Frozen in time. Imagine stumbling across a perfectly preserved mammoth, or a woolly rhino, trapped in ice, their ancient lives frozen for thousands of years. These incredible discoveries are not just relics—they’re windows into a world long gone.
From the frozen tundras to the icy depths, animals have been trapped in ice for centuries, preserving their bodies as though nature itself hit the pause button. The thrill of unearthing these specimens is nothing short of awe-inspiring, offering us a chance to connect with creatures from the distant past.
In this post, we’ll uncover 20 animals that have been shockingly found frozen in ice—each discovery telling a story of survival, extinction, and a world that once was. Get ready for some jaw-dropping finds that will make you see ice in a whole new light!
Woolly Mammoth

The woolly mammoth, an iconic symbol of the Ice Age, has been discovered frozen in ice in Siberia. These majestic creatures roamed the Earth thousands of years ago and were well-adapted to cold environments.
Their preserved remains offer a glimpse into the prehistoric world. This particular specimen, found in the permafrost, provides valuable insights into the species’ diet and lifestyle.
Researchers marvel at the pristine condition of the mammoth, with even its fur and skin intact. Such discoveries fuel scientific curiosity and open new avenues for understanding prehistoric life.
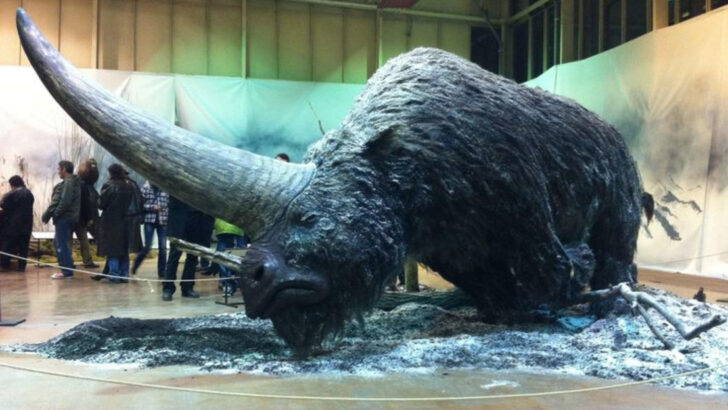
Siberian Rhino
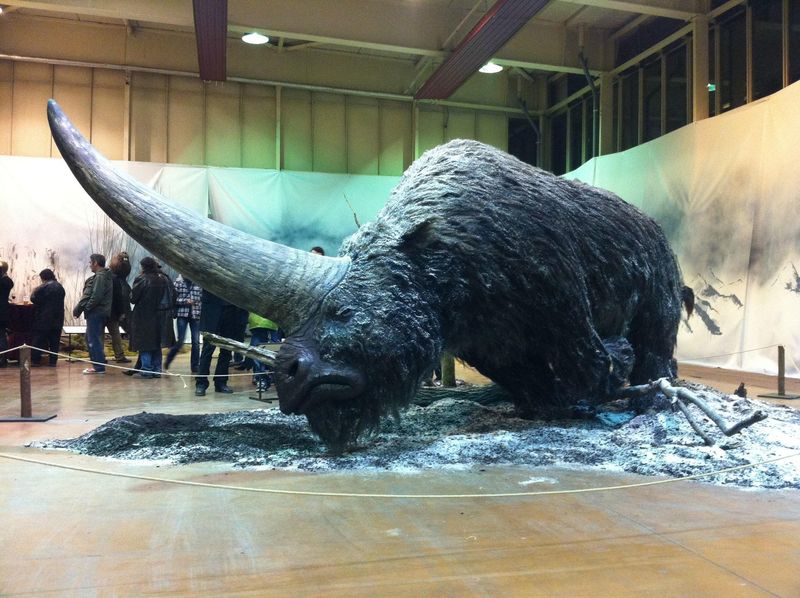

The Siberian rhino, known for its thick skin and resilience to harsh climates, was found perfectly preserved in ice. This ancient creature roamed the cold steppes alongside mammoths and other megafauna.
Its discovery in Siberia has shed light on the Pleistocene epoch’s rich biodiversity. The rhino’s preservation allows scientists to study its anatomy and evolutionary adaptations.
Enthusiasts and paleontologists alike are captivated by this rare glimpse into a world long gone. The frozen rhino serves as a testament to the Earth’s changing climate and its impact on ancient species.
Cave Lion Cub
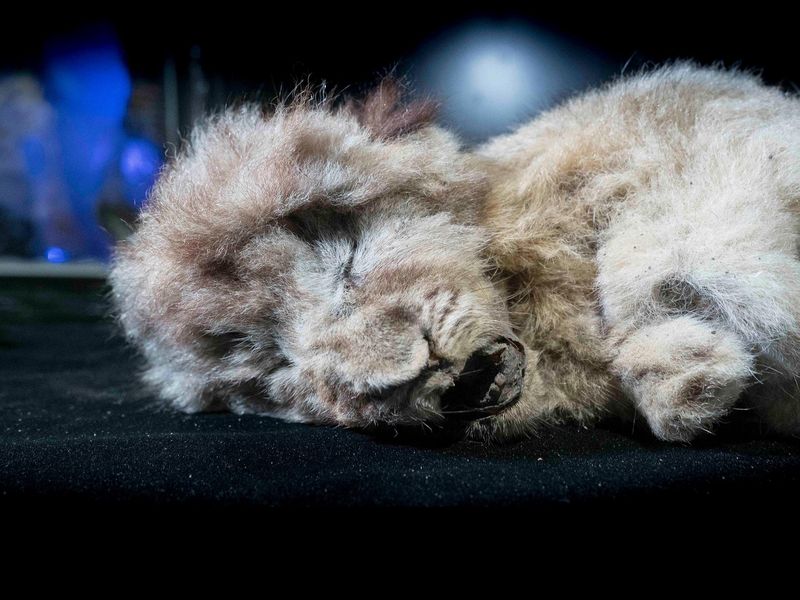

