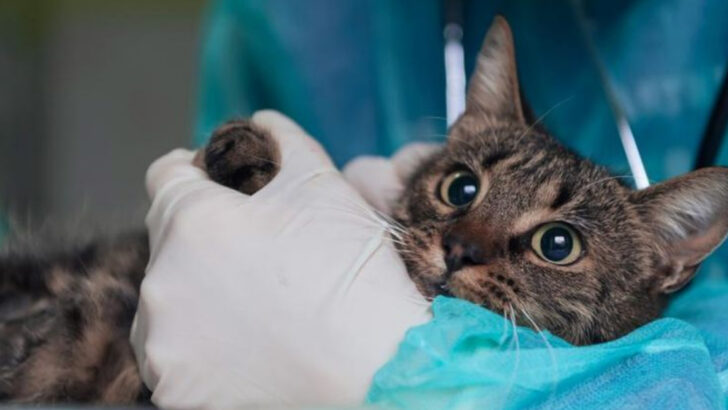
One minute your dog’s chasing a tennis ball.
The next, you’re racing to the emergency vet—and your wallet’s about to cry.
Pet emergencies hit fast, hard, and horrifyingly deep into your savings. A swallowed sock? That’s thousands. A broken leg? Start sweating. And don’t even ask about pancreatitis.
These aren’t rare, freak accidents.
They happen to regular pets in regular homes every single day.
But here’s the good news: a little prevention goes a long way.
You don’t need a medical degree or a fortune—just some basic know-how and a sharp eye.
Let’s break down the seven emergencies that bankrupt the most pet parents—and seven easy ways to stop them before they start.
Gastric Dilatation-Volvulus (GDV)
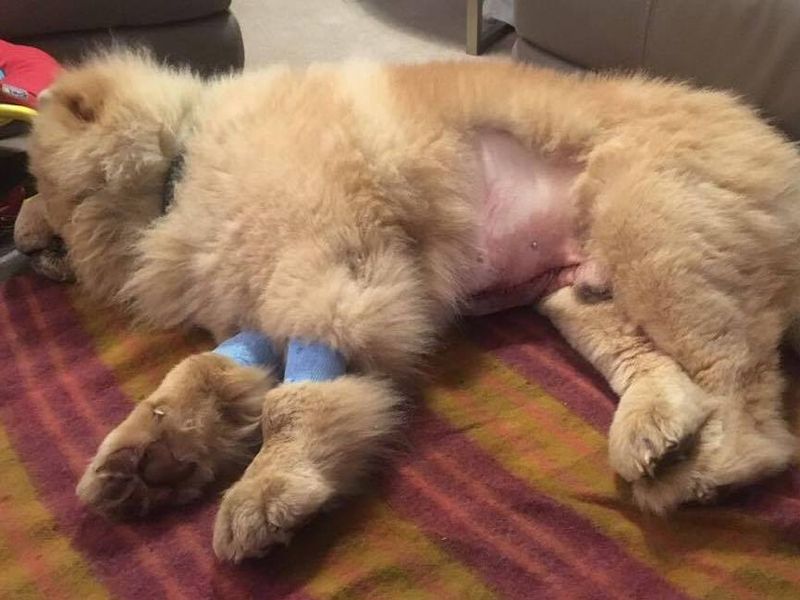
Known as bloat, GDV is a rapid-onset, life-threatening condition. Large, deep-chested dogs like Great Danes are particularly at risk. The stomach fills with gas and twists, cutting off blood supply. Without immediate veterinary intervention, the situation can quickly become fatal.
To prevent GDV, feed your dog smaller, more frequent meals and avoid vigorous exercise immediately after eating. The use of a slow-feeder bowl can also help curb rapid eating, which is a risk factor.
Fun Fact: Did you know some dogs have a genetic predisposition to GDV? It’s worth discussing with your vet.
