn to mirrors or shiny surfaces. Their fascination with reflections can cause them to spend considerable time staring at what appears to be nothing, yet to them, it’s an intriguing encounter with an ‘other’ creature.
Intriguing Shadows

Shadows can be mesmerizing to animals. A cat or dog may become fixated on a moving shadow, such as one cast by a tree branch swaying in the wind. This attention to shadows can seem like they’re staring at nothing to us.
However, for the animal, it’s a dynamic and captivating display. These shadows can offer endless amusement and mental stimulation, turning what seems like a blank stare into a moment of focused observation and curiosity.
Scent Detection

Animals have an extraordinary sense of smell, often described as their primary way of experiencing the environment. When a dog or cat seems to stare into space, they might actually be intently sniffing the air, picking up scents wafted over from a distance.
This olfactory exploration can lead them to pause and concentrate, appearing to be lost in thought. Their ability to detect scents can open up a world of information unavailable to us, filling their senses with stories carried on the breeze.
Meditation and Relaxation

Sometimes animals, particularly cats, may simply be enjoying a moment of relaxation, much like meditation. They might appear to be staring at nothing, but in reality, they are in a tranquil state, soaking in their surroundings.
This behavior can be a sign of contentment, allowing them to unwind and de-stress. It highlights their ability to live in the present moment, savoring the serenity of their environment without the need for constant stimulation.
Light and Color Perception

Animals perceive light and color differently from humans. A lizard might be drawn to a sunlit area on the floor, fascinated by the colors and patterns of light. These visual stimuli can be very engaging to animals.
Their unique vision allows them to see aspects of light and color that we might miss, leading to moments where they appear to be staring at nothing. For them, however, these are vibrant displays that capture their attention and imagination.
Peripheral Vision
Animals often have a more developed peripheral vision than humans, allowing them to detect movements and changes out of the corner of their eyes. A sudden shift in their gaze can be triggered by something moving in their periphery.
What seems like a blank stare may actually be a response to these subtle changes in their environment. This heightened awareness helps animals stay alert and responsive, even when it appears they’re staring at nothing specific.
Imaginary Playmates

Young animals, like kittens and puppies, often engage in play that seems to involve imaginary companions. They might jump, pounce, or stare at empty spaces as they engage in this imaginative play.
This behavior is a normal part of their development, helping them to hone their hunting and social skills. While it might look like they’re interacting with nothing, these playful antics are full of purpose and energy, demonstrating their vibrant imagination and instinctual learning.
Ghostly Presence

There are those who believe animals may perceive entities beyond our physical world, such as ghosts or spirits. A dog or cat may stare into an empty room with a look of curiosity or apprehension, drawing speculation about their sensitivity to supernatural phenomena.
While this remains a topic of debate, it’s a fascinating possibility that adds to the mystery of why animals sometimes stare at nothing. Their reactions can fuel our own imaginations and appreciation for the unseen elements of existence.
Fixed Gaze as Communication

Animals often use eye contact as a form of communication. A dog might fix their gaze on their owner to express a need, whether it’s for food, a walk, or simply attention. This direct stare can seem like they’re looking at nothing, especially if the human doesn’t immediately notice the silent request.
Understanding this gaze as a form of non-verbal communication highlights the deep bond shared between humans and their animal companions.
Boredom-Induced Staring

Boredom can lead animals to stare blankly, simply due to a lack of stimulation. A hamster, for instance, might appear to gaze into nothingness if their environment lacks enrichment.
Providing toys, activities, and interaction can alleviate this behavior, encouraging more engagement and mental stimulation. Recognizing this as a sign of boredom can help pet owners enhance the well-being of their animals by creating a more dynamic living space.
Attention to Subtle Movements

Cats and other animals are often captivated by tiny, subtle movements that we might overlook. A gently swaying curtain or the flicker of a shadow can hold their attention, making it seem like they’re staring at nothing.
These small movements provide both entertainment and mental engagement, showcasing their keen observational skills and sensitivity to environmental changes that might go unnoticed by human eyes.
Night Vision Curiosity

Certain animals, like raccoons, have excellent night vision, allowing them to see clearly in low-light conditions. When they appear to be staring into the darkness, they’re often observing things beyond our sight.
This ability to navigate and explore their environment at night adds depth to why they might seem fixated on nothing. Their eyes capture details in the shadowy depths, offering a glimpse into a world invisible to us during nighttime.
Responding to Vibrations