Frozen in time, a cave lion cub was discovered in the permafrost of Siberia. This young predator, part of a species that once dominated the Ice Age landscape, captures the imagination of scientists and wildlife enthusiasts.
The cub’s preservation is remarkable, with its fur and even internal organs intact, providing a rare opportunity to study its physiology. Such finds enrich our understanding of the extinct cave lion’s life and environment.
The cub reminds us of the vast and varied wildlife that once roamed our planet, now lost to the ages.
Prehistoric Bison
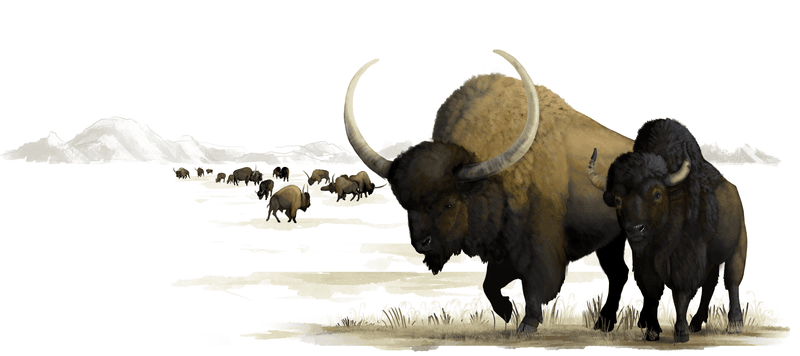
The prehistoric bison, a formidable ancestor of the modern buffalo, was unearthed from the icy grounds of Alaska. Its massive frame and thick fur speak to its adaptability to cold climates.
These frozen remains offer invaluable insights into the bison’s diet and habitat. Researchers are particularly intrigued by its well-preserved organs, which reveal details of its digestive system.
The discovery of such an intact specimen enhances our understanding of the ecological dynamics during the Ice Age. This bison’s frozen state continues to captivate the scientific community.
Woolly Rhinoceros
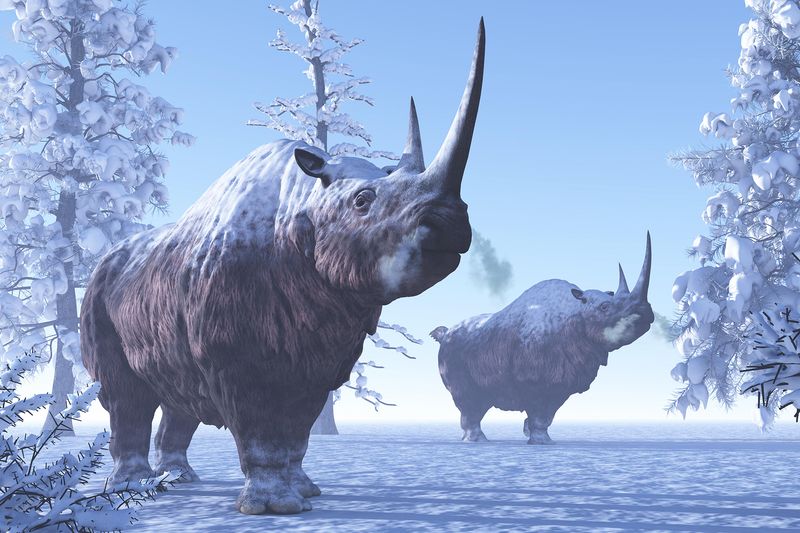

The woolly rhinoceros, a once-common sight across the cold steppes, has been found encased in ice, providing a window into the past. Known for its thick, shaggy coat and impressive horn, this creature thrived during the last Ice Age.
Its frozen state offers scientists a chance to examine its anatomy and environmental interactions. The discovery highlights the diversity of Pleistocene fauna and aids in reconstructing ancient ecosystems.
As researchers delve into its past, the woolly rhinoceros continues to intrigue and inspire, standing as a symbol of resilience in a changing world.
Siberian Musk Ox
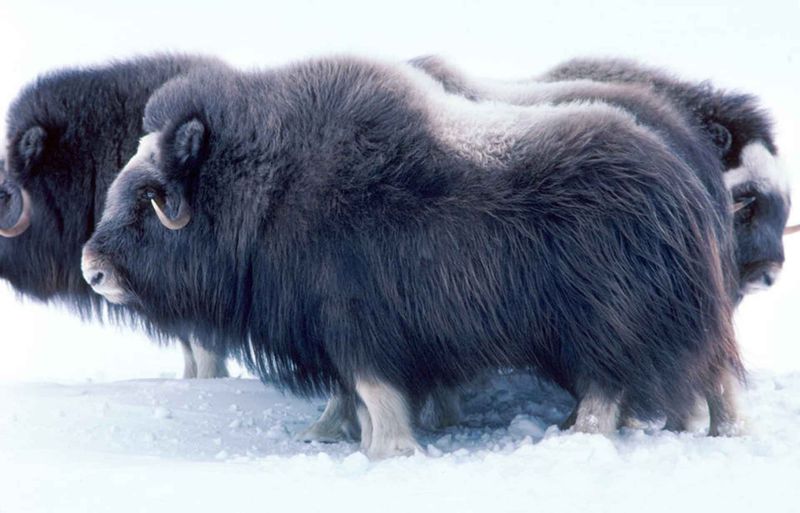

