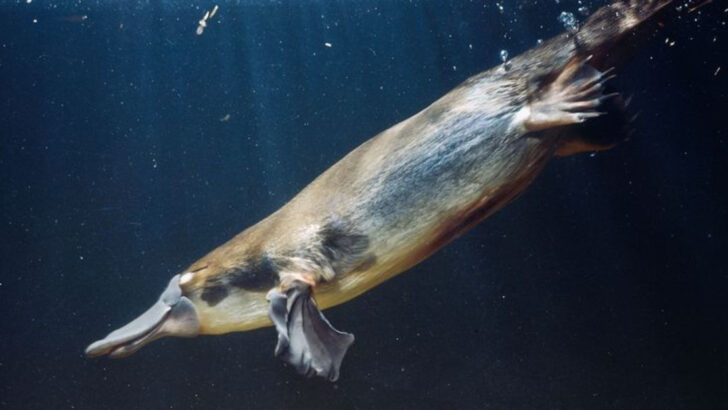
The platypus is nature’s strangest joke—and no one’s laughing harder than science. It lays eggs but nurses its babies. It has venom, glows under UV light, and senses electricity with its bill. It’s a mashup of bird, reptile, and mammal—and somehow, it’s real. Scientists have poked, prodded, sequenced, and studied it for years. Still, this creature refuses to give up all its secrets. Every answer brings a new mystery. Why does its milk kill bacteria? Why does it have 10 sex chromosomes? Why does it glow? If animals had a conspiracy theory subreddit, the platypus would be the top post. And science? Still scratching its head.
The Platypus’s Venomous Spur
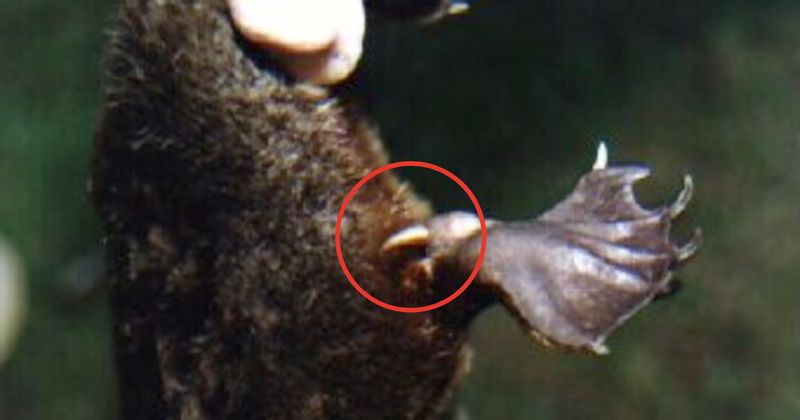

With a surprising twist, the platypus possesses venomous spurs on its hind legs, a feature rare among mammals. In male platypuses, these spurs deliver a painful venom capable of incapacitating small animals and causing severe pain in humans. The evolutionary purpose of this venom remains uncertain, though it may play a role in male competition or defense. Interestingly, the venom’s composition changes seasonally, adding another layer of complexity to this enigmatic trait. What drives this venomous adaptation, and why it exists in such a unique animal, continues to puzzle scientists.
Electroreception in Platypuses
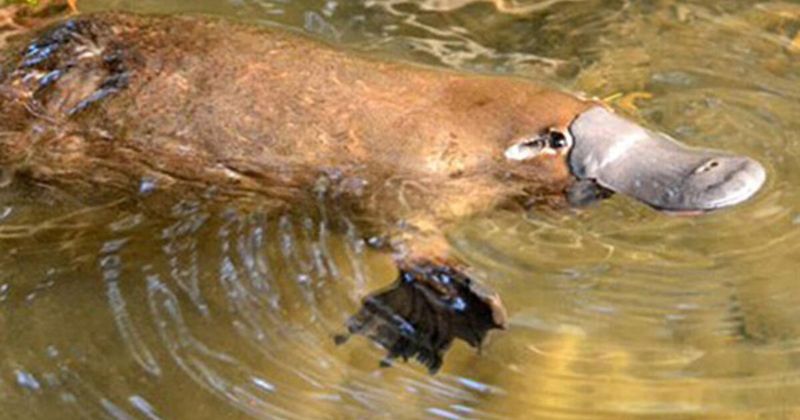

