Some animals laugh in the face of aging—and a few barely age at all. While we humans wrinkle, slow down, and count candles, there are creatures out there gliding through decades without a care in the world. No sagging skin. No fading senses. Just endless vitality, like nature forgot to set a timer. From jellyfish that seem to reset their biological clocks to turtles who barely look older at 100 than they did at 10— these species make you question everything you thought you knew about getting older. So what’s their secret? Is it genetics, environment… or something a little more magical? Let’s take a look at nine animals that break the rules of time— and discover how some manage to keep going strong while we’re reaching for reading glasses.
Tardigrade
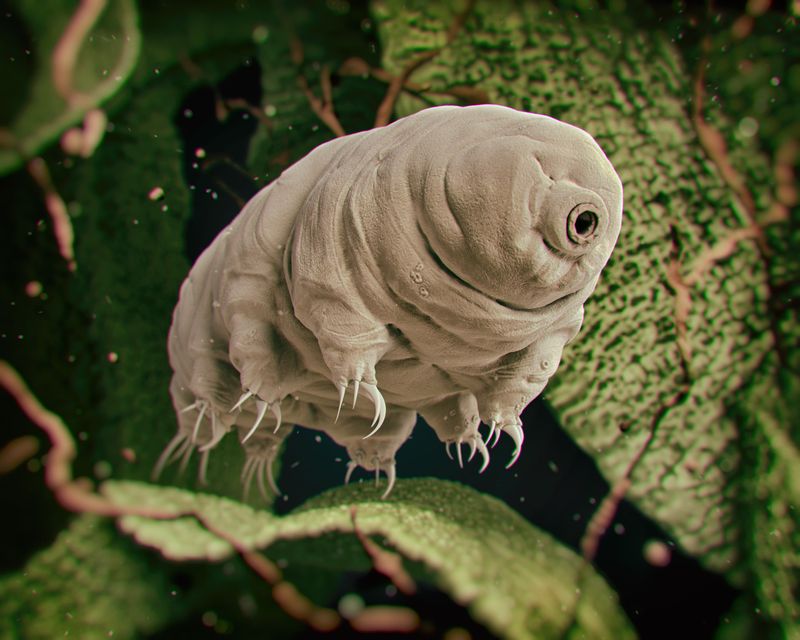

Tiny yet mighty, the tardigrade is often referred to as a water bear. These microscopic creatures are renowned for their ability to survive extreme conditions, from the freezing Arctic to the vacuum of space. Their resilience is attributed to a unique protein that protects their cells.
Amazingly, tardigrades can enter a state called cryptobiosis, suspending their metabolism and aging. This ability allows them to endure harsh environments for years.
Studies continue to explore how these creatures achieve such remarkable feats, potentially unlocking secrets to longevity and survival.
Greenland Shark
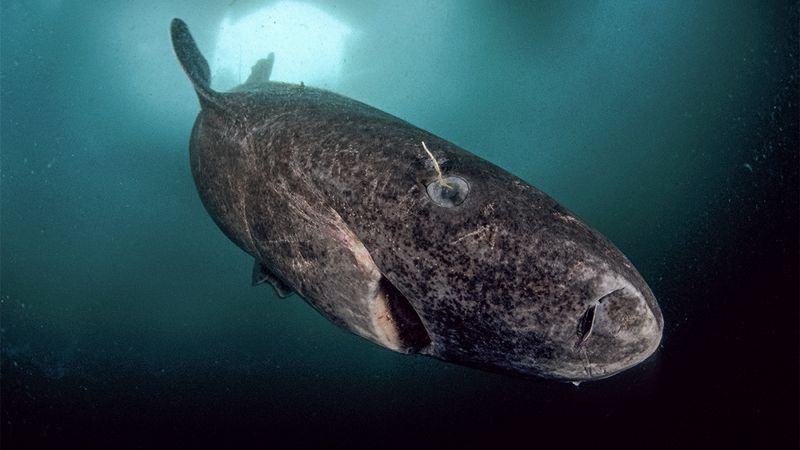