The Siberian musk ox, adapted to the frigid environments of the Ice Age, was discovered in the permafrost, astonishing scientists with its state of preservation. Its dense fur and robust build are testament to its survival skills.
This frozen specimen allows for detailed study of its physiology and adaptation strategies. The musk ox’s remains contribute to our understanding of Ice Age ecosystems and the species it coexisted with.
As researchers analyze its features, they gain insights into the challenges faced by these ancient creatures, fostering appreciation for their resilience and adaptability.
Aurochs
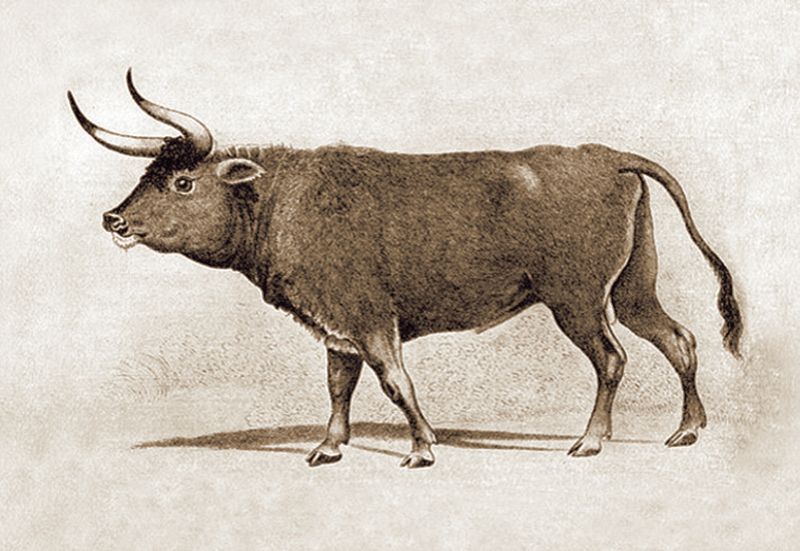