The platypus stands out with its extraordinary electroreception abilities, a feature it shares with only a few other creatures like sharks. Using special sensors in its bill, the platypus can detect electric fields generated by the movements of prey. This ability guides it while hunting underwater, since its eyes and ears close while submerged. The mechanics behind this perceptual talent are not entirely understood, particularly how it integrates such sensory data to navigate and capture prey effectively. This sensory marvel exemplifies the platypus’s mysterious adaptations.
Bill Resembling a Duck’s Beak
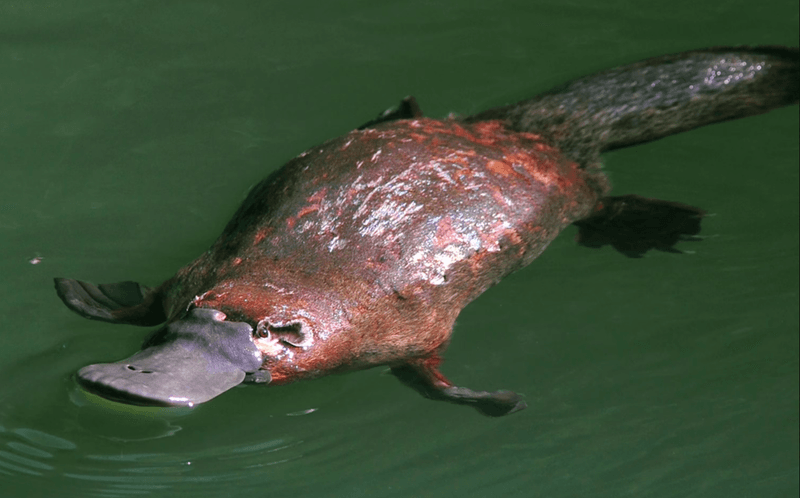

Sporting a bill that resembles a duck’s beak, the platypus challenges traditional mammalian features. This soft and rubbery bill is equipped with thousands of sensory receptors, allowing it to sense the environment like a sophisticated radar. The function and evolutionary origin of this feature have puzzled researchers, especially since it resembles bird anatomy. Unlike a bird’s beak, it serves as a critical tool for detecting prey in murky waters. The evolutionary journey that led to this distinctive bill shape is still unclear, sparking intrigue in the scientific community.
Platypus Egg-Laying Mystery
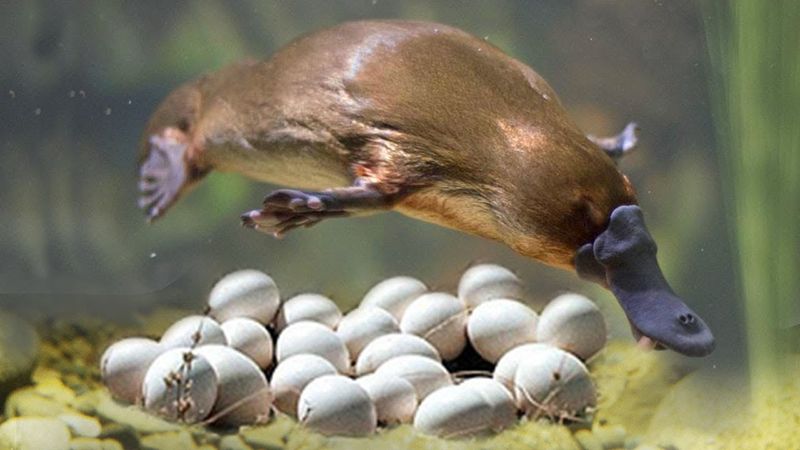

