Wolves are the wild heart of America’s ecosystems—but not everyone agrees.
For centuries, these incredible predators have shaped the land they roam, balancing prey populations and boosting biodiversity. Without them, nature would lose its rhythm, and we’d see the collapse of vital habitats.
But not everyone is ready to embrace the wolf’s role as a key player in our wilderness. Ranchers and hunters, in particular, raise alarms about their impact on livestock and local economies. The clash between conservationists and those who see wolves as a threat to their way of life is fierce.
America’s wolves spark both awe and fear, standing at the crossroads of nature’s power and human interests. It’s time to explore why these animals are essential to the wild—and why their place in the landscape is still a battleground.
Biodiversity Boosters

Wolves contribute to biodiversity by regulating prey populations, mainly deer and elk. This predation pressure prevents overgrazing, allowing plant species to thrive. With diverse plant life, insects, birds, and small mammals find suitable habitats, enhancing ecosystem complexity.
In this way, wolves indirectly support a multitude of species. Some argue, however, that the pressure on prey can be intense, affecting local hunting industries. Nonetheless, the long-term ecological benefits often outweigh these concerns, ensuring rich, vibrant ecosystems where wolves are present. Balancing these interests is crucial for maintaining harmony between nature and human activity.
Trophic Cascade Effects
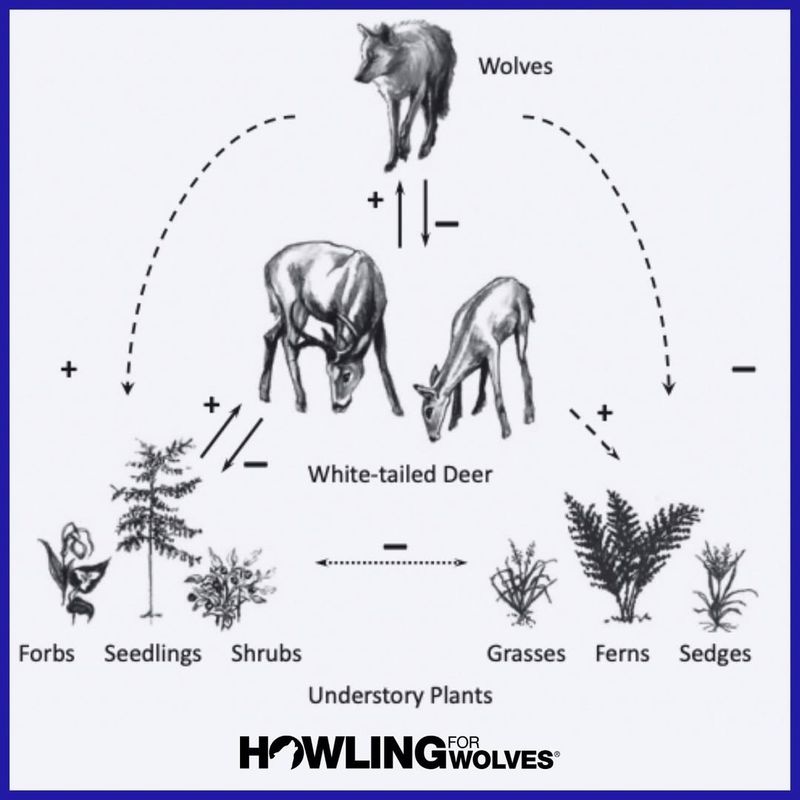
Wolves’ presence triggers trophic cascades, influencing entire ecosystems. By controlling herbivore populations, they prevent vegetation overconsumption, allowing plants to regenerate. This regeneration supports a wider range of species, fostering biodiversity.
Healthy plant life stabilizes riverbanks, reducing erosion and improving water quality. Such changes highlight wolves’ integral role in ecosystem health. Opponents worry about economic impacts on industries reliant on large herbivore populations. This dynamic underscores the complexity of ecological management, where the benefits of wolves must be weighed against human economic needs, striving for coexistence between wildlife and community interests.
Prey Population Control
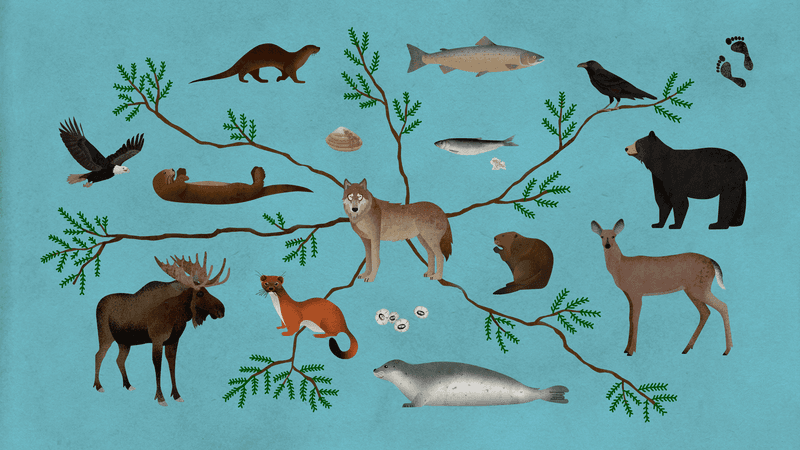