The aurochs, a powerful ancestor of modern cattle, was discovered frozen in a European ice sheet. Known for its large size and strength, this animal was a key player in prehistoric ecosystems.
Its preservation offers a rare opportunity to study its genetics and evolutionary history. The aurochs’ remains provide clues about its diet and habitat, enriching our knowledge of ancient wildlife.
As scientists examine this colossal creature, they uncover stories of survival and adaptation, deepening our connection to the natural world. This discovery continues to fuel fascination with evolutionary history.
Ice-Age Wolf
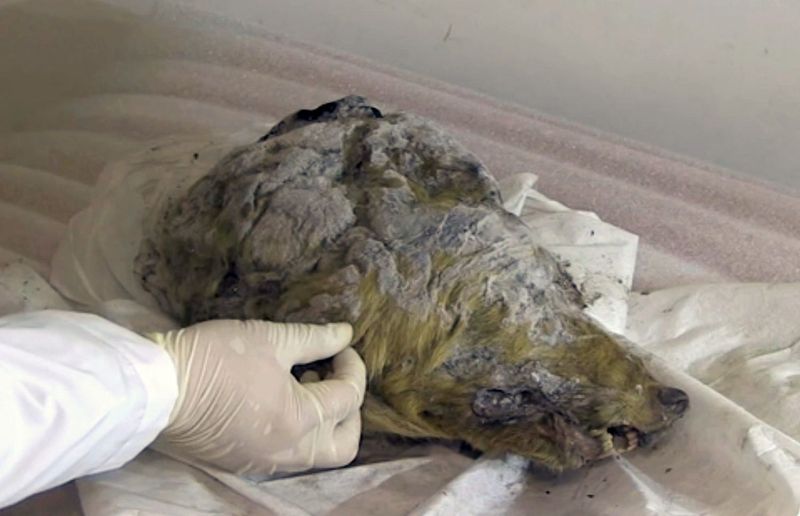
An Ice-Age wolf, found preserved in ice, offers a glimpse into the life of a top predator from millennia ago. This formidable hunter roamed the frozen landscapes, a testament to survival against the odds.
The wolf’s preservation, including its fur and skeletal structure, provides valuable insights into its diet and social behavior. Researchers are eagerly studying this specimen to understand its role in Ice Age ecosystems.
Such discoveries illuminate the complex interplay between predators and prey during this era, enriching our understanding of the natural world and its ancient inhabitants.
Frozen Cave Bear
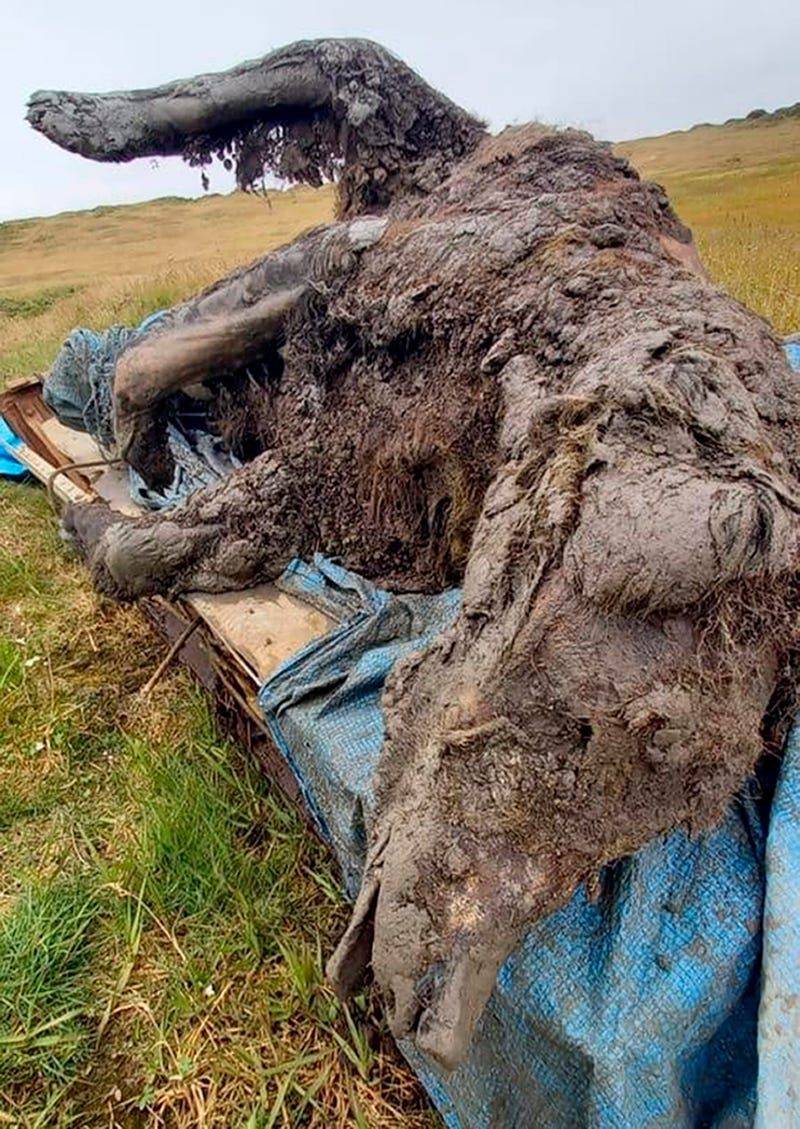

The cave bear, a massive prehistoric creature, was discovered in the harsh Siberian permafrost. This extraordinary find had its fur, teeth, and internal organs impeccably preserved.
With its intimidating stature, the bear offers a rare glimpse into the Pleistocene era, captivating scientists and the public alike. The intact nature of this specimen allows researchers to delve deeper into the diet and lifestyle of these ancient giants.
Its discovery underscores the importance of permafrost as a natural freezer, preserving the planet’s ancient history for millennia.
Frozen Macrauchenia
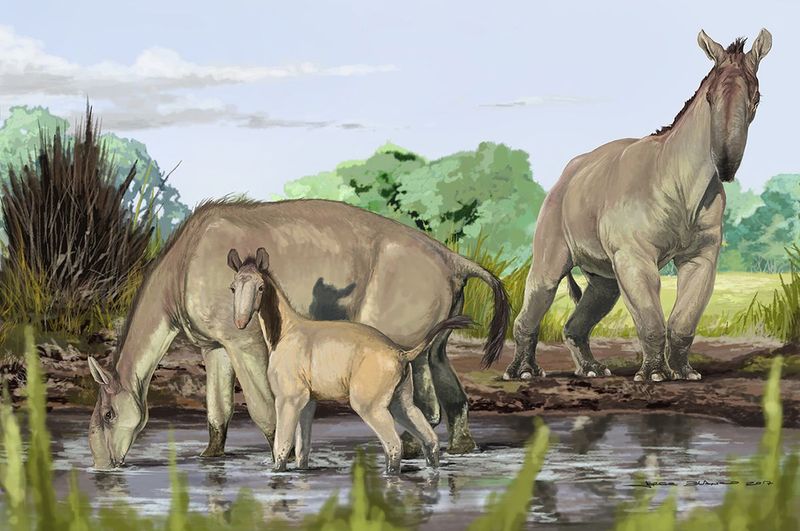

The macrauchenia, an unusual mammal with a giraffe-like neck and a trunk, was found frozen in the Andes Mountains. Rediscovered in an almost mythical state, its body was astonishingly well-preserved.
This fascinating creature provides a link to South America’s prehistoric fauna, offering insights into its adaptation strategies for survival. The finding is a testament to the diverse forms of life that once roamed the continent.
The frozen macrauchenia continues to be a subject of intrigue, inspiring further exploration into prehistoric ecosystems.
Ancient Squirrel