Animals can be incredibly sensitive to vibrations, which may cause them to stare at what appears to be nothing. A cat might react to slight tremors in the ground, perhaps sensing footsteps or the distant rumble of a vehicle.
This heightened sensitivity can lead them to pause and pay attention, reflecting their finely tuned awareness of their surroundings. Their ability to detect these vibrations adds another layer to their complex interaction with the world around them.
Environmental Changes

Animals are often attuned to environmental changes, such as shifts in weather. A dog might suddenly become alert, staring at the sky as clouds gather and signals of an impending storm appear.
These behavioral changes can seem like they’re staring at nothing, but they are actually responding to subtle cues in the atmosphere. This instinctual awareness helps them anticipate changes, sometimes long before humans are aware of them.
Hunger Signals
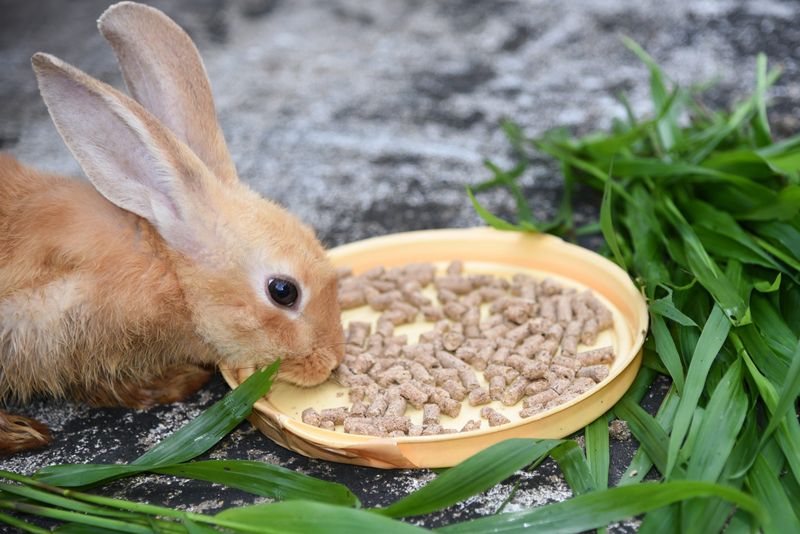

Hunger can drive animals to fixate on locations associated with feeding. A rabbit might stare at its food bowl, anticipating the arrival of a meal. This focused gaze can appear to be directed at nothing, but it’s actually tied to their understanding of routine and the expectation of food.
These behaviors highlight how animals use visual cues to communicate their needs and manage their daily rhythms with the help of their human caregivers.
Territorial Surveillance
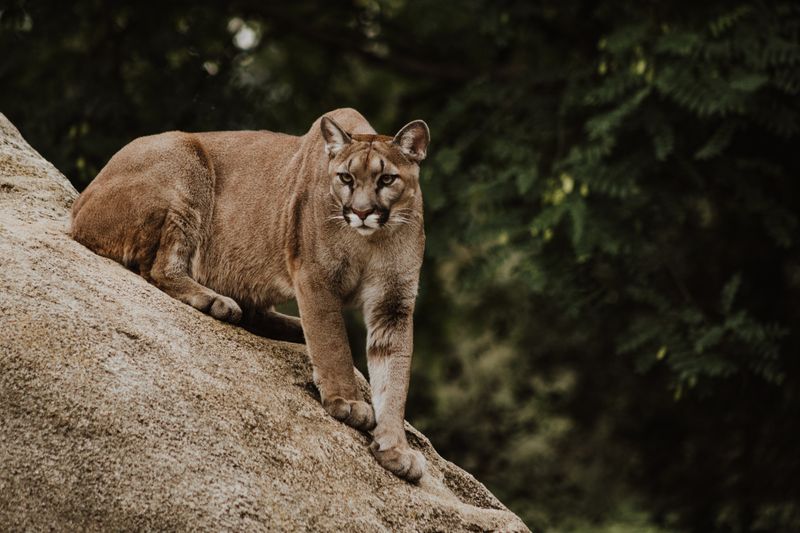