Foreign Object Ingestion
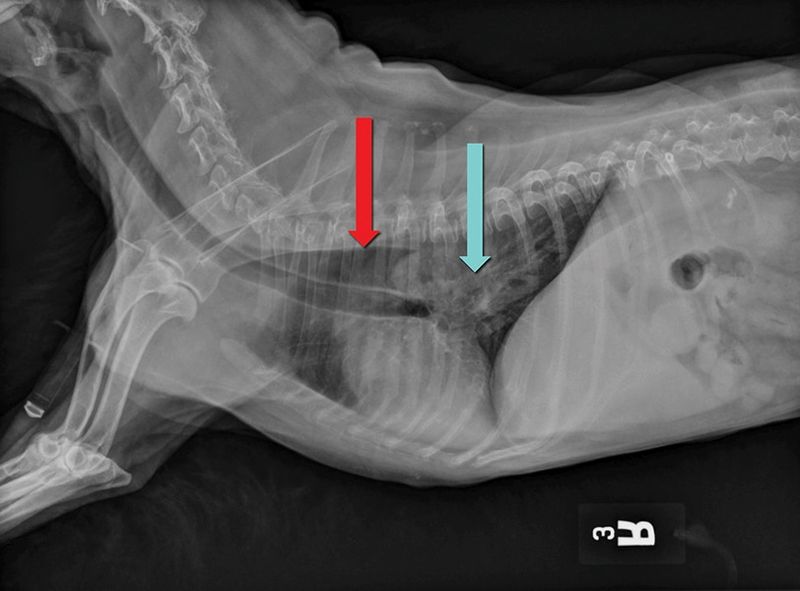
Puppies are naturally curious and love to explore with their mouths. Ingesting foreign objects is a common emergency that can lead to intestinal blockages or perforations. Immediate surgery is often required to remove the obstruction and prevent further complications.
To prevent this, keep small, chewable items out of reach from your pet. Regular training can also discourage this behavior.
Fact: Puppies often outgrow this habit as they mature, but vigilance is key during their early years.
Urinary Tract Obstructions
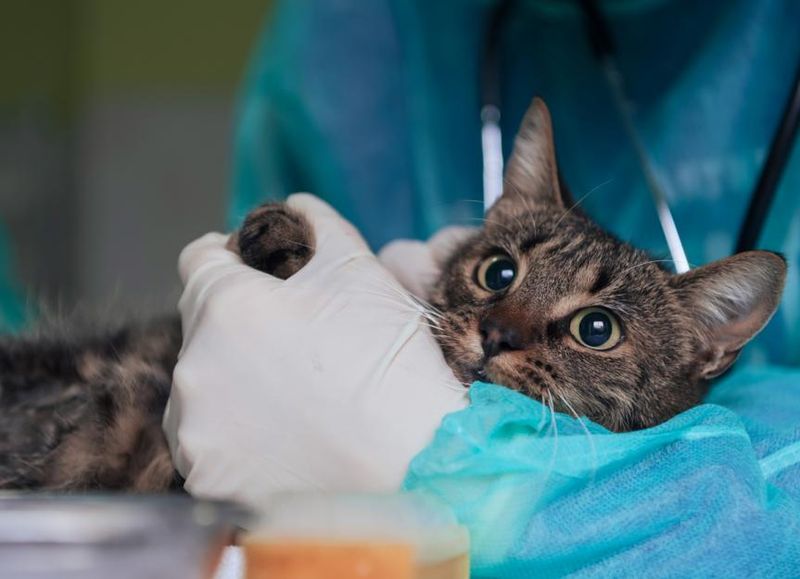
Urinary tract obstructions can be particularly dangerous in male cats due to their narrow urethras. Symptoms include straining to urinate, blood in urine, and vocalizing. Without treatment, it can lead to kidney damage or rupture of the bladder.
To prevent urinary tract issues, ensure your cat has constant access to fresh water and a diet that supports urinary health.
Prevention Tip: Stress reduction can also play a part in preventing urinary issues. Keep your cat’s environment calm and provide plenty of litter boxes.
