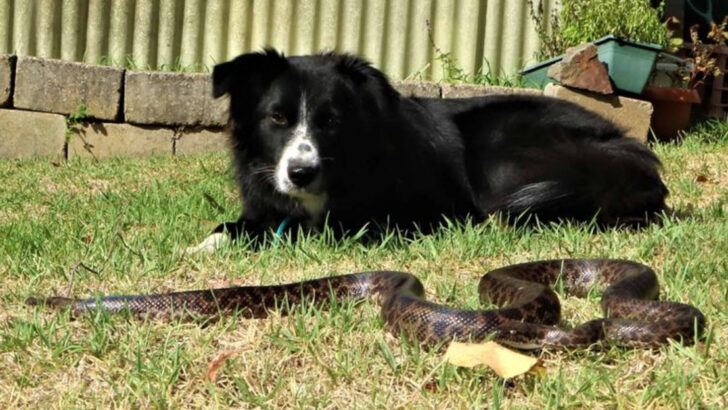
Some dangers lurk where you least expect them. The great outdoors might seem like paradise for a dog, but it’s also home to creatures that see them as a threat—or worse, a meal.
From the depths of the forest to your own backyard, wild animals don’t play by human rules. A peaceful hike can turn into a life-or-death situation in seconds, and even a casual sniff in the wrong place can lead to a terrifying encounter.
Some predators are obvious, with sharp claws and piercing eyes. Others? Sneaky, silent, and waiting for the perfect moment to strike. And let’s not forget the ones that don’t attack with teeth or talons but with venom, disease, or sheer force.
Knowing the risks is the first step in keeping your dog safe. Here are 27 wild animals that could turn your pet’s outdoor adventure into a dangerous game of survival.
Coyotes
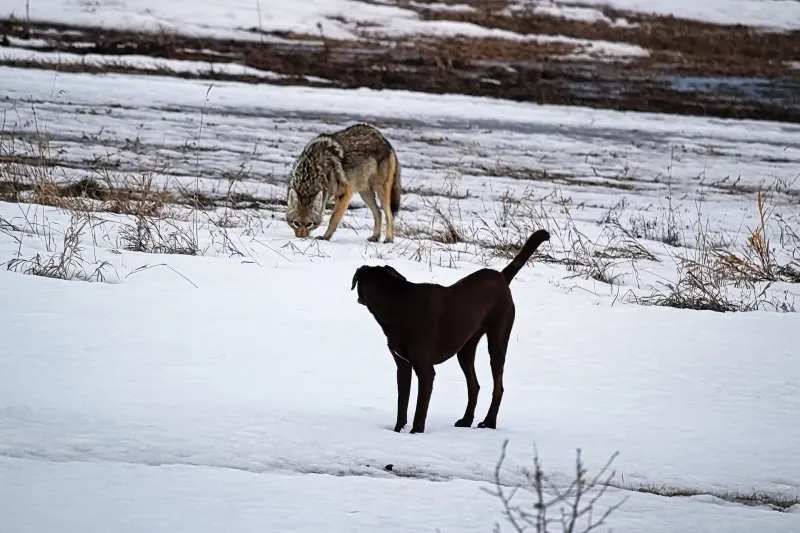

Coyotes are highly adaptable and can be found in urban areas, posing a threat to domestic dogs. These opportunistic predators are known for their cunning nature and may attack smaller dogs, especially during mating season when they are more territorial.
To protect your dog, avoid leaving them unattended in areas known for coyote activity.
Keeping dogs on a leash during walks and securing trash bins can reduce encounters. Understanding coyote behavior can help prevent dangerous interactions, ensuring your dog’s safety.
Bobcats
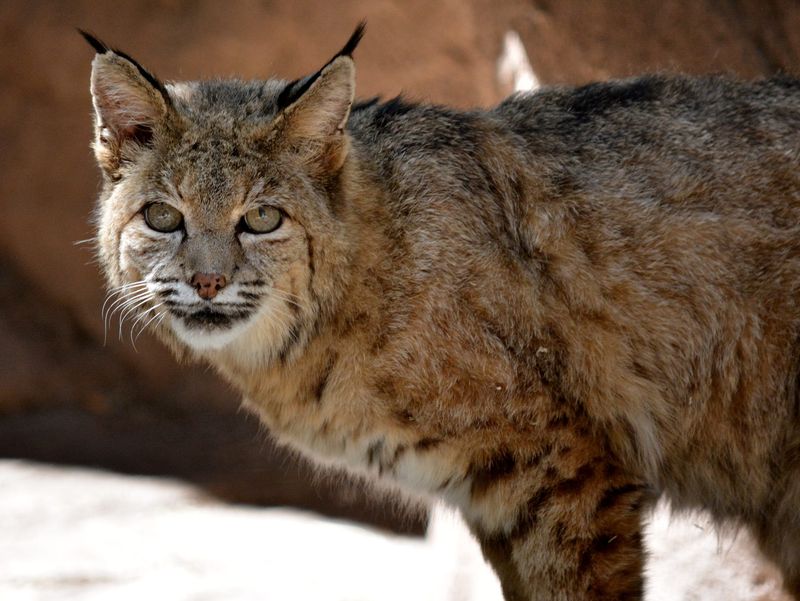

