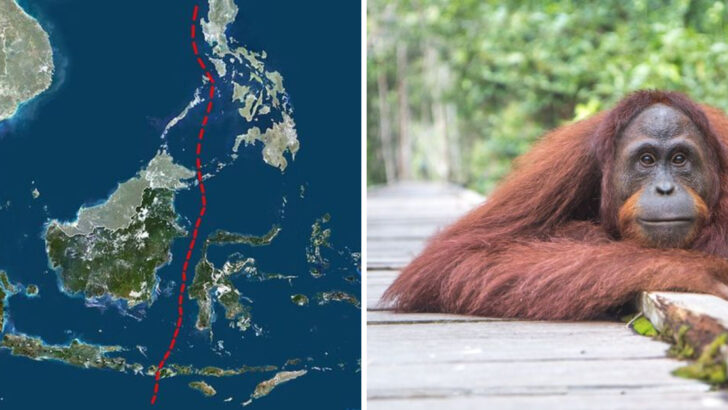
The Wallace Line, an invisible boundary that separates the ecozones of Asia and Wallacea, presents a fascinating natural division.
It was named after Alfred Russel Wallace, the British naturalist who noticed the stark contrast in species on either side of this line.
This imaginary boundary runs through Indonesia, delineating the distinct wildlife of the Asian and Australian continents.
The line has puzzled biologists and explorers alike for centuries due to the abrupt changes in flora and fauna.
Explore these ten intriguing facts about the Wallace Line that highlight its ecological significance and the mysteries it holds.
The Origin of the Wallace Line

Named after Alfred Russel Wallace, the Wallace Line marks a fascinating biogeographical boundary between Asia and Wallacea.
During the 19th century, Wallace was intrigued by the sudden change in species across the islands of Indonesia. This line separates the distinct flora and fauna of the Asian and Australian continents, showcasing the rich biodiversity on either side.
Wallace’s observations led to a deeper understanding of species distribution and evolutionary biology, influencing future explorations. His pioneering work highlighted the unique characteristics of this region, making it a significant area of study for scientists and naturalists.
Location of the Wallace Line
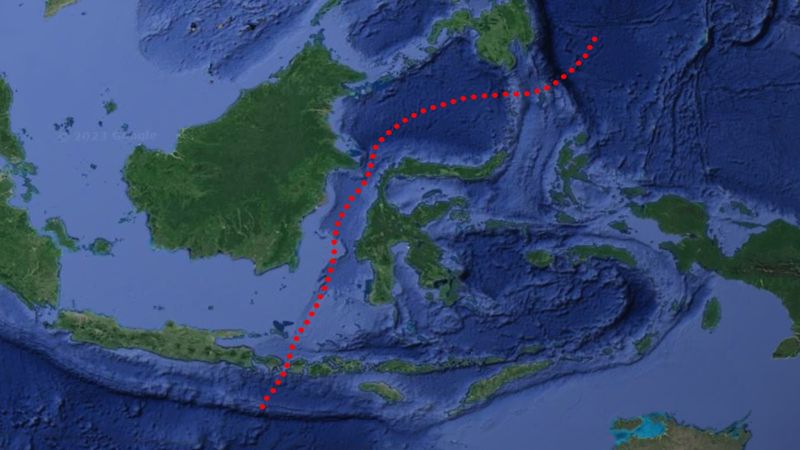
The Wallace Line runs through the Indonesian archipelago, primarily between Borneo and Sulawesi, and Bali and Lombok. This imaginary boundary symbolizes one of Earth’s most significant biological divides, separating the lush ecosystems of Asia from the unique species of Australia.
The differing ocean depths and currents contribute to this ecological distinction, preventing the migration of many terrestrial species. The location of this line has fascinated geographers and biologists, who study the influences of geography on species evolution.
The Wallace Line remains a subject of intrigue, illustrating the complexities of Earth’s biodiversity.
Unique Species of the Wallace Line