Severe Trauma
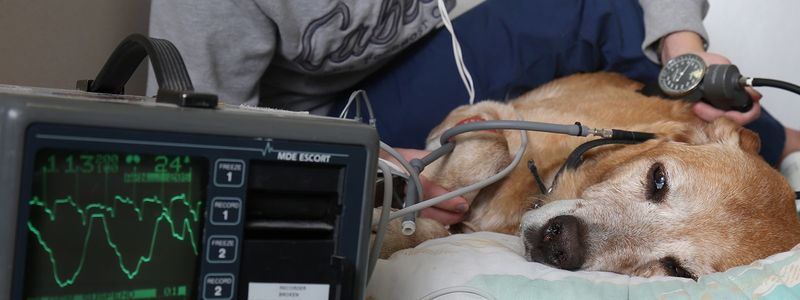
Accidents such as car collisions or falls can result in severe trauma, leading to broken bones, internal injuries, or shock. Quick medical attention is crucial.
To minimize risks, always keep your pet on a leash when near roads or in unfamiliar areas. Secure your home to prevent falls from heights.
Anecdote: A well-fitted harness, rather than just a collar, can provide better control and reduce injury risk during unexpected events.
Pancreatitis
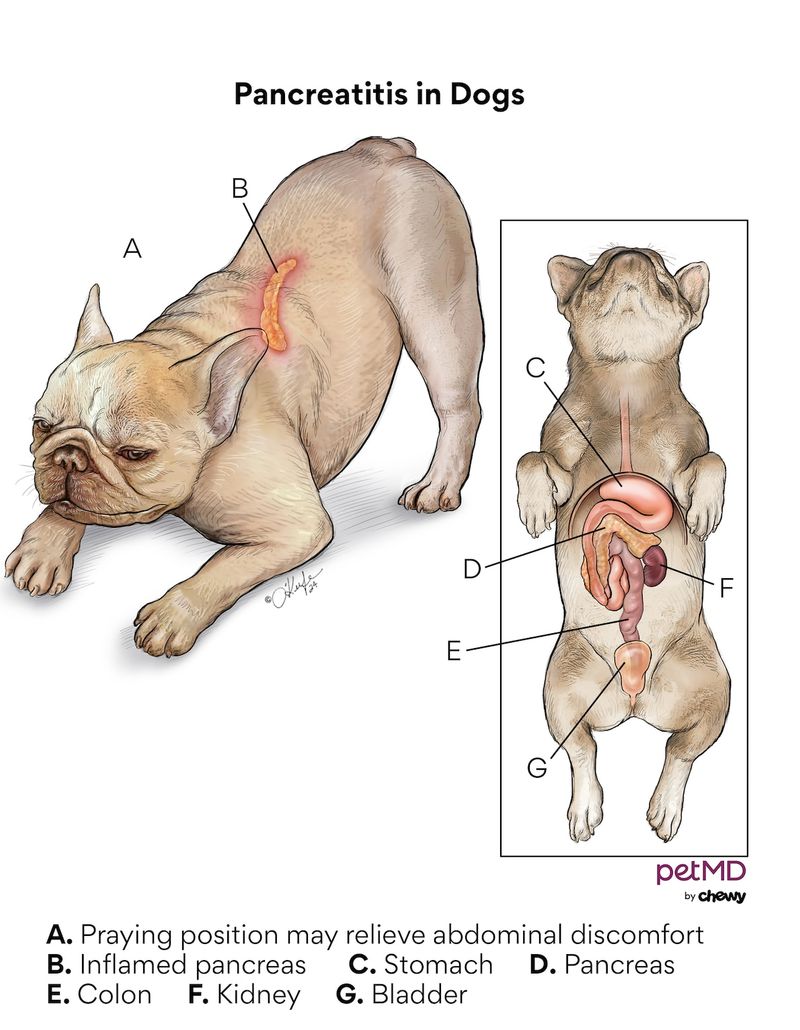
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas, often triggered by a high-fat diet. Dogs with pancreatitis exhibit vomiting, abdominal pain, and lethargy. Immediate veterinary care is needed to stabilize the condition.
To prevent pancreatitis, maintain a balanced diet for your dog and avoid feeding table scraps, particularly those high in fat.
Fun Fact: Certain breeds, like Miniature Schnauzers, are genetically predisposed to pancreatitis, requiring extra caution with their diet.