Bobcats, with their stealthy nature and powerful build, can pose a risk to dogs, particularly in rural or wooded areas. They are solitary hunters, often preying on small mammals and occasionally targeting pets.
Bobcats are most active during twilight hours, so keeping dogs indoors during these times can reduce risks.
Install motion-activated lights around your property to deter these elusive predators. Being aware of their presence is key to safeguarding your dog.
Rattlesnakes
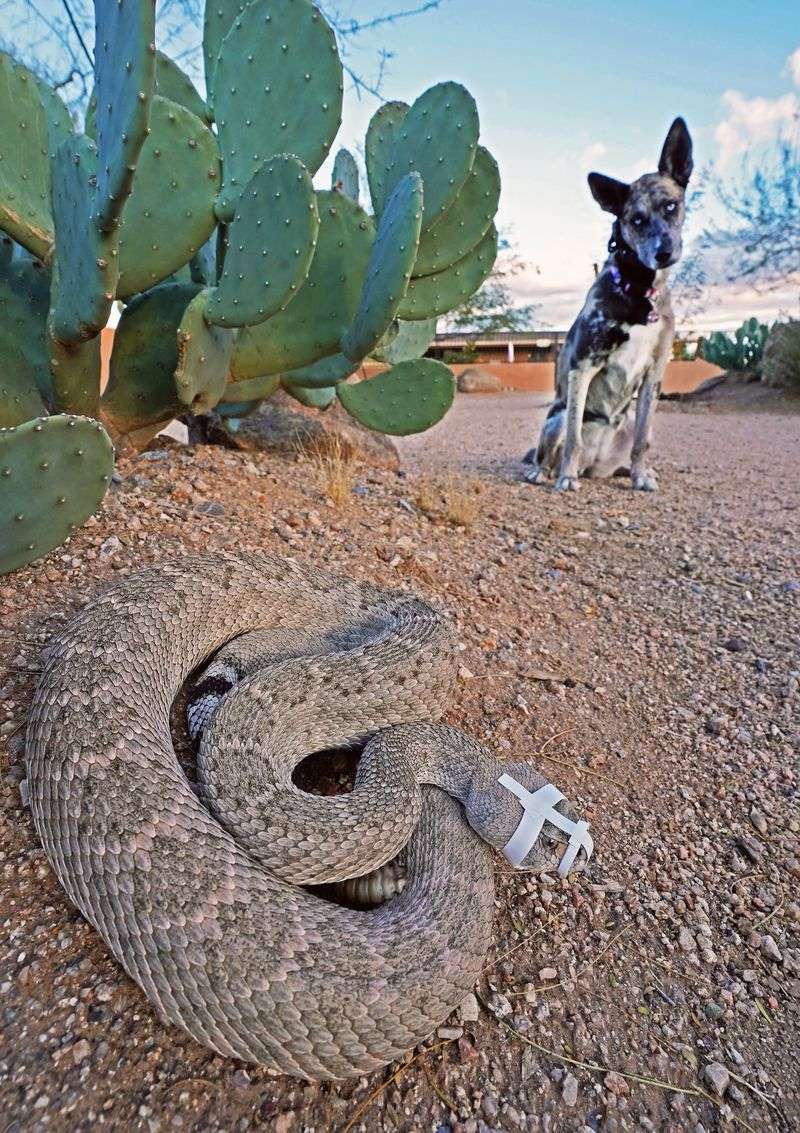

Rattlesnakes are venomous reptiles that inhabit arid regions and can be highly dangerous to unsuspecting dogs. Their bite delivers potent venom capable of causing severe harm or even death.
When walking in snake-prone areas, keep dogs on a leash and steer clear of tall grass or rocky outcrops where snakes may hide.
Familiarize yourself with snakebite first aid and keep emergency veterinary contact information handy. Swift action can save your dog’s life in case of an encounter.
Mountain Lions
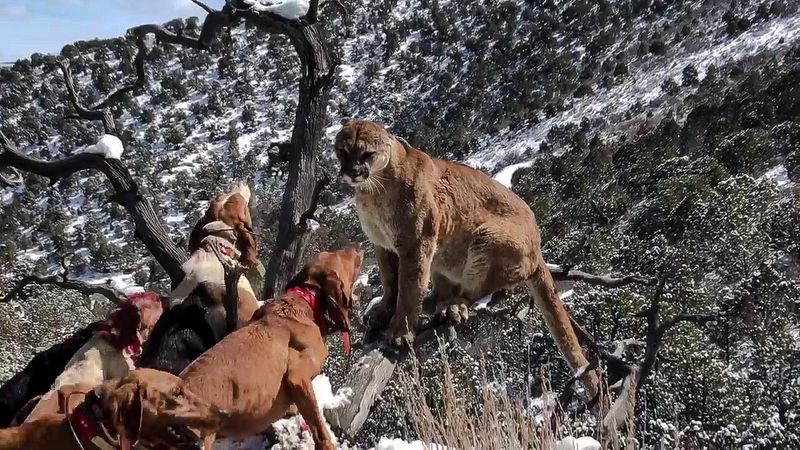

Mountain lions, also known as cougars, are powerful predators that pose a significant threat to dogs, especially in mountainous regions. Their stealth and agility make them formidable hunters, capable of ambushing unsuspecting prey.
To protect your dog, avoid hiking during dawn or dusk when these predators are most active.
Keeping dogs on a leash and making noise while walking can help deter attacks. Awareness of mountain lion habitats and behaviors is essential for dog safety.
Hawks
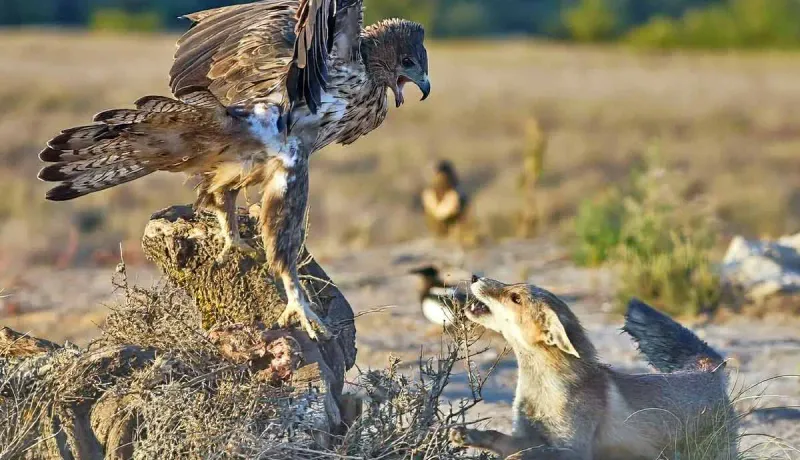