The Greenland shark, often called the Methuselah of the sea, can live for centuries. Found in the icy waters of the North Atlantic, these sharks grow slowly but steadily, reaching impressive ages.
Their secret? A slow metabolism and cold environment that contribute to an extended lifespan. Remarkably, they can live for over 400 years, making them one of the longest-living vertebrates.
Researchers study these sharks to understand aging better, hoping to apply their findings to human longevity. Such ancient creatures hold keys to the mysteries of time.
Hydra
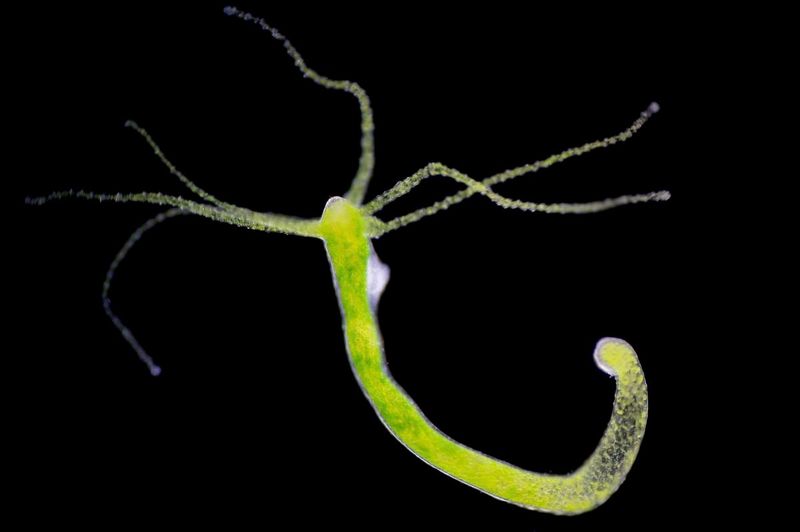
With its ability to regenerate, the hydra defies aging spectacularly. This simple, freshwater organism can replace any part of its body, hinting at a form of biological immortality.
The hydra’s cells continuously divide without losing functionality, a trait scientists find intriguing. This regeneration process prevents typical aging signs, making the hydra a subject of intense study.
As researchers delve into its genetic makeup, they aim to uncover mechanisms that could inspire medical advancements. The hydra’s eternal youth is more than myth; it’s a reality.
Bowhead Whale
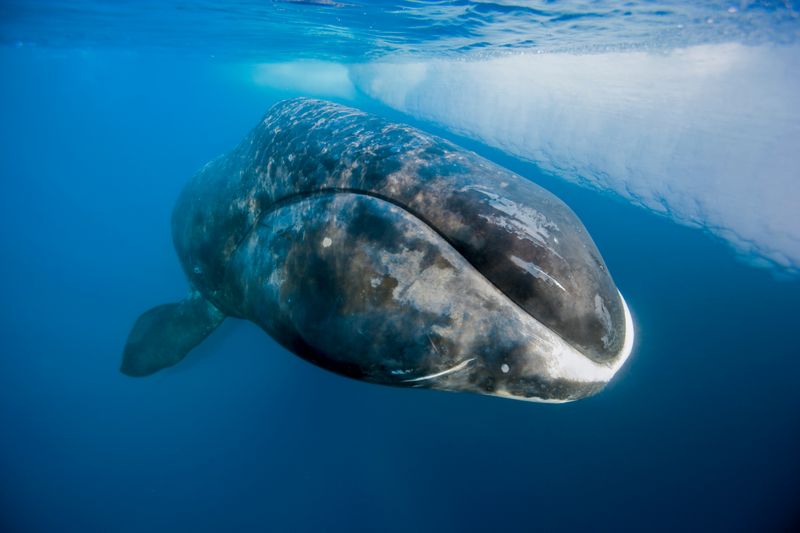

Bowhead whales are giants of longevity, residing in Arctic waters. Known for living over 200 years, their endurance in harsh environments marks them as exceptional.
These whales have unique genetic adaptations, including efficient DNA repair mechanisms, which contribute to their long lives. Their massive size and slow reproductive rate also play roles in their survival strategy.
As a fascinating subject of research, bowhead whales offer insights into natural longevity and resilience. Their history and biology remain a focus for scientists seeking to extend healthy human lifespans.
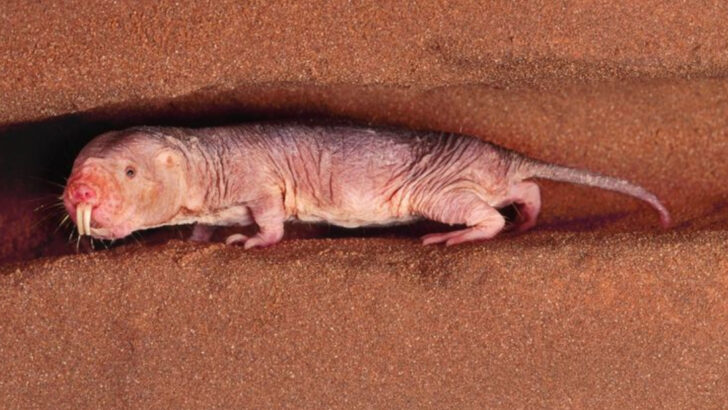
Naked Mole Rat
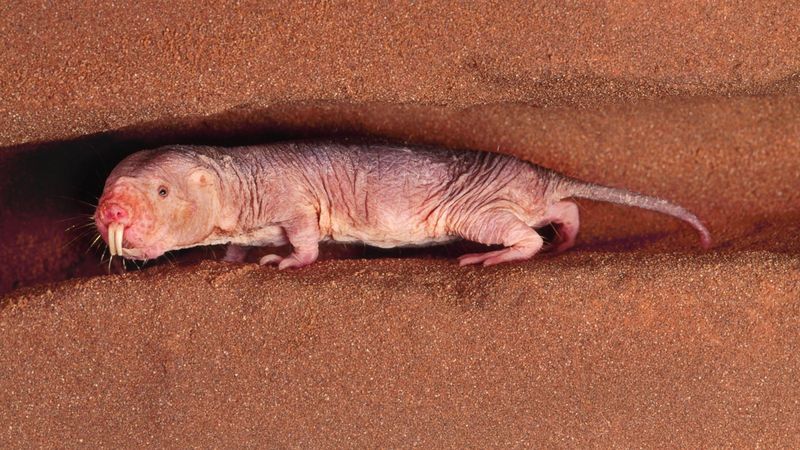