The platypus defies mammalian norms with its egg-laying ability. Belonging to the monotreme family along with echidnas, it lays eggs instead of giving live birth. This ancient reproductive method ties it closer to reptiles and birds than typical mammals. Scientists are curious about why the platypus retained this primitive trait while evolving other unique features. The eggs themselves are leathery, similar to those of reptiles, further complicating its classification. The platypus’s reproductive behavior continues to be a subject of fascination and study, offering glimpses into evolutionary history.
Unique Milk Secretion Method
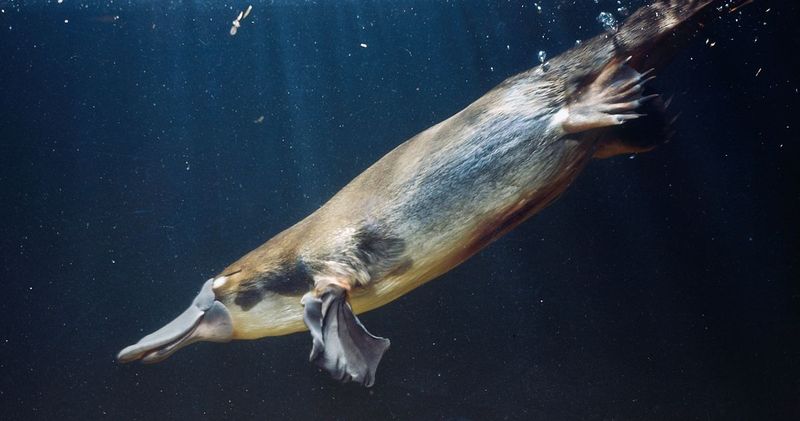

Instead of nursing young through teats, the platypus secretes milk through openings in the skin. This unusual method raises questions about the evolutionary paths leading to such a feature. The milk pools in grooves on the mother’s abdomen, where the young lap it up, exposing them to environmental bacteria. Despite lacking defined mammary glands, the milk itself is rich in unique antibacterial properties, protecting the offspring. Scientists continue to study how this peculiar milk delivery system developed and its impact on platypus health and survival.
Chromosome Count Conundrum
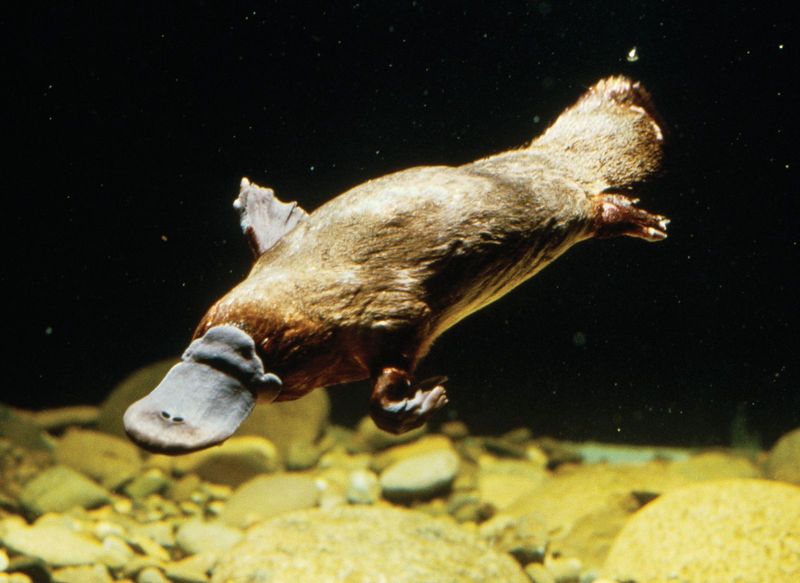

The platypus boasts a staggering 52 chromosomes, an uncommonly high number for mammals. This includes ten sex chromosomes, which complicates genetic studies and understanding of its development. The arrangement and function of these chromosomes challenge conventional genetic paradigms. Particularly intriguing is the mix of mammalian and reptilian characteristics found within its genetic material. Scientists are keenly exploring how such a diverse genetic makeup influences the platypus’s physiology and evolutionary history, hinting at its ancient lineage.
Platypus Glow-in-the-Dark Fur