Hawks are birds of prey known for their sharp talons and keen eyesight, capable of targeting small dogs. These aerial hunters can swoop down swiftly, posing a threat in open areas.
To protect small dogs, supervise them in open spaces, especially during hawk nesting seasons.
Installing bird netting or providing sheltered areas can reduce the risk of attacks. Understanding raptor behavior can help ensure the safety of your pet.
Wolves
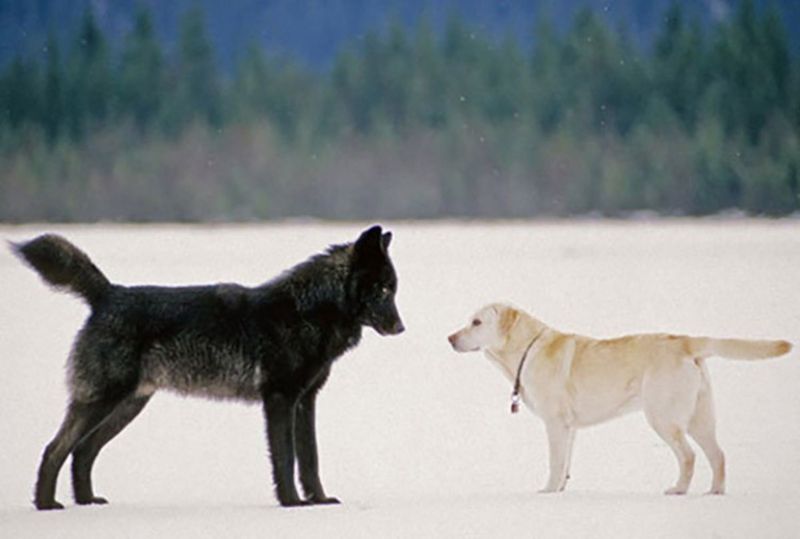

Wolves, with their pack mentality and hunting prowess, are dangerous to dogs, particularly in rural and wilderness areas. They may perceive dogs as threats or competitors.
Keeping dogs on a leash and avoiding wolf-inhabited regions during peak activity times can minimize risks.
If you’re in wolf territory, make noise to alert them of your presence. Educating yourself about wolf behavior is crucial to safeguarding your dog.
Alligators
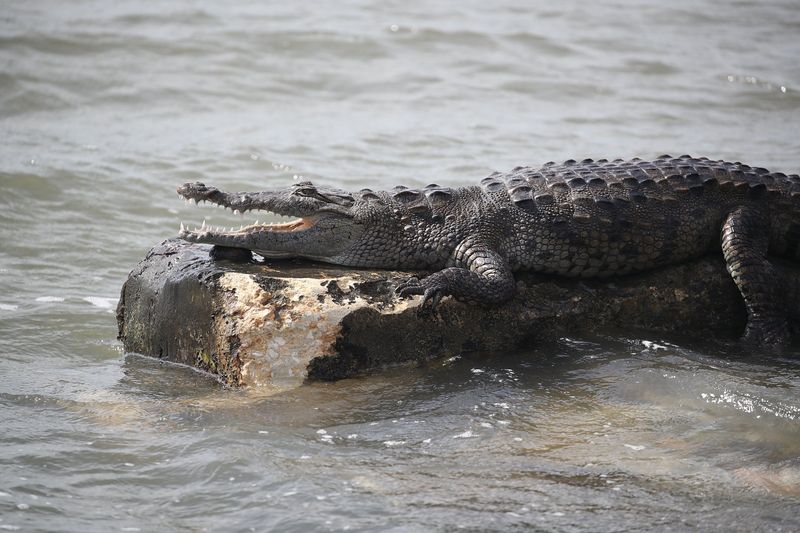

Alligators, found in freshwater environments like swamps and rivers, pose a significant threat to dogs. Their camouflaged appearance and quick strikes make them formidable predators.
Keep dogs on a leash near water bodies known for alligator presence and avoid letting them swim in these areas.
Awareness of alligator habitats and behaviors can help prevent dangerous encounters, ensuring your dog’s safety.
Scorpions
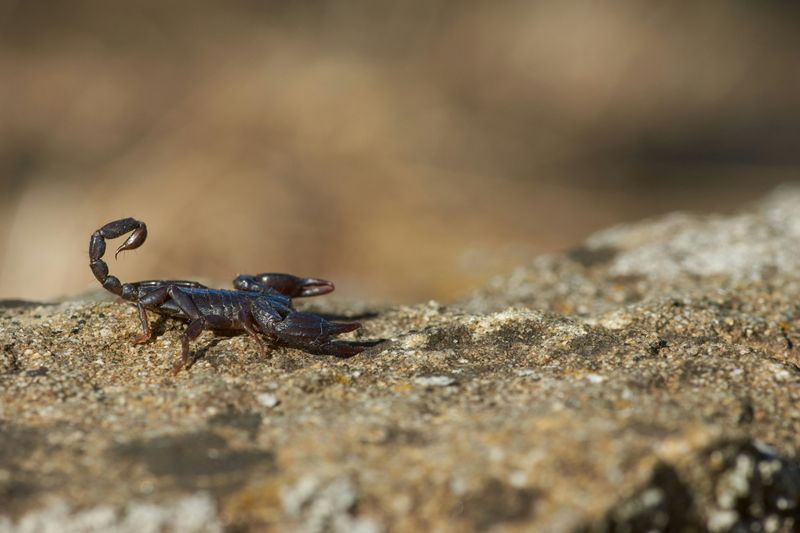

Scorpions, especially in desert regions, can pose a threat to curious dogs. Their stings can cause pain and potentially serious reactions.
Keep dogs away from areas where scorpions are likely to hide, such as under rocks or debris.
Regularly check and clean your home and yard to reduce scorpion presence. Knowing how to respond to a scorpion sting can prevent serious harm to your pet.
Jaguars
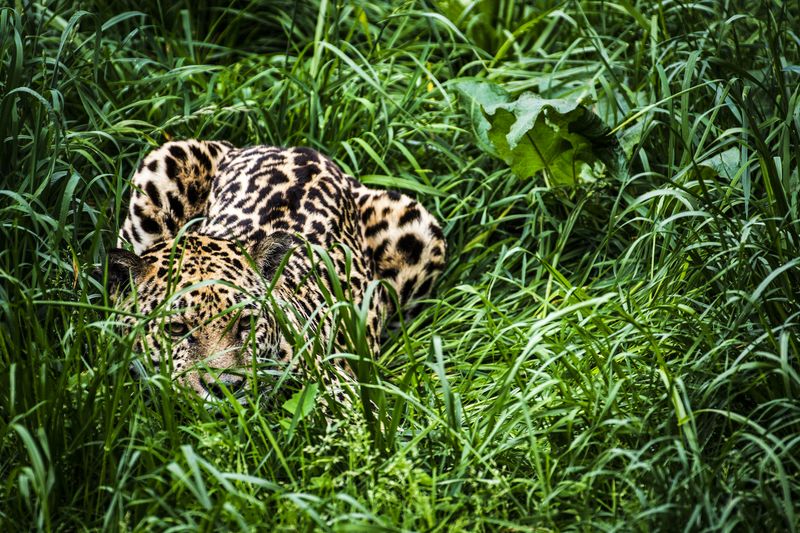