Poisoning
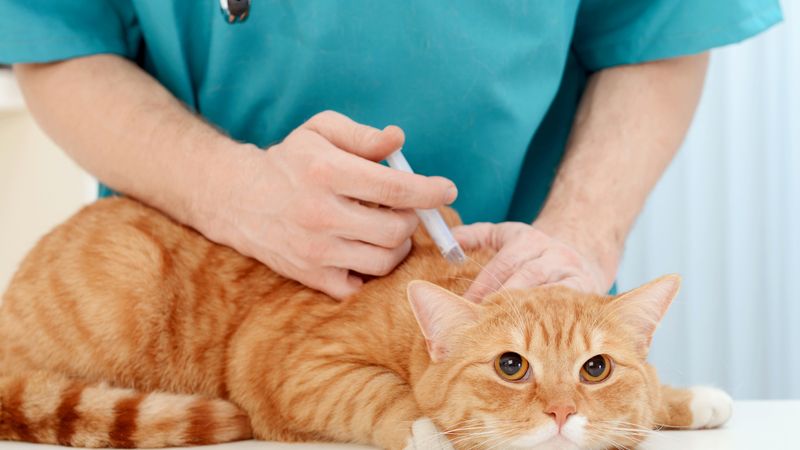
Pets are often exposed to toxic substances such as household cleaners, plants, or human medications. Signs of poisoning can include vomiting, diarrhea, tremors, or seizures. Immediate vet care is essential to manage the symptoms.
Prevention involves keeping hazardous materials out of reach and educating yourself on substances toxic to pets.
Tip: Familiarize yourself with the ASPCA’s list of common pet toxins to better safeguard your home.
Heatstroke
Heatstroke is a life-threatening emergency, especially in hot climates or during summer months. Dogs, particularly brachycephalic breeds, can quickly overheat, leading to organ failure or death. Symptoms include excessive panting, drooling, and lethargy.
Prevent heatstroke by ensuring access to shade and water, and avoid exercise during peak heat.
Pro Tip: Know your pet’s limits—some breeds are more sensitive to heat than others, requiring extra care during warm weather.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups

Routine vet visits are crucial for early detection of potential health issues. They provide an opportunity for vaccinations, parasite prevention, and overall health assessments. Regular check-ups can catch problems early, preventing expensive emergencies.
Schedule annual or bi-annual vet visits for proactive health management.
Fun Fact: Pets that receive regular vet care tend to live longer, healthier lives, making these visits a worthwhile investment.
Proper Nutrition

Balanced nutrition is the cornerstone of preventive pet health care. It ensures that pets receive essential nutrients for growth, energy, and overall health. A balanced diet can prevent obesity, improve digestion, and enhance coat quality.
Consult your vet for dietary recommendations tailored to your pet’s age, size, and health needs.
Tip: Avoid overfeeding and monitor your pet’s weight regularly to prevent obesity-related health issues.
Exercise and Mental Stimulation
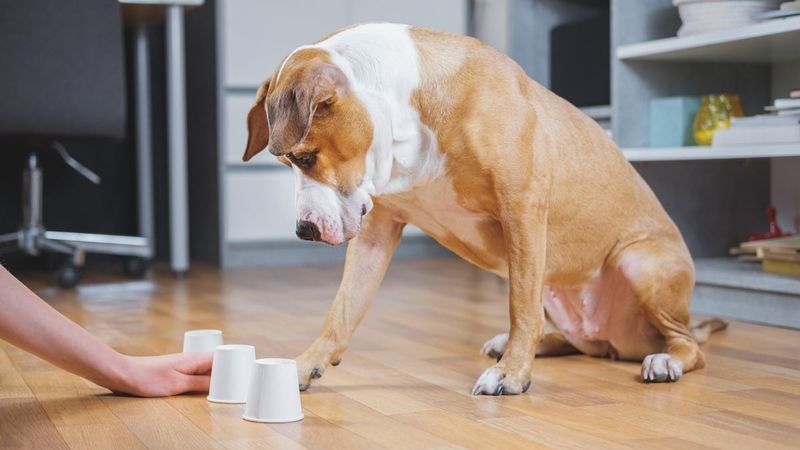

Regular exercise and mental stimulation are vital for maintaining a pet’s physical and mental health. Exercise prevents obesity and strengthens muscles, while mental activities keep pets engaged and happy.