For many animals, keeping watch over their territory is crucial. A dog might take up a position in the garden and stare out at the surroundings, seemingly at nothing. However, they are actually surveying their domain, ensuring no intruders encroach on their space.
This surveillance behavior is instinctual, rooted in their need to protect their home and family. It helps them maintain a sense of control and security, demonstrating their role as guardians.
Anticipation of Playtime
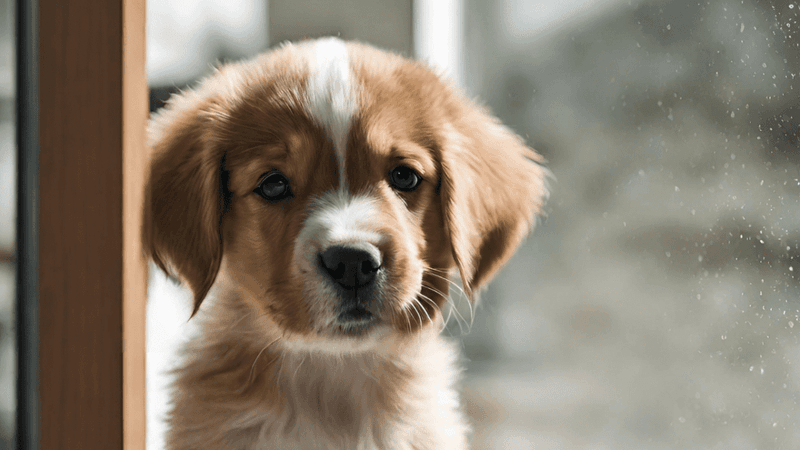

Anticipation can lead animals to focus intently on objects or areas associated with play. A puppy might stare eagerly at a toy, waiting for playtime to begin. This behavior appears as if they’re staring at nothing, but it’s filled with excitement and readiness.
Their focused gaze reflects their enthusiasm and the joy they find in interacting with their human companions, turning a simple object into a source of happiness and connection.
Sudden Noise Distraction
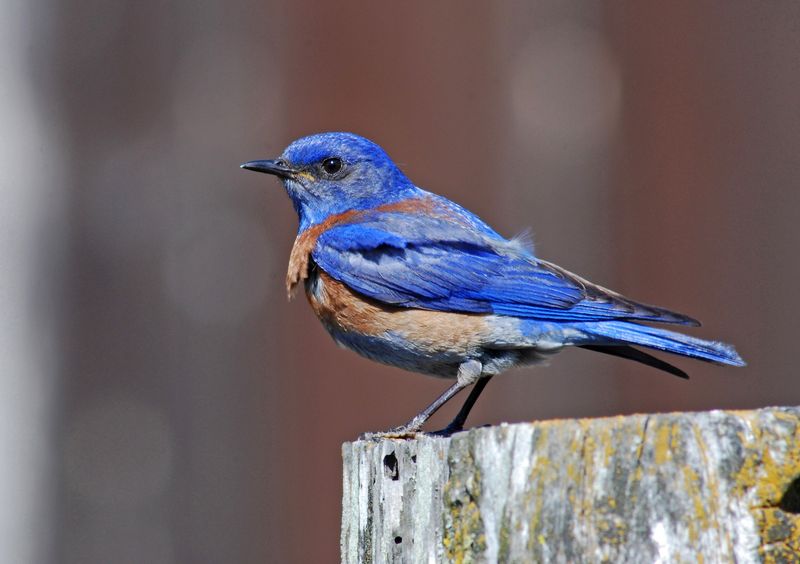

Sudden or unfamiliar noises can captivate an animal’s attention, leading them to pause and stare. A bird might stop mid-song, fixating its gaze as it listens intently to an unexpected sound.
This response is part of their survival mechanism, helping them identify potential threats or changes in their environment. The ability to quickly react to auditory stimuli ensures they remain alert and aware, even when it appears they’re staring at nothing.
Emotional Reflection
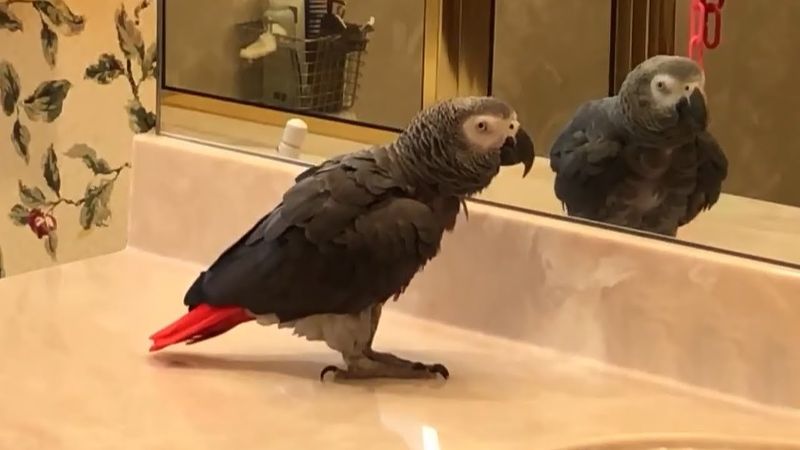