Jaguars, strong and stealthy predators, pose a danger to dogs in regions where their habitats overlap. They are powerful hunters, capable of taking down larger prey.
Avoiding known jaguar territories and keeping dogs on a leash during outdoor activities are crucial for safety.
Understanding jaguar behaviors and habitats helps prevent potentially deadly encounters, ensuring your dog’s well-being.
Owls
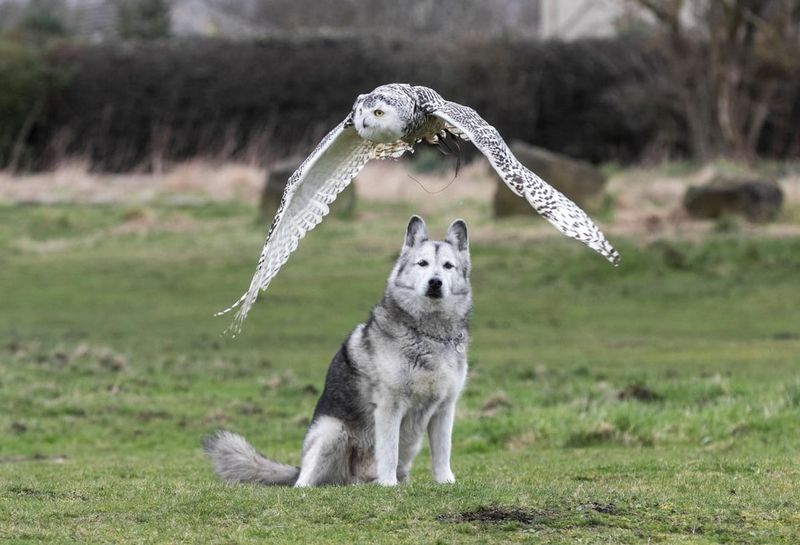

Owls, with their silent flight and sharp talons, can pose a risk to small dogs, especially in rural areas. These nocturnal hunters often target small animals.
To protect your dog, supervise them outside at night and provide sheltered spaces where owls cannot reach.
Awareness of owl activity in your area helps minimize risks and ensures your pet’s safety.
Bees
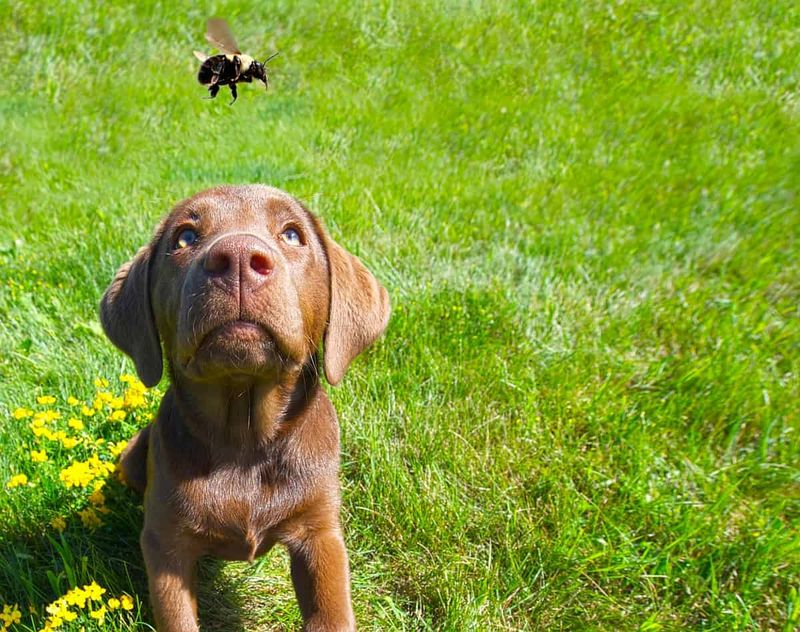

Bees, while generally not aggressive, can pose a threat to dogs if provoked. A swarm or sting can cause severe reactions, especially in allergic dogs.
Keep dogs away from areas with active hives and be mindful of their presence in gardens.
In case of a sting, monitor your dog for allergic reactions and seek veterinary care if needed. Understanding bee behavior helps ensure your pet’s safety during outdoor adventures.
Skunks
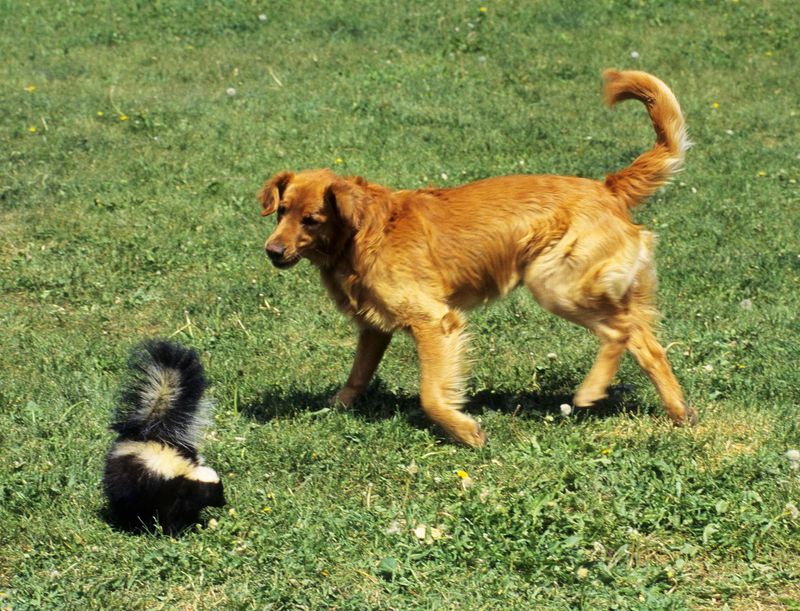