The discovery of an ancient squirrel, preserved in ice, offers a unique glimpse into the life of small mammals during the Ice Age. This agile creature, adapted to cold environments, showcases nature’s resilience.
Its frozen state allows scientists to study its anatomy and dietary habits, providing insights into the ecosystem dynamics of the time. The squirrel’s preservation, including its fur and skeletal structure, enriches our understanding of small mammal evolution.
Such finds continue to inspire curiosity and admiration for the adaptability of wildlife throughout history.
Frozen Steppe Bison

Embedded in the Arctic ice, the steppe bison is another marvel of preservation. With its thick fur coat and imposing horns, it paints a vivid picture of life during the Ice Age.
This remarkable find helps paleontologists understand the environmental conditions of the time. The bison’s preserved stomach contents have even provided a snapshot of its last meal, offering clues about the Ice Age diet.
Discoveries like these bridge the gap between past and present, deepening our understanding of historical biodiversity.
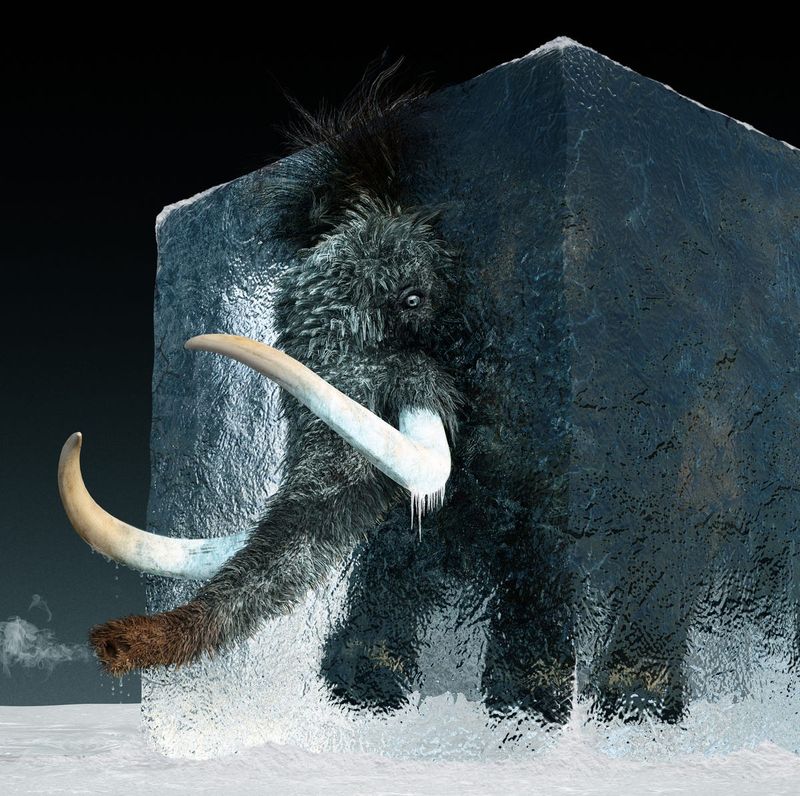
Frozen Baby Mammoth
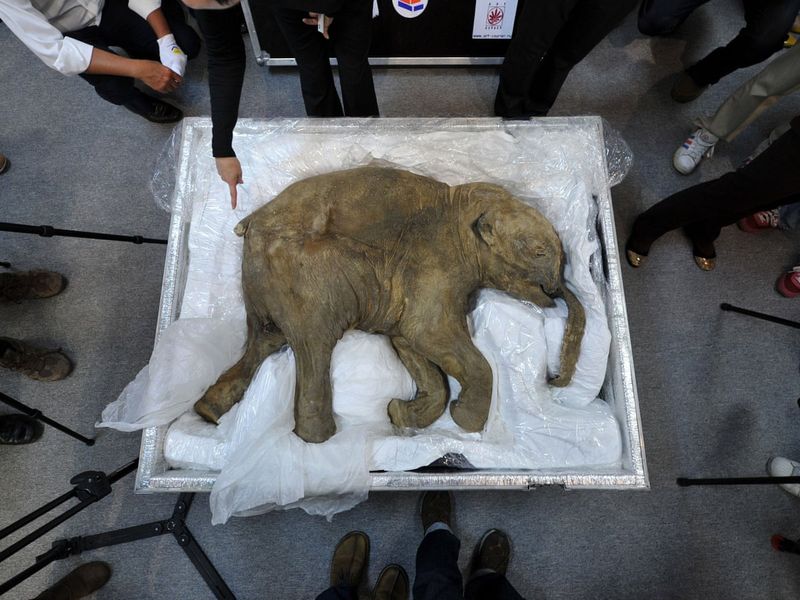