The Wallace Line divides a fascinating array of species, with marsupials like kangaroos found to the east and primates like monkeys to the west.
This division is not merely a geographical curiosity; it highlights the distinct evolutionary paths taken by animals on either side. Researchers have identified numerous unique species along this line, contributing to the rich tapestry of life.
These species’ adaptations to their specific environments offer insights into evolutionary biology. The Wallace Line serves as a living laboratory, allowing scientists to study the processes that drive biodiversity and shape ecosystems.
Climatic Influences on the Wallace Line
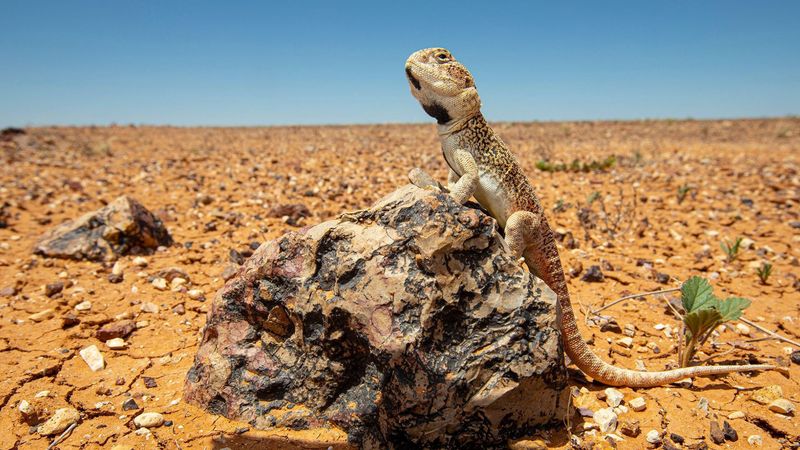

The contrasting climates on either side of the Wallace Line play a crucial role in species distribution. To the west lies the humid tropical rainforests of Asia, while the east features the drier savannas and woodlands of Australia.
These climatic differences have shaped the evolution of flora and fauna, creating distinct ecological zones. The line’s location acts as a climatic barrier, influencing migration patterns and species interactions.
Understanding these climatic influences helps scientists predict how ecological zones might shift with climate change, offering a glimpse into future biodiversity scenarios.
Wallace Line’s Geological Origins
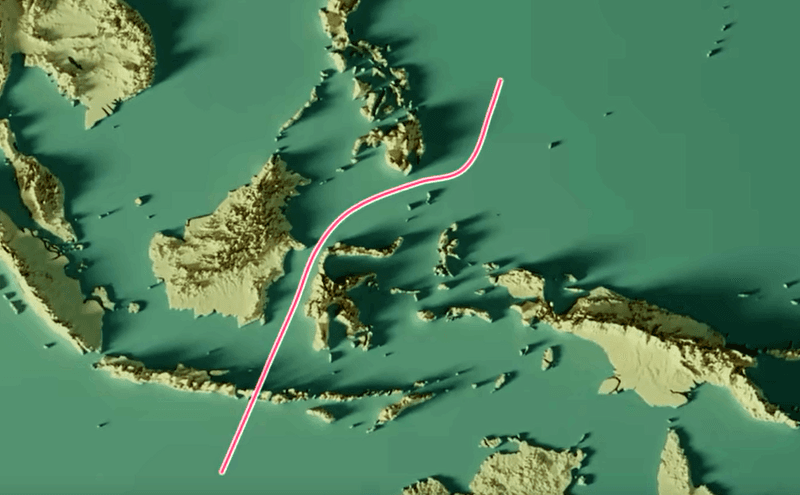
The geological origins of the Wallace Line are rooted in tectonic plate movements, which created the Indonesian archipelago. These geological processes have shaped the region’s unique landscapes, influencing species distribution.
The differing oceanic and continental plates result in varied habitats across the line, affecting species migration. This geological history provides a framework for understanding the distribution of species and the ecological characteristics of the region.
The Wallace Line’s formation illustrates the intricate connections between Earth’s geological history and its biodiversity, offering a window into the planet’s dynamic processes.
Historical Significance of the Wallace Line
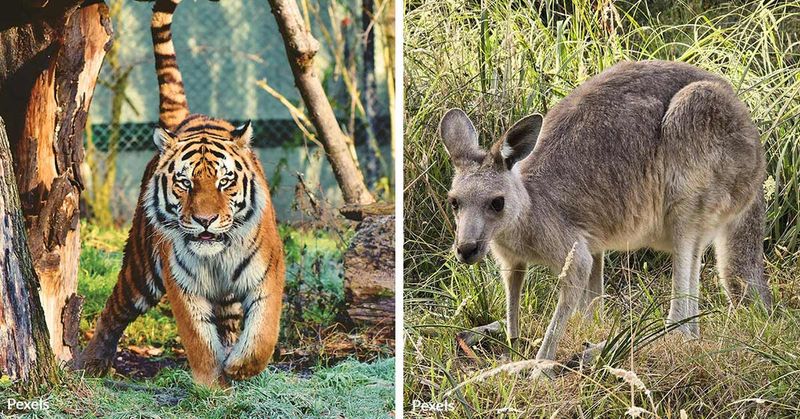