Wolves are expert hunters, keeping prey populations in check. This natural control mechanism is vital for preventing overpopulation and its associated problems, such as disease outbreaks and resource depletion.
In areas where wolves are absent, unchecked prey populations can degrade habitats. Critics argue that wolves diminish hunting opportunities for humans, sparking economic concerns. However, managing wildlife populations naturally helps maintain ecological balance. Finding ways to harmonize human and wildlife interests can lead to sustainable solutions that benefit both nature and local communities, showing the importance of collaborative wildlife management efforts.
Scavenger Support

Wolves leave behind carcasses that provide food for scavengers like ravens, eagles, and bears. This scavenging boosts these species’ survival and contributes to nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
As scavengers feed, they disperse nutrients across the landscape, enriching soil and supporting plant growth. Some critics say wolves create competition for hunters targeting the same prey. Despite this, the ecological benefits from scavengers thriving due to wolves underscore the interconnectedness of nature. Recognizing wolves’ role in supporting scavengers can help address human-wildlife conflicts, fostering ecosystems where multiple species coexist and thrive.
Habitat Restoration

Wolves’ influence extends to habitat restoration, as their hunting habits allow vegetation to recover in overgrazed areas. This recovery supports a broader range of flora and fauna, enhancing habitat quality and biodiversity.
Restored habitats provide better conditions for species to flourish, creating robust ecosystems. Concerns arise about wolves’ impact on livestock and agriculture. Yet, methods like predator-friendly farming can mitigate conflicts. Emphasizing wolves’ role in habitat restoration highlights their contribution to ecological health. Encouraging coexistence and understanding can lead to innovative strategies that protect both wolves and human interests.
Disease Control

By preying on weak or sick animals, wolves help control diseases in prey populations. This natural selection ensures healthier herds and prevents disease outbreaks, promoting overall ecosystem health.
Healthier animal populations reduce the risk of disease transmission to domestic livestock. Opponents worry about the threat wolves pose to livestock. However, understanding wolves’ role in disease control emphasizes the importance of their presence. Implementing measures like better herd management can reduce conflicts, supporting healthier ecosystems and livestock. Balancing these factors can create a sustainable environment where both wildlife and agriculture prosper.
Cultural Significance

Wolves hold significant cultural value, especially for Indigenous communities, where they symbolize strength and wisdom. This cultural heritage emphasizes the deep connection between humans and nature.
Wolves often feature in folklore and traditions, highlighting their role in cultural identity and storytelling. Some view wolves as threats to livestock, challenging traditional livelihoods. Yet, recognizing wolves’ cultural importance fosters respect and understanding. Bridging the gap between cultural heritage and modern challenges can lead to a richer appreciation of wolves. Encouraging dialogue between communities can help integrate cultural perspectives into wildlife conservation efforts.
Economic Impact