In the heart of Siberia, a well-preserved baby mammoth was found, offering a glimpse into the Ice Age era. The cold conditions kept its skin, hair, and even organs intact, allowing scientists to study its diet and habitat. Such discoveries provide valuable information about the mammoth’s environment and the challenges it faced.
The baby mammoth, estimated to be around two years old at the time of its death, was perfectly encased in a block of ice. Detailed analysis revealed traces of milk in its stomach, suggesting it was still nursing at the time of its demise.
Its discovery has sparked interest in the potential for cloning these majestic creatures, though ethical and practical challenges remain. The find adds a tangible piece to the puzzle of Ice Age life, sparking the imagination of scientists and enthusiasts alike.
Ice Age Hare
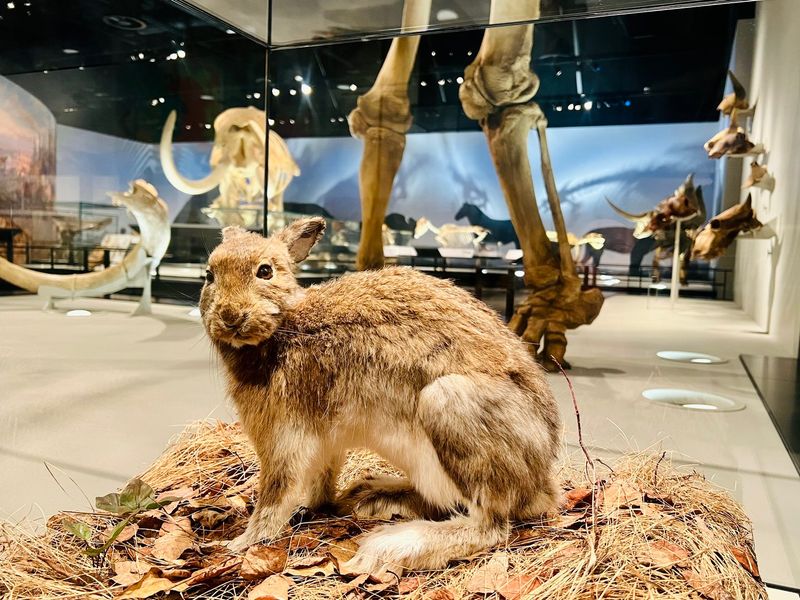

The Ice Age hare, found preserved in ice, offers a remarkable view into the life of small herbivores from the past. Known for its speed and agility, this hare navigated the icy landscapes with finesse.
Its state of preservation provides valuable data on its diet and environmental interactions. Researchers are particularly interested in its role within the ancient food web and its survival strategies.
This discovery enhances our understanding of the ecological dynamics of the Ice Age, showcasing the adaptability and resilience of small mammals in challenging environments.
Frozen Bat
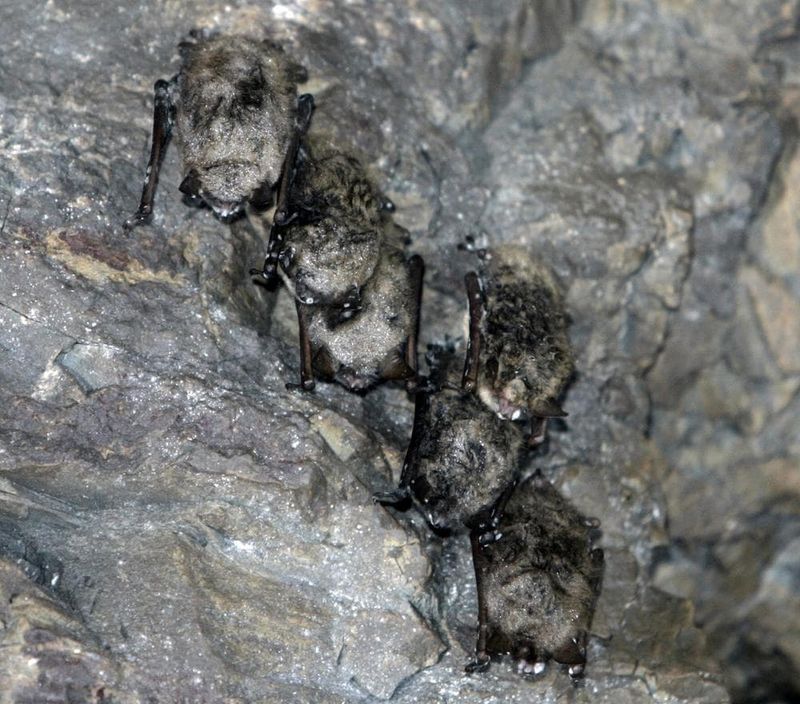