Skunks, though not aggressive, can pose a threat to dogs with their potent spray. A startled skunk will release a foul-smelling liquid as a defense mechanism.
To prevent encounters, keep dogs on a leash during dusk and dawn when skunks are active.
In case of a skunk spray, know how to properly clean your pet to remove the odor. Awareness of skunk behavior helps ensure peaceful coexistence and a less smelly experience.
Porcupines
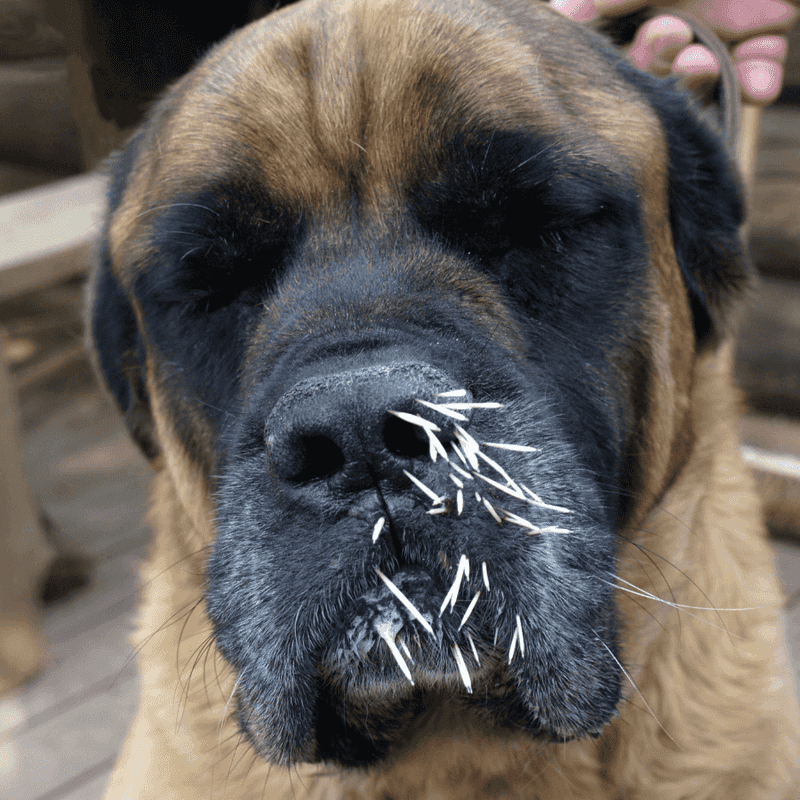

Porcupines, with their sharp quills, pose a particular risk to curious dogs. A defensive porcupine will release quills when threatened, potentially injuring a pet.
To avoid quill encounters, keep dogs on a leash in areas where porcupines are common.
If your dog gets quilled, seek veterinary assistance promptly to safely remove the quills. Understanding porcupine behavior is key to preventing painful encounters and keeping your pet secure.
Snapping Turtles
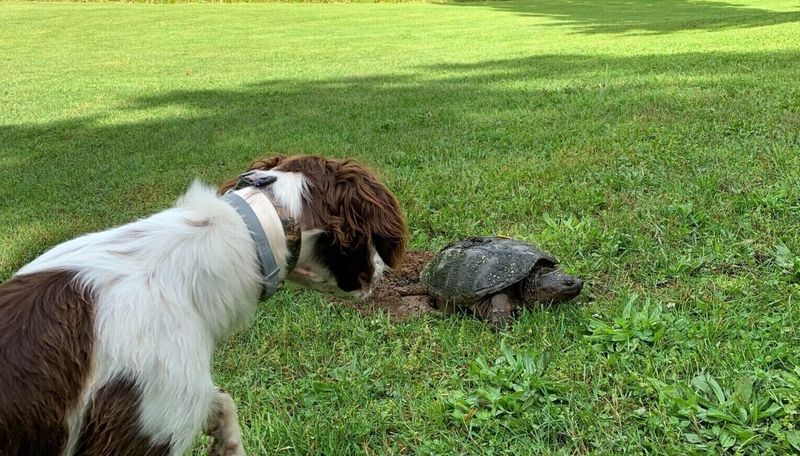

Snapping turtles, found near water bodies, can be a threat to dogs due to their strong jaws and aggressive nature. They can deliver a painful bite if provoked.
Keep dogs on a leash near ponds and lakes, and avoid allowing them to approach turtles.
Awareness of snapping turtle habitats and behaviors can help prevent painful encounters, ensuring your dog’s safety during outdoor activities.
Racoons
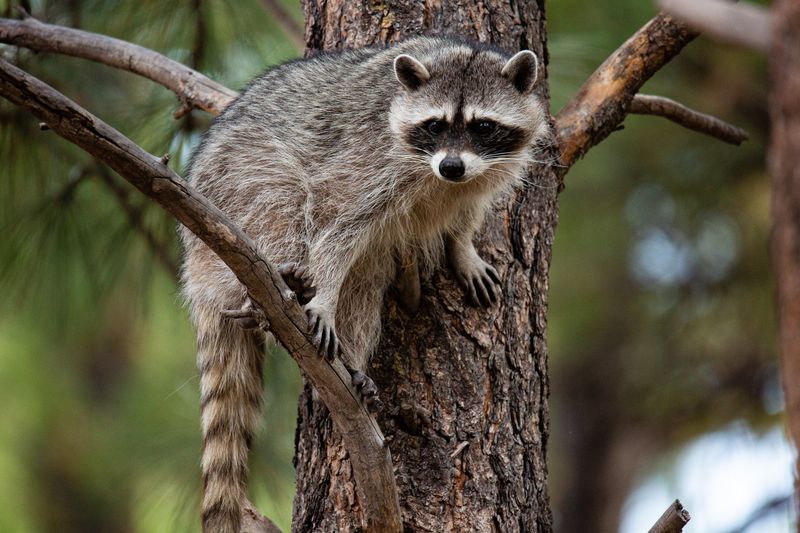