Quirky and unusual, the naked mole rat challenges aging norms in its subterranean habitat. Unlike typical rodents, these creatures can live over 30 years, exhibiting resistance to cancer and pain.
Their social structure and unique biological features, such as low oxygen consumption, contribute to their extended lifespan.
Studies on naked mole rats focus on their cellular mechanisms, which could offer insights into combating age-related diseases in humans. Their peculiar lifestyle and resilience make them a subject of fascination and scientific inquiry.
Immortal Jellyfish
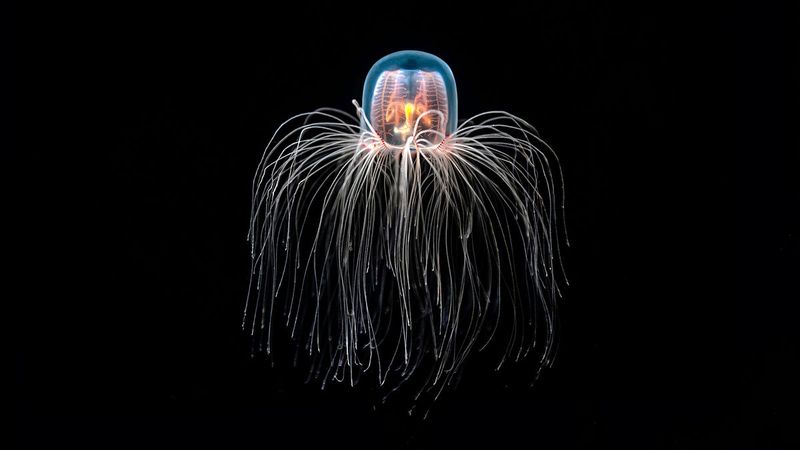

The immortal jellyfish, Turritopsis dohrnii, seems to reverse the hands of time. By reverting its cells to a previous stage of development, this jellyfish can essentially start life anew.
Such a cycle of rejuvenation allows it to avoid death, barring disease or predation. This remarkable ability has sparked interest in its potential applications for human aging and rejuvenation.
Floating gracefully through warm waters, the immortal jellyfish embodies nature’s endless possibilities and the mysteries of biological immortality.
Aldabra Giant Tortoise
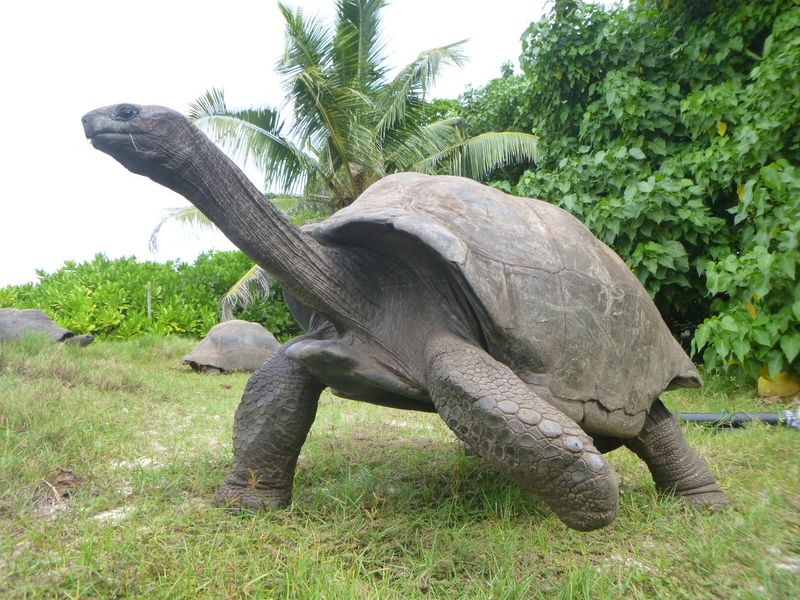