A frozen bat, discovered in an icy cave, unveils mysteries of nocturnal life during the Ice Age. This small, winged mammal, known for its echolocation abilities, thrived in the cooler climates of the past.
Its preservation allows scientists to study its morphology and dietary habits, offering insights into its ecological niche. The frozen bat contributes to our understanding of the diversity of life during this era, highlighting the complex interplay between species.
As researchers explore its past, the bat continues to intrigue and inspire, shedding light on the adaptability of nature.
Frozen Cave Hyena
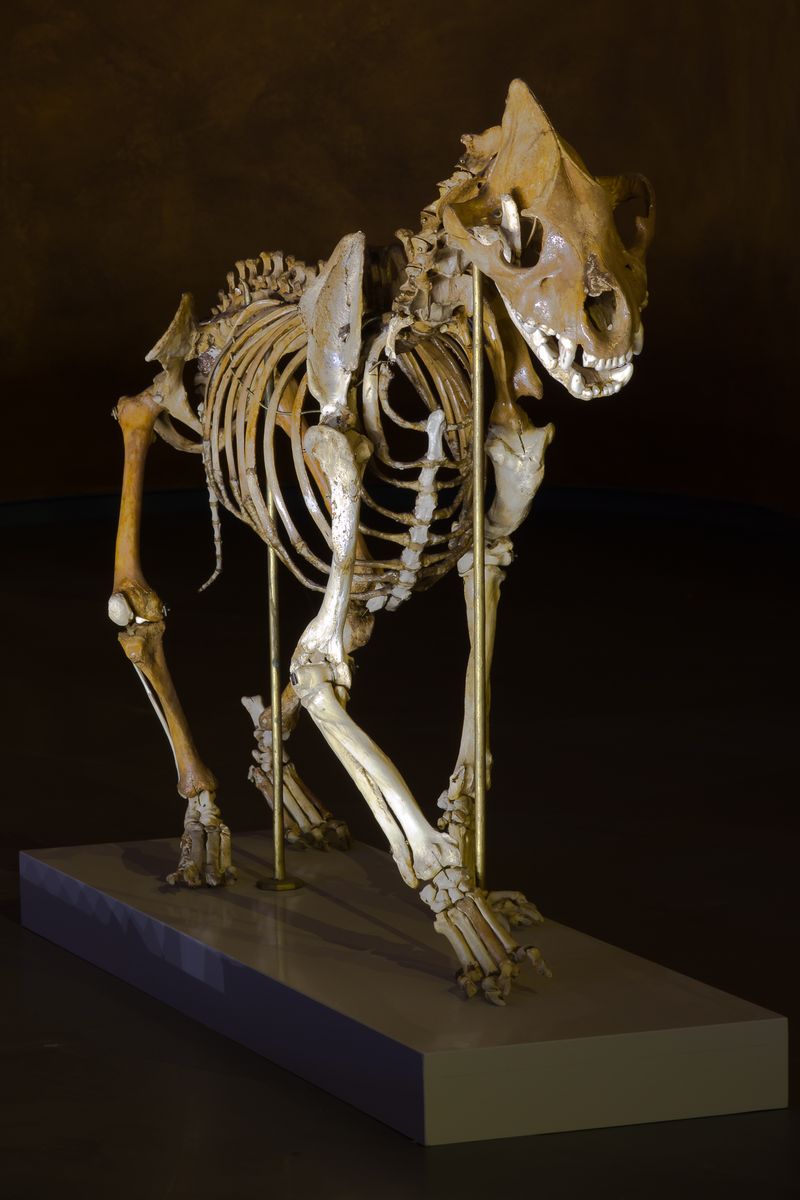

The discovery of a frozen cave hyena in the Siberian permafrost provides a rare opportunity to study this extinct predator. Known for its powerful build and pack hunting behavior, the cave hyena roamed Europe and Asia during the Pleistocene epoch.
This particular specimen was found with its teeth and fur remarkably well-preserved, allowing researchers to delve into its dietary habits and ecological role. The intact state of the carcass offers insights into the causes and conditions of its extinction.
Scientists are keen to learn more about the social structure and behavior of these creatures, which dominated their habitat before disappearing around 11,000 years ago. The frozen find is a testament to the harsh climate of the time and the adaptability required for survival.
Saber-toothed Tiger Cub
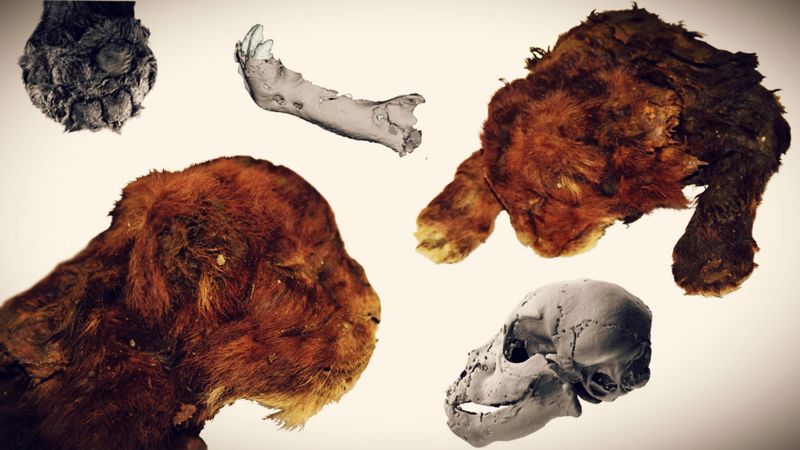
A saber-toothed tiger cub, discovered frozen in ice, provides a rare glimpse into the life of one of history’s most formidable predators. Known for their elongated fangs, these cats were apex predators of their time.
The cub’s preservation offers valuable insights into its growth and development. Researchers are keen to study its anatomy and understand its interactions within the predator hierarchy.
This find enriches our understanding of prehistoric life, highlighting the diversity and complexity of ancient ecosystems. As scientists delve into its past, the cub continues to captivate and inspire.
Frozen Prehistoric Fish