The Wallace Line has a rich historical significance, attracting explorers and naturalists since the 19th century. Alfred Russel Wallace’s studies laid the foundation for biogeography, inspiring generations of scientists.
This boundary captured the attention of Charles Darwin and others, fostering a deeper understanding of species evolution. The line represents a milestone in scientific exploration, where theories of natural selection and species distribution took shape.
Today, it continues to be a focal point for research, reflecting the enduring legacy of those who first ventured into this mysterious part of the world.
Cultural Impact of the Wallace Line

The Wallace Line not only influences biodiversity but also impacts local cultures in Indonesia. Communities living near this boundary have adapted to the unique environments on either side, developing distinct cultural practices.
Traditional knowledge and practices are often intertwined with the natural surroundings, reflecting the line’s ecological significance. The cultural impact of the Wallace Line is evident in the way communities interact with their environment, showcasing a harmonious relationship between people and nature.
This cultural richness adds another layer of complexity to the study of the Wallace Line, highlighting its multifaceted influence.
Modern Research on the Wallace Line
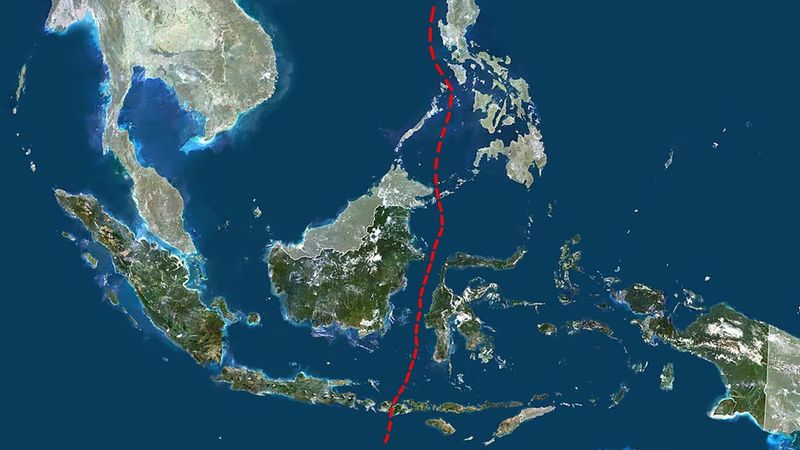
Modern research on the Wallace Line employs cutting-edge technology to study its ecological dynamics. Scientists use satellite imagery, genetic analysis, and other tools to understand species distribution and environmental changes.
This research has unveiled new species and offered insights into conservation strategies. The Wallace Line serves as a natural laboratory where scientists can explore the effects of climate change and human activities on biodiversity.
These studies contribute to global understanding of ecological resilience and adaptation, emphasizing the importance of preserving this unique boundary for future generations.
Conservation Efforts at the Wallace Line

Conservation efforts at the Wallace Line are crucial for protecting its unique ecosystems. Collaborative initiatives between governments, NGOs, and local communities aim to preserve the region’s biodiversity.
These efforts focus on habitat restoration, sustainable resource management, and species protection. Education and awareness programs empower local communities to engage in conservation activities, fostering a sense of stewardship.
The Wallace Line’s conservation serves as a model for other regions, demonstrating the importance of integrating scientific research with community involvement. These efforts underscore the need to safeguard the planet’s biodiversity hotspots.
Wallace Line in Popular Culture

The Wallace Line has permeated popular culture, inspiring films, books, and documentaries. Its mysterious allure and rich biodiversity captivate audiences, fueling interest in the natural world.
Writers and filmmakers often use the line as a backdrop for stories exploring themes of exploration and discovery. This cultural portrayal helps raise awareness about the ecological significance of the Wallace Line, engaging a broader audience.
By highlighting this unique boundary, popular culture plays a role in promoting conservation and appreciation for nature’s wonders. The Wallace Line continues to inspire creativity and curiosity around the globe.