The Aldabra giant tortoise, a symbol of longevity, roams the Seychelles islands. Known for living over 150 years, these tortoises exhibit slow metabolisms and sturdy bodies.
Their leisurely pace of life is complemented by a diet rich in vegetation, contributing to their long lifespan. As one of the largest tortoises, they are an emblem of endurance and stability.
By studying these creatures, scientists hope to glean insights into the biology of aging and long life, learning from their enduring existence.
Planarian Flatworm
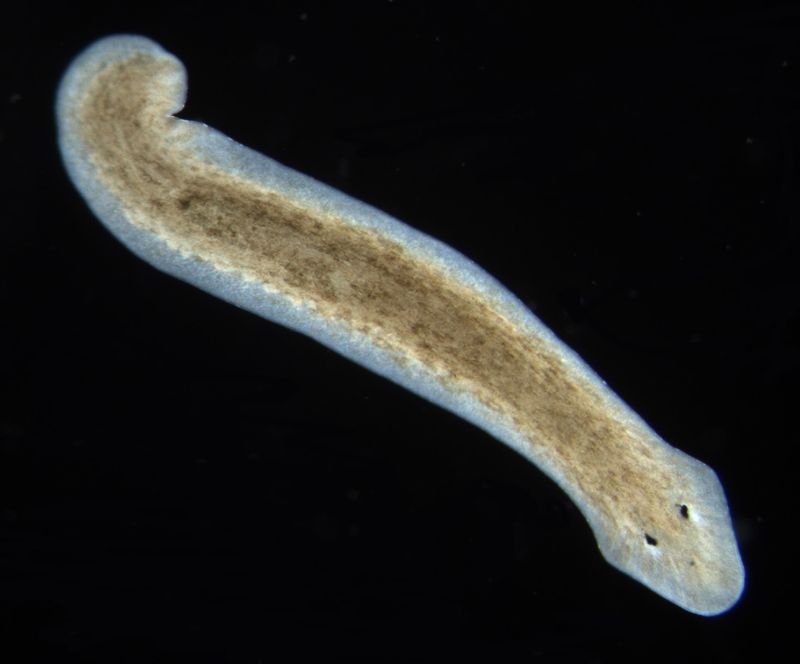
Planarian flatworms intrigue scientists with their regenerative prowess. When cut into pieces, each segment can grow into a new organism, showcasing an extraordinary ability to renew themselves.
This remarkable trait is due to a rich supply of stem cells, allowing these flatworms to maintain youthfulness indefinitely.
Research into their regenerative capabilities may hold the key to advances in medical technology and age-reversal techniques. The planarian’s seemingly endless vitality sparks curiosity and hope for future scientific breakthroughs.
Rougheye Rockfish
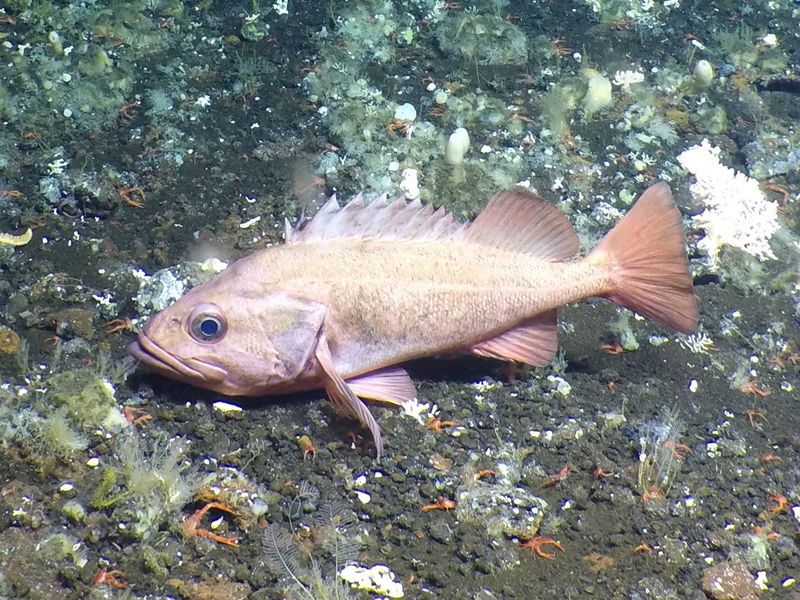

The rougheye rockfish, a resident of the Pacific’s depths, is known for its lengthy lifespan, often exceeding 200 years. Its slow growth and late maturity contribute to its enduring presence.
This fish’s resilience to aging and adaptability to deep-sea environments make it a subject of scientific interest. Researchers study the rougheye rockfish to understand how it maintains health over such extended periods.
Insights gained may provide clues to enhancing human longevity, illustrating the wonders of nature’s diverse aging processes.