Raccoons, while generally not aggressive, can pose a risk to dogs through diseases like rabies. Their curious nature often leads them into urban areas, increasing potential contact.
Secure trash cans and avoid leaving pet food outside to deter raccoons.
Supervising your dog outdoors and ensuring they are vaccinated can mitigate health risks. Understanding raccoon behavior helps ensure safe interactions and protects your pet’s health.
Bears
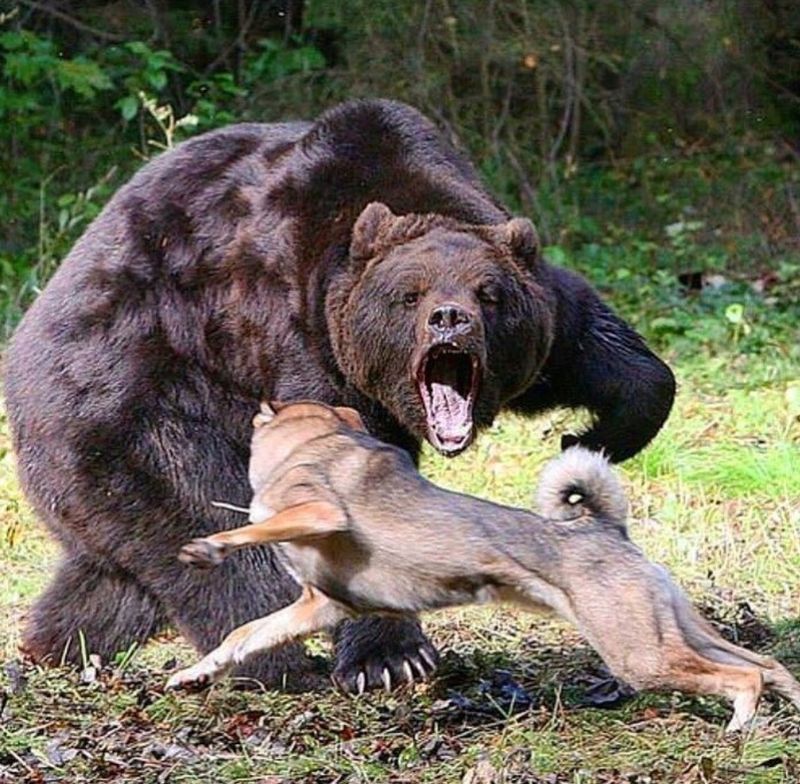

Bears, with their immense size and strength, pose a danger to dogs, especially in forested regions. They can be aggressive if they feel threatened or if their cubs are approached.
To protect your dog, avoid hiking in known bear territories during peak activity times.
Keeping dogs on a leash and making noise can help prevent unexpected encounters. Awareness of bear behavior and habitats is crucial to ensuring your dog’s safety.
Vultures
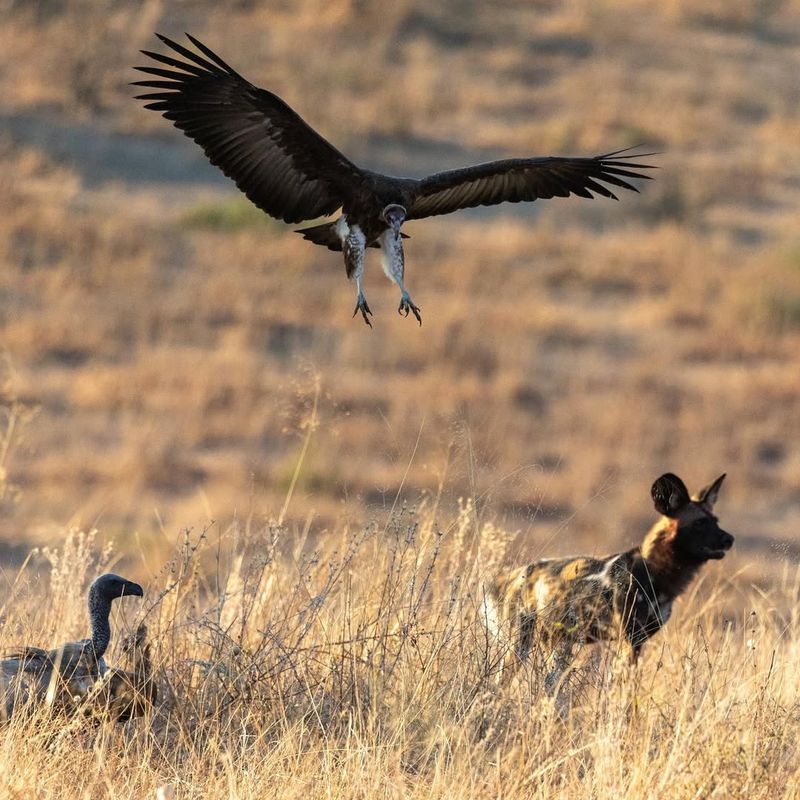

Vultures, though primarily scavengers, can pose a threat to small or injured dogs. They may see a vulnerable pet as an opportunity.
To protect your dog, supervise them in open spaces and ensure they are healthy and mobile.
Understanding vulture behavior and keeping your pet well can prevent potentially dangerous interactions.
Ants

Ants, particularly fire ants, can be a nuisance and a threat to dogs. Their bites can cause pain and allergic reactions.
To protect your dog, avoid areas with active ant mounds and be vigilant during outdoor activities.
If your dog is bitten, monitor for any adverse reactions and consult a veterinarian if needed. Awareness of ant behavior and habitats can help ensure your pet’s comfort and safety.
Lynx
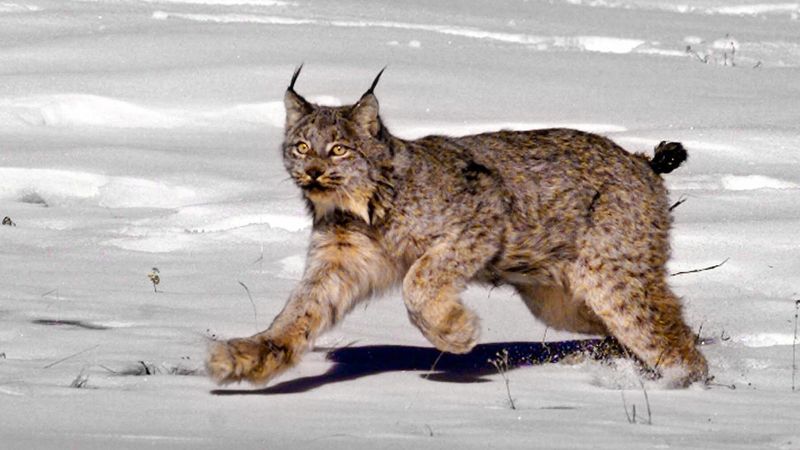