Animals are capable of experiencing a range of emotions, and sometimes they might stare into space as they reflect on their feelings. A parrot might observe its owner quietly, contemplating their bond and the shared experiences.
This reflective behavior highlights the depth of connection animals can have with humans, suggesting moments of introspection and emotional awareness, even when it seems they’re gazing at nothing.
Watching for Predators
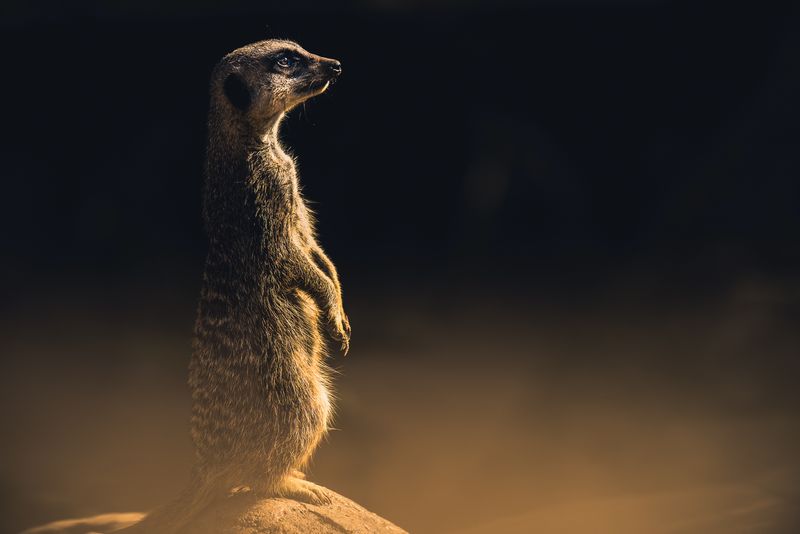

In the wild, staying vigilant for predators is a matter of survival. A meerkat might stand on its hind legs, staring intently at the horizon as it watches for danger.
This seemingly blank stare is actually a critical behavior for safety and protection. Their constant awareness of potential threats ensures they can react quickly, safeguarding themselves and their group from harm.
Unseen Magnetic Fields
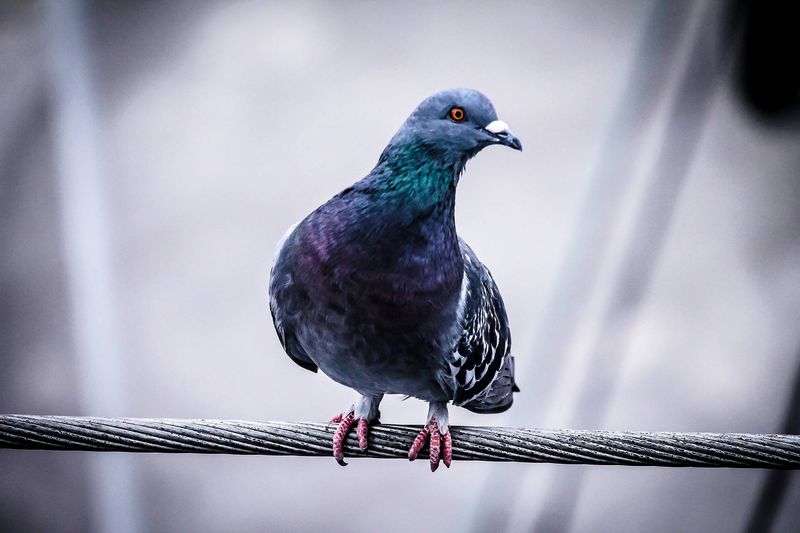