Adding to its mystique, the platypus boasts fur that glows under ultraviolet light, a feature discovered only recently. This biofluorescence is not well understood and is uncommon among mammals. Scientists speculate it might provide advantages, like camouflage or communication, but these hypotheses remain unproven. Observing this glowing phenomenon raises questions about its ecological and evolutionary purposes. The discovery of such a feature in an already peculiar animal only deepens the scientific intrigue surrounding the platypus, driving further research into its biology.
The Mystery of the Platypus’s Ankle Spurs
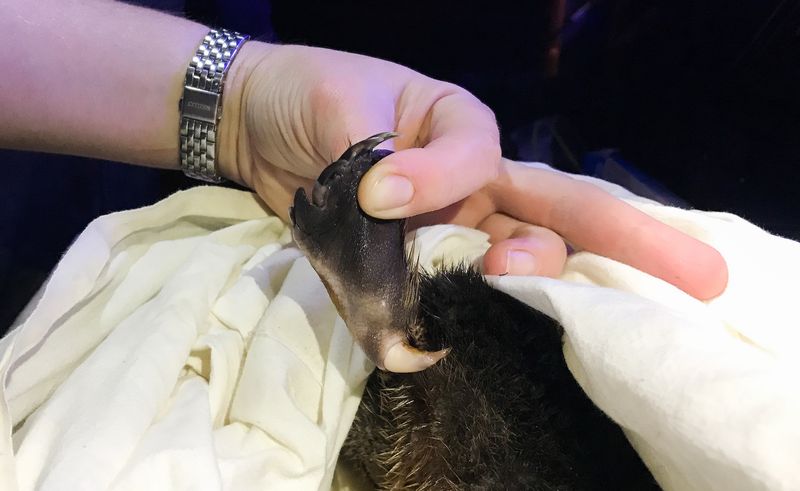
Male platypuses have another curious feature: ankle spurs. These are not venomous like the hind leg spurs but their purpose is equally enigmatic. They might be used during mating rituals or territorial disputes, but their function is not entirely clear. Researchers are eager to uncover the significance and evolutionary origin of these spurs. Their presence adds another layer to the already complex puzzle of the platypus’s anatomy. Understanding these features could shed light on behavioral aspects of the species often hidden from observation.
Platypus Burrow Engineering
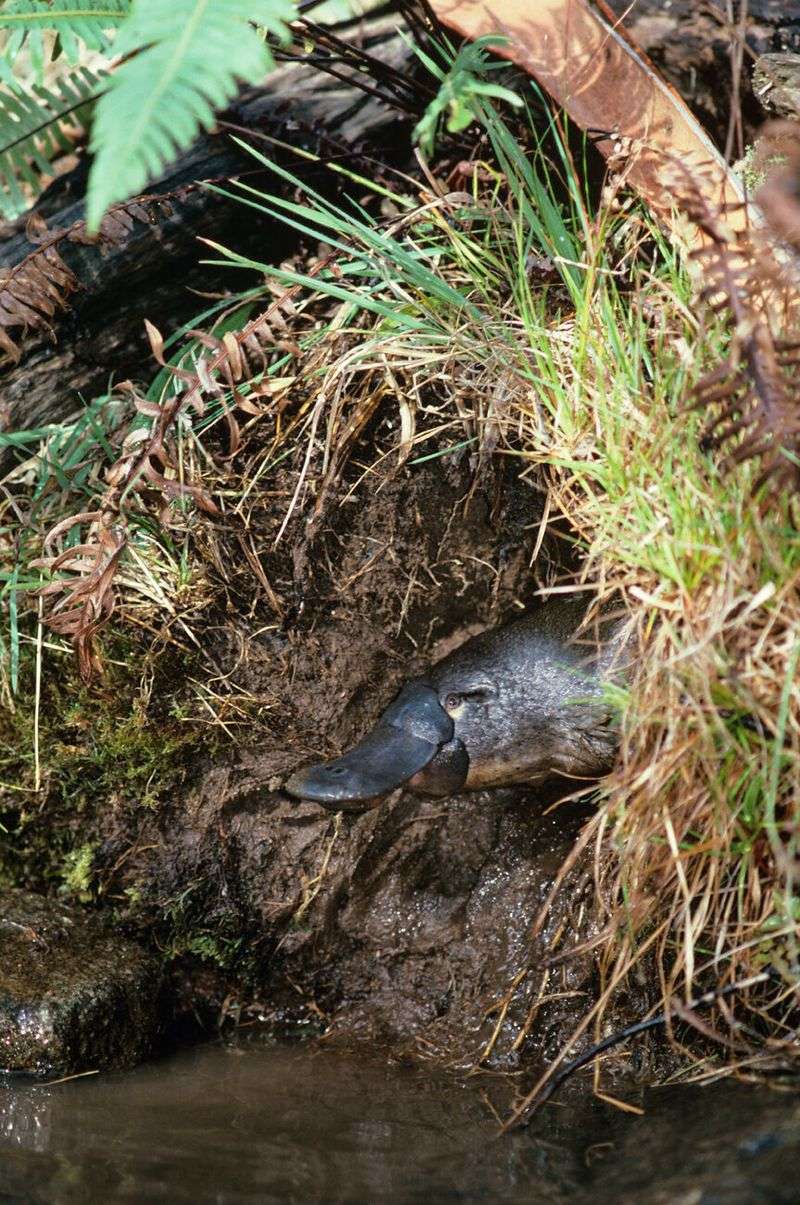