Lynx, with their elusive nature and unique appearance, can pose a threat to dogs, especially in forested areas. They are agile hunters, capable of targeting pets.
To safeguard your dog, avoid areas known for lynx activity, especially during dawn and dusk.
Keeping dogs on a leash and staying aware of your surroundings can prevent unexpected encounters. Understanding lynx behavior is key to ensuring your pet’s safety.
Foxes
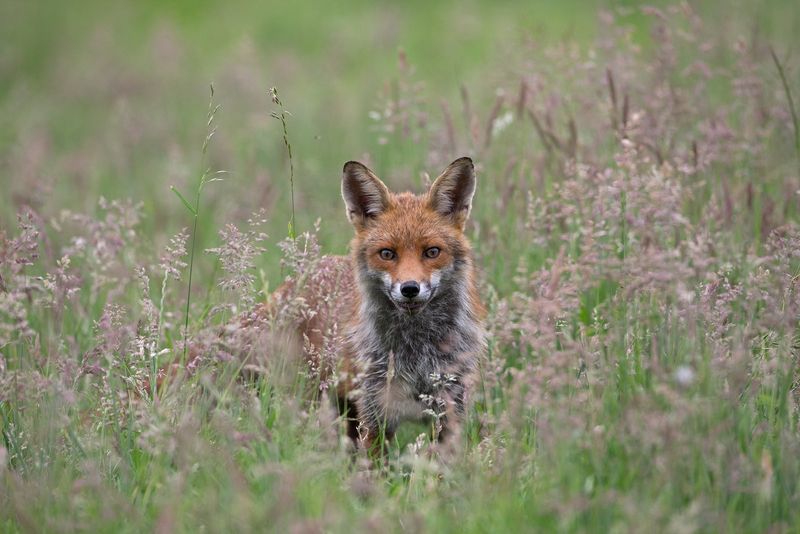

Foxes, while generally shy, can pose a risk to dogs through territorial behavior or disease transmission. They are clever scavengers often found near human habitations.
To protect your dog, keep them on a leash and secure outdoor waste that might attract foxes.
Ensure your dog is vaccinated to prevent disease transmission. Understanding fox behavior can help ensure peaceful coexistence and protect your pet’s health.
Mosquitoes

Mosquitoes, though small, can pose a significant threat to dogs by transmitting diseases like heartworm. Their bites can cause irritation and allergic reactions.
To protect your dog, use veterinarian-approved repellents and avoid areas with high mosquito activity.
Ensuring your dog is on a heartworm prevention regimen is crucial. Being aware of mosquito behavior and habitats can help keep your pet safe and healthy.
Cougars
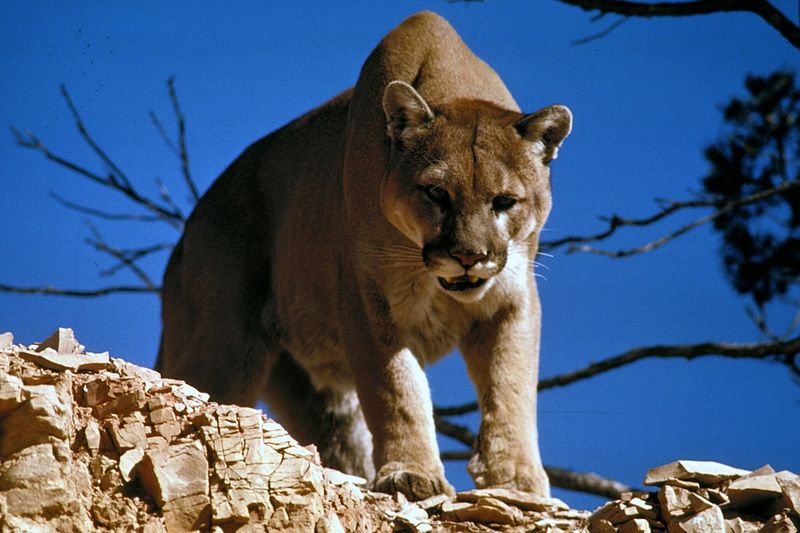

Cougars, also known as mountain lions, are formidable predators that pose a threat to dogs, especially in rural areas. Their stealthy nature makes them difficult to detect until it’s too late.
To protect your dog, avoid hiking during dawn or dusk when cougars are most active.
Keeping dogs on a leash and making noise while walking can help deter attacks. Awareness of cougar habitats and behaviors is essential for dog safety.
Ticks
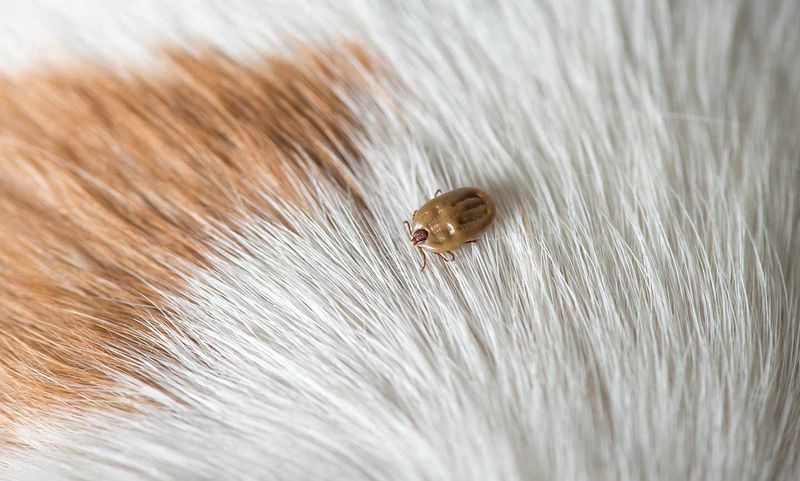
Ticks, though small, can pose a significant health threat to dogs by transmitting diseases like Lyme disease. These parasites latch onto the skin and feed on blood.
To protect your dog, check for ticks after outdoor activities and use preventive treatments.
Ensuring your dog is vaccinated against tick-borne diseases is essential. Awareness of tick behavior and habitats helps ensure your pet’s health and safety.
Snakes
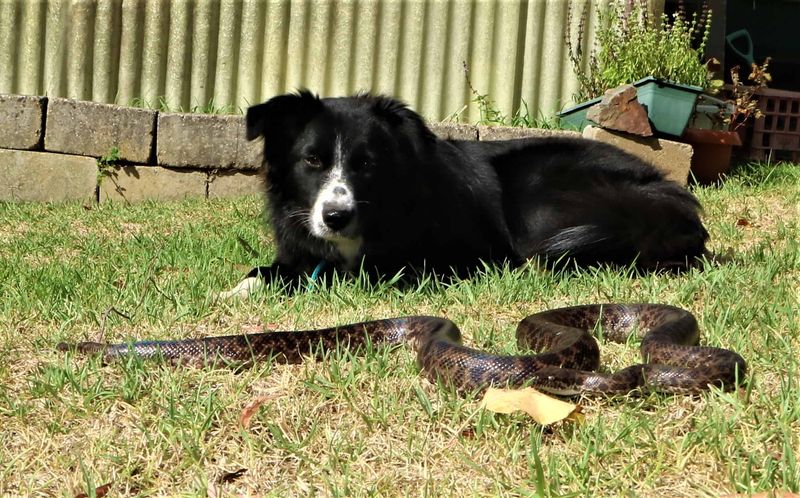