Deep beneath the icy surface of an Antarctic lake, a prehistoric fish was discovered, perfectly encased in ice. This find offers a rare glimpse into aquatic life forms that existed millions of years ago, adapted to the extreme cold.
The fish’s scales and fins are preserved in exquisite detail, providing a window into its evolutionary adaptations. Scientists are fascinated by its ability to thrive in such a harsh environment, contributing to our understanding of ancient marine ecosystems.
This discovery raises intriguing questions about ancient biodiversity and the climatic conditions of the time. It continues to intrigue researchers, who hope to unlock more secrets from this frozen aquatic world.
Frozen Ancient Horse
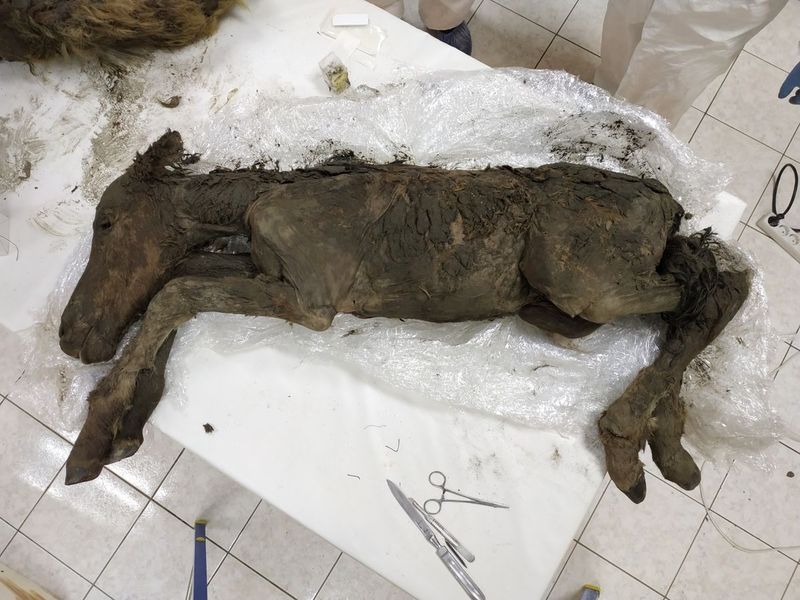

An ancient horse, frozen in time, was uncovered in the Canadian Arctic, showcasing its well-preserved mane and hooves. This remarkable find sheds light on the equine species that roamed the tundra during the last Ice Age.
The horse’s preservation allows scientists to examine its genetic material, offering clues about its lineage and the evolutionary pressures it faced. The specimen’s condition also provides data on the climate and vegetation of its era.
As researchers study this ancient equine, they are piecing together the ecological and environmental challenges it encountered. The discovery contributes to a broader understanding of Ice Age megafauna and the factors leading to their extinction.
Frozen Beaver
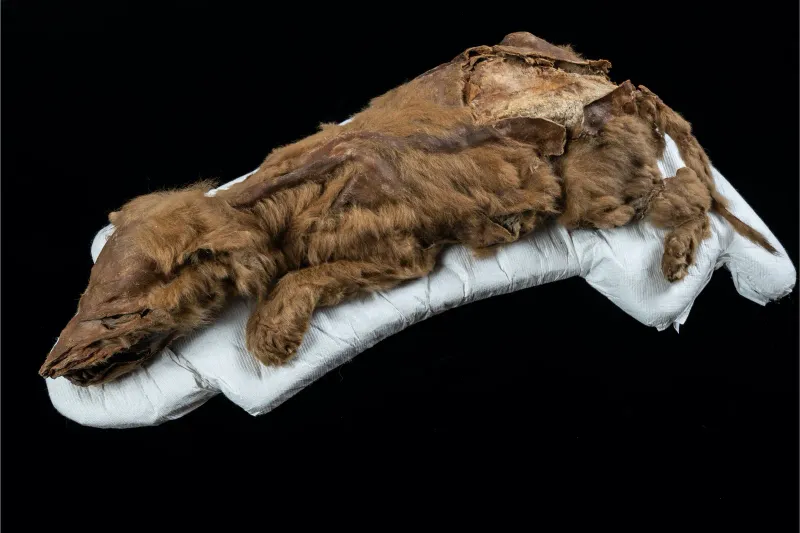

A frozen beaver, discovered in an icy forest, offers a fascinating look at the life of industrious rodents during the Ice Age. Known for their dam-building skills and adaptability, beavers played a crucial role in shaping their environment.
Its preservation allows scientists to study its anatomy and ecological impact, offering insights into its survival strategies. Researchers are particularly interested in its role within the ancient ecosystem and its interactions with other species.
This discovery enhances our understanding of forest habitats and the ingenuity of nature’s architects, showcasing the resilience and resourcefulness of wildlife.
Frozen Tree Frogs

Imagine stumbling upon a cluster of tree frogs, perfectly preserved in ice. These tiny creatures, with their striking green skin, offer a fascinating glimpse into a time when the climate was much colder. Each frog is encased in a crystal-clear block of ice, revealing intricate details of their bodies.
Such discoveries provide invaluable insights into the evolutionary adaptations of amphibians. The preserved frogs challenge scientists to rethink their understanding of how these resilient creatures survived through different climatic epochs. Enthusiasts and researchers alike marvel at the impeccable state of these frozen wonders.
The find serves as a reminder of the delicate balance of life and the ever-changing nature of our environment. As the ice slowly melts, these frogs continue to tell their extraordinary story, frozen in time.