Platypuses are remarkable engineers, crafting intricate burrow systems along riverbanks. These burrows provide shelter and protection for their young, showcasing the species’ instinctual architectural skills. The complexity and design of these burrows vary, with some reaching up to 30 meters long. The motivations and methods behind such construction remain an area of active research. Scientists wonder how these structures impact their survival and reproductive success. Observing platypus burrowing behavior reveals another layer of their ecological adaptations, offering insights into their secretive lives.
Male Platypus Territorial Behavior
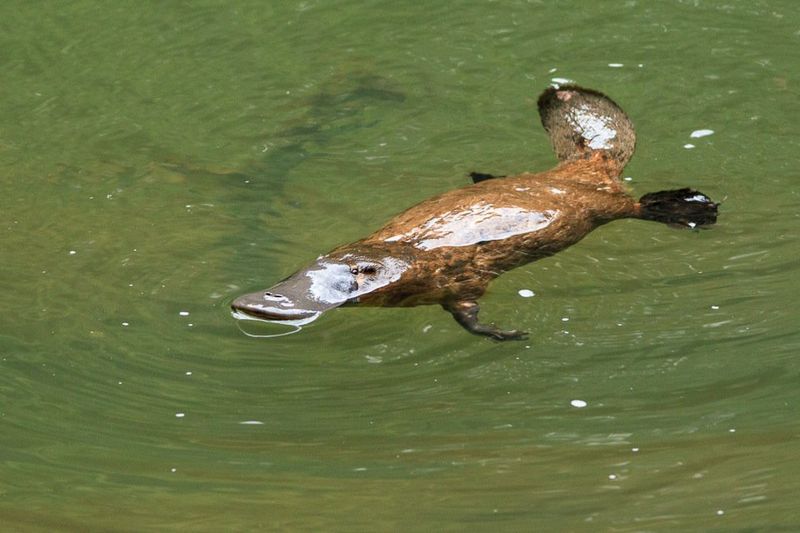

Male platypuses exhibit intriguing territorial behaviors, often engaging in aggressive encounters during the breeding season. These behaviors include using their venomous spurs against rivals and displaying elaborate maneuvers to establish dominance. The motivations behind such behavior and its evolutionary benefits are still being studied. Scientists are eager to understand how these interactions influence mating success and social structure within platypus populations. Investigating these behaviors offers a glimpse into the complex social dynamics of this solitary yet fascinating animal.
Platypus Aquatic Adaptations
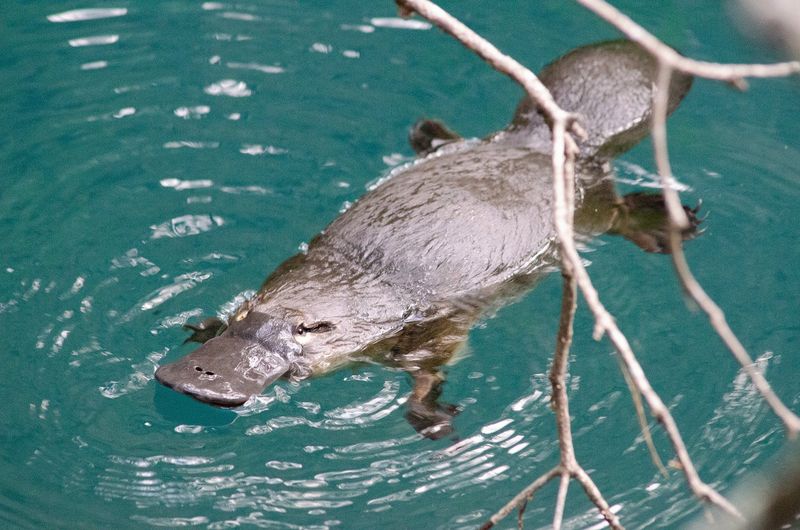