Snakes, both venomous and non-venomous, can pose a threat to dogs. A curious dog may disturb a snake, leading to a defensive bite.
To protect your dog, be cautious in snake-prone areas and keep them on a leash.
Familiarize yourself with snakebite first aid and seek immediate veterinary care if bitten. Understanding snake behavior and habitats helps ensure your pet’s safety during outdoor adventures.
Wild Boars
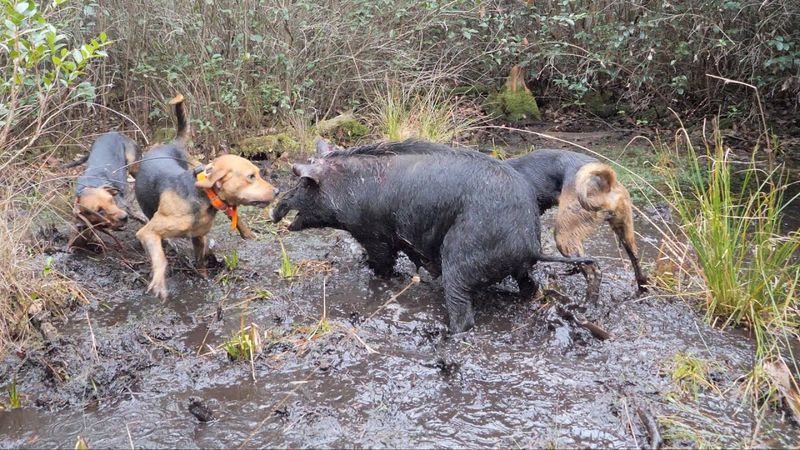

Wild boars, with their aggressive nature and sharp tusks, can pose a threat to dogs, especially in rural areas. They can be highly territorial and defensive.
To safeguard your dog, avoid boar-inhabited regions and keep them on a leash during walks.
If you encounter a wild boar, remain calm and slowly back away. Understanding wild boar behavior is crucial to preventing dangerous encounters and ensuring your pet’s safety.
Pumas
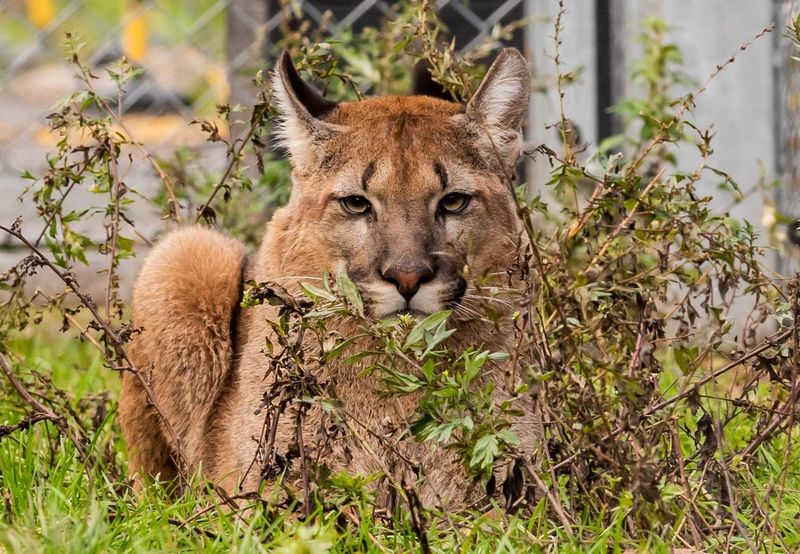

Pumas, powerful and elusive predators, pose a threat to dogs in areas where their habitats overlap. Their ambush hunting style makes them formidable opponents.
To protect your dog, avoid hiking during peak activity times and keep them on a leash.
Making noise while exploring can help deter these predators. Awareness of puma behavior and habitats ensures your dog’s safety during outdoor activities.
Crocodiles
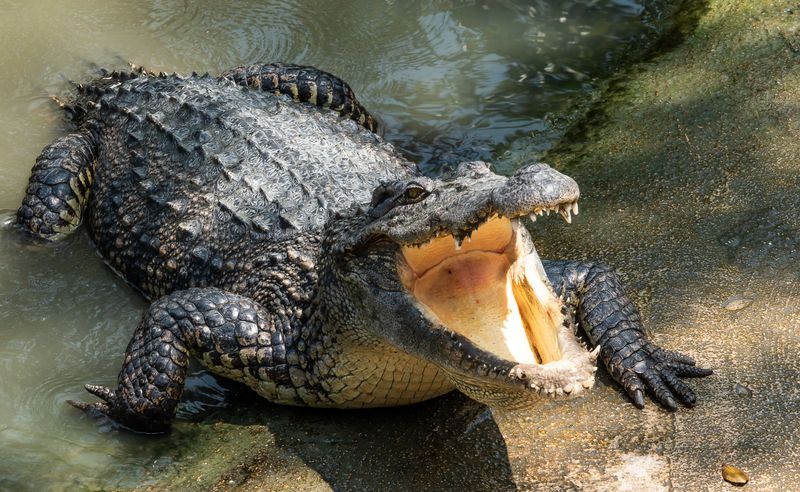

Crocodiles, found in tropical regions, pose a significant threat to dogs near water bodies. Their stealth and powerful jaws make them deadly predators.
Keep dogs on a leash near crocodile habitats and avoid allowing them to swim in these areas.
Understanding crocodile behavior and habitats can help prevent dangerous encounters and ensure your dog’s safety.