Some animals, like pigeons, are believed to be sensitive to the Earth’s magnetic fields. This ability might cause them to align themselves or stare in certain directions, seemingly at nothing.
Their navigation skills are enhanced by this sensitivity, allowing them to orient themselves and find their way across vast distances. This connection to unseen forces expands our understanding of animal behavior, revealing a hidden layer of interaction with the environment.
Social Hierarchy Observation
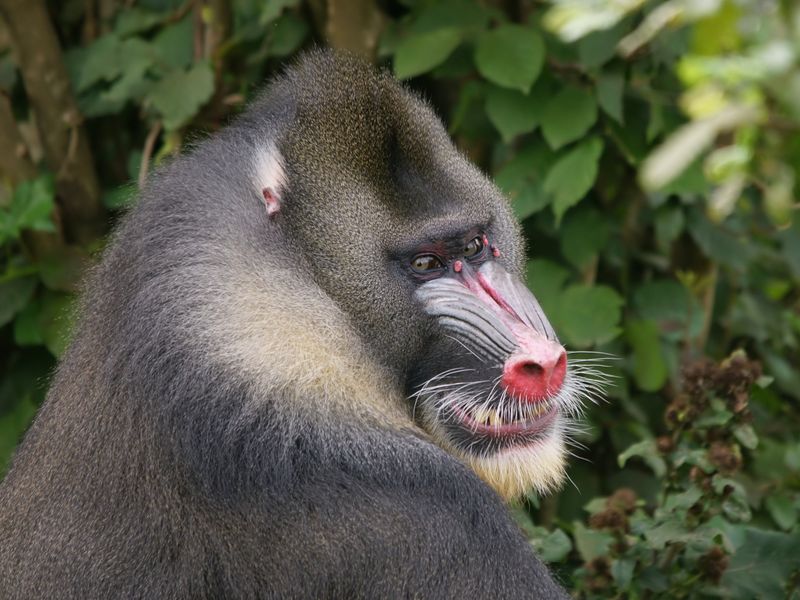

Animals living in social groups often pay close attention to the interactions and hierarchies within their community. A monkey might stare as it observes the dynamics of its group, understanding social cues and relationships.
This behavior is crucial for maintaining harmony and balance, allowing them to navigate their social world effectively. Their focused observation ensures they remain informed about their place within the group, even when it appears they’re gazing at nothing.
Learning Through Observation
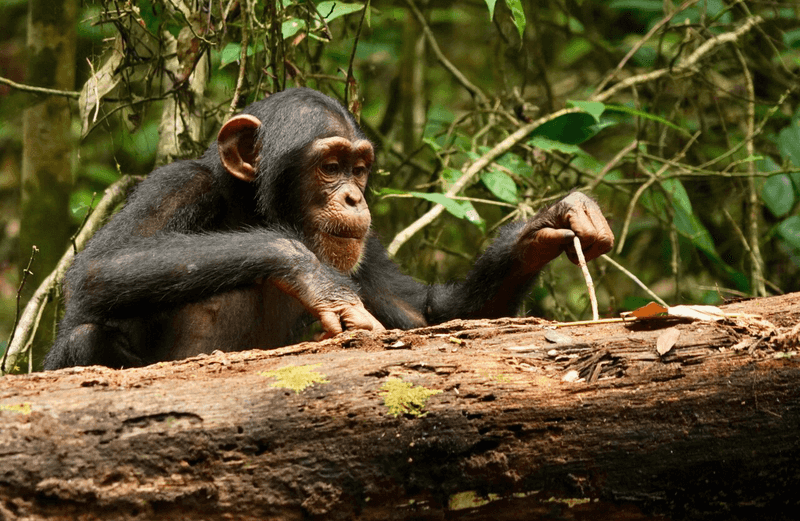

Young animals often learn by observing their elders. A young chimpanzee might watch an adult use a tool, carefully studying the technique. This observation is a critical learning process, enabling them to acquire skills needed for survival.
Their intense focus on this task might look like they’re staring at nothing, but it’s a vital part of their education. This method of learning through observation is a testament to the intelligence and adaptability of animals.
Sensory Overload

Sometimes animals experience sensory overload, especially in busy environments like parks. A dog might appear dazed, staring off into space as it processes the multitude of sights, sounds, and smells.
This behavior can occur when the sensory input becomes too intense, requiring them to take a moment to adjust. Understanding this need for a ‘reset’ can help pet owners provide support and create a more comfortable environment.
Anticipation of Routine

Animals thrive on routine, and anticipation of these daily rituals can lead them to focus intently on spots associated with these activities. A hamster might wait by its wheel, eager for its regular exercise time.
This focused gaze reflects their understanding of time and routine, highlighting the importance of structure in their lives. Their anticipation is not just about routine but also about the enjoyment and satisfaction these activities bring.
Curiosity About New Objects

Curiosity drives animals to explore and understand their surroundings. A puppy might approach a new object with caution, staring at it as it tries to comprehend what it is.
This behavior is a natural part of their development, fostering learning and adaptation. Their inquisitive nature ensures they remain engaged and stimulated, turning ordinary moments into opportunities for discovery and growth. Embracing their curiosity can lead to richer, more fulfilling relationships with our animal companions.