The platypus showcases remarkable adaptations for an aquatic lifestyle. Its webbed feet and streamlined body allow for efficient swimming, while its dense fur provides insulation in cold waters. Despite these adaptations, how the platypus balances its life between land and water remains a mystery. Researchers are exploring the trade-offs and benefits of these features in the platypus’s daily life. These adaptations highlight the platypus’s unique evolutionary path, offering a fascinating study in how mammals can thrive in diverse environments.
Dietary Puzzles of the Platypus
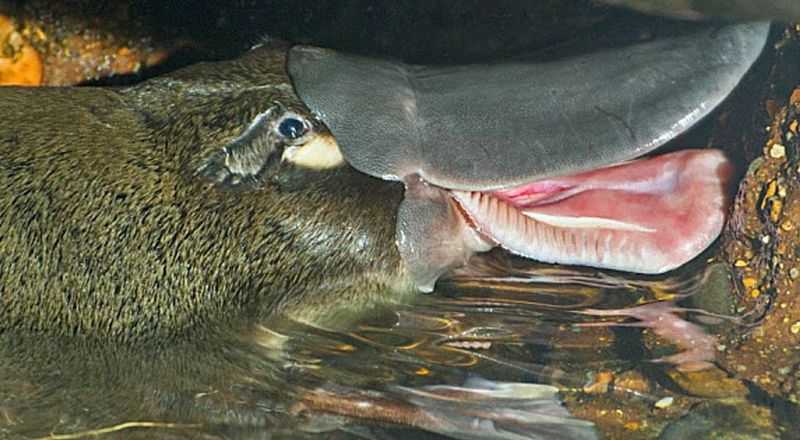

The dietary habits of the platypus are as bizarre as the creature itself. Feeding primarily on aquatic invertebrates, it hunts underwater with closed eyes and ears, relying on its electroreceptive bill. How this diet supports its energy needs and influences its behavior is not fully known. The dietary choices and foraging strategies of the platypus offer insights into its ecological role and evolutionary history. Scientists continue to investigate these behaviors to understand better how this unique mammal fits into its ecosystem.
The Platypus’s Role in Indigenous Culture
For Indigenous Australians, the platypus holds cultural significance, featuring in stories and art for generations. The animal’s unique characteristics and elusive nature have inspired myths and legends. Despite its place in traditional narratives, many aspects of the platypus’s cultural role remain underexplored. Researchers are beginning to delve into these cultural connections, enriching the understanding of the platypus in human history. The intertwining of cultural and biological studies offers a holistic view of this enigmatic creature, celebrating its impact beyond the scientific realm.
Conservation Challenges Facing Platypuses
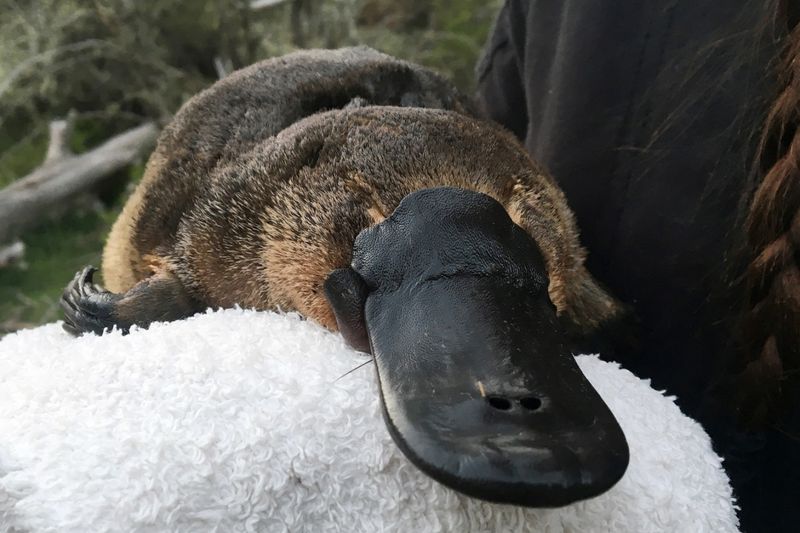

The platypus faces numerous conservation challenges, with habitat destruction and climate change threatening its survival. Despite its iconic status, efforts to protect the platypus are complicated by its elusive nature and habitat requirements. Conservationists are working to understand and mitigate these threats, emphasizing habitat preservation and restoration. The platypus serves as a symbol for broader environmental concerns, illustrating the delicate balance between human activity and wildlife conservation. Protecting this unique species requires coordinated efforts and a deep understanding of its ecological needs.