Wolves attract wildlife enthusiasts and tourists, boosting local economies through ecotourism. These activities generate income and create jobs in rural communities reliant on natural attractions.
Tourism supports conservation efforts by funding habitat protection and education programs. Critics argue wolf-related tourism is inconsistent and seasonal. Yet, the economic advantages provided by wolf tourism can offset challenges faced by other industries. Promoting ecotourism as a viable economic strategy can help align conservation goals with community needs, demonstrating the potential for economic development alongside wildlife preservation. Such initiatives highlight the value of natural treasures like wolves.
Genetic Diversity

Wolves contribute to genetic diversity by dispersing over large areas and interbreeding with different packs. This gene flow prevents inbreeding, ensuring resilient and adaptable populations.
Genetically diverse populations are better equipped to withstand environmental changes and disease threats. Some believe wolf populations can become too large, impacting other wildlife. However, the genetic benefits underscore the importance of maintaining healthy wolf numbers. Strategies focusing on habitat connectivity can support genetic diversity, fostering robust ecosystems. Encouraging adaptive management practices helps balance the needs of wolves with broader environmental considerations.
Public Awareness

Wolves spark public interest and awareness about wildlife conservation. Educational programs and media coverage highlight their ecological roles, fostering a deeper appreciation for nature.
Increased awareness can lead to more support for conservation initiatives and informed policy decisions. Critics argue that media portrayals of wolves can be sensationalized, impacting public perception. By focusing on accurate information, conservation messages can educate and inspire action. Engaging communities in conservation efforts through workshops and outdoor activities can strengthen connections to nature, empowering individuals to support sustainable practices and informed wildlife management.
Human-Wildlife Conflict Solutions

Addressing human-wildlife conflicts is crucial for wolf conservation. Non-lethal deterrents and proactive livestock management can reduce conflicts, promoting peaceful coexistence.
Strategies like fencing, guard animals, and noise devices have proven effective, allowing wolves and humans to share landscapes. Some argue these measures are costly and labor-intensive. Yet, innovative solutions demonstrate potential for coexistence, encouraging collaboration between wildlife agencies and communities. Sharing successful strategies can inspire more communities to adopt humane conflict resolution methods. This approach fosters environments where both agricultural interests and wolf populations can thrive, highlighting the importance of cooperative conservation efforts.
Scientific Research Opportunities

Wolves provide valuable research opportunities, enhancing understanding of predator-prey dynamics and ecosystem health. Studies on wolves’ behavior contribute to ecological and biological knowledge.
Research findings aid in developing effective conservation strategies and wildlife management plans. Some question the funding priorities for wolf research over other species. However, the insights gained underscore wolves’ significance in scientific endeavors. Encouraging collaborative research initiatives can expand our understanding of ecosystems, paving the way for informed conservation policies. Supporting research on wolves and their habitats can foster broader ecological awareness and sustainable management practices.
Climate Change Resilience

Wolves enhance ecosystem resilience to climate change by maintaining balanced populations and supporting healthy habitats. Their interactions with prey and vegetation contribute to ecosystems’ adaptive capacity.
Resilient ecosystems can better withstand climate impacts, preserving biodiversity. Some contend that wolves’ effects are minimal compared to larger climate issues. Yet, every species plays a role in ecological resilience. Highlighting wolves’ contributions can inspire integrated conservation efforts addressing climate challenges. By recognizing wolves as part of broader climate solutions, we can foster ecosystems capable of adapting to environmental changes, ensuring long-term ecological stability.
Legal and Policy Frameworks

The legal protection of wolves involves complex policy frameworks balancing conservation and economic interests. Laws like the Endangered Species Act support wolf recovery efforts.
Regulations ensure sustainable management, but debates continue over delisting and hunting policies. Some advocate for stronger protection, while others seek more flexible management. Navigating these legal landscapes requires collaboration between policymakers, conservationists, and communities. Understanding diverse perspectives can lead to policies that support wolf recovery while addressing human concerns. Effective legal frameworks are vital for ensuring wolves’ survival and coexistence with human activities, reflecting society’s commitment to biodiversity.