Incorporate daily walks, play sessions, and interactive toys to keep your pet active.
Fun Fact: Dogs that engage in regular physical activity tend to have fewer behavioral issues, making exercise a win-win for both pets and owners.
Pet Proofing Your Home

Pet-proofing your home protects pets from hazards like electrical cords, toxic plants, and accessible trash. Inquisitive pets can get into trouble without proper precautions.
Survey your home for potential dangers and secure them to prevent accidents.
Pro Tip: Regularly update your pet-proofing efforts as your pet’s behavior and environment change.
Grooming and Hygiene
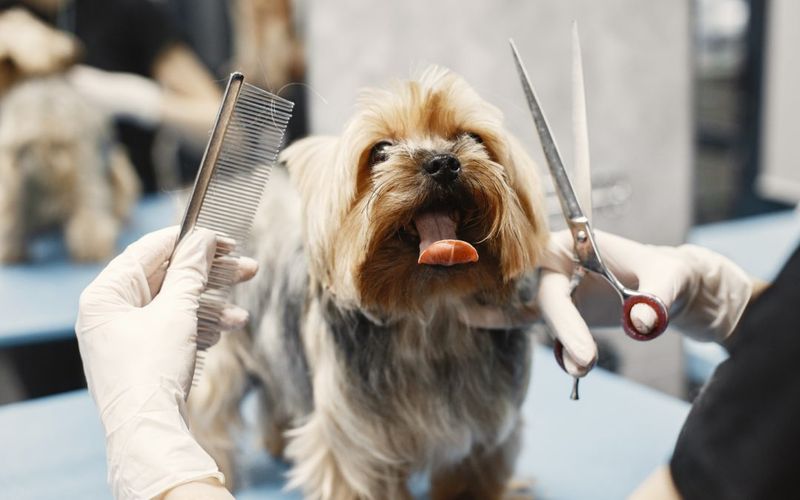

Regular grooming and hygiene practices prevent skin infections, matting, and other health issues. Grooming also offers an opportunity to check for abnormalities like lumps or parasites.
Establish a grooming routine suitable for your pet’s breed and coat type.
Fun Fact: Some pets grow to enjoy grooming sessions, making it a bonding experience with their owners.
Socialization
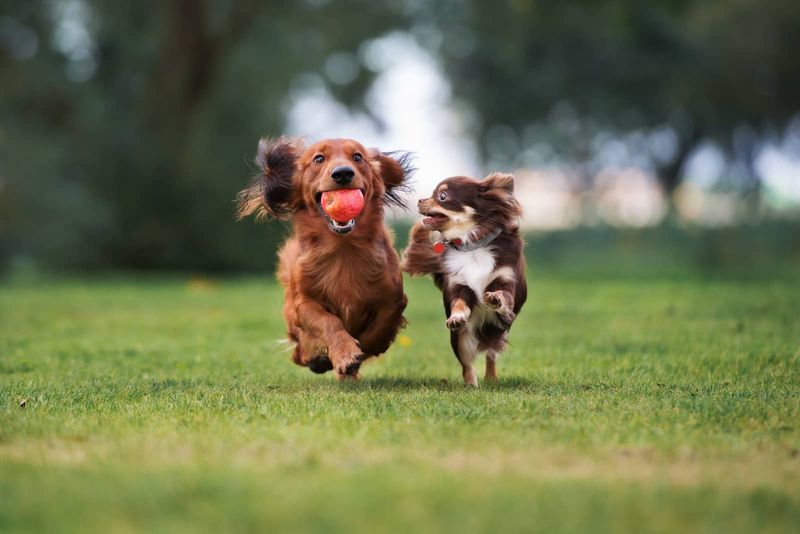

Socialization is crucial during a pet’s early developmental stages. It helps them adapt to new environments and reduces fear-based behaviors. Well-socialized pets are generally happier and more confident.
Introduce your pet to new experiences gradually and positively.
Fact: Early socialization can prevent many behavioral issues, fostering a more relaxed and enjoyable companionship.
Obedience Training
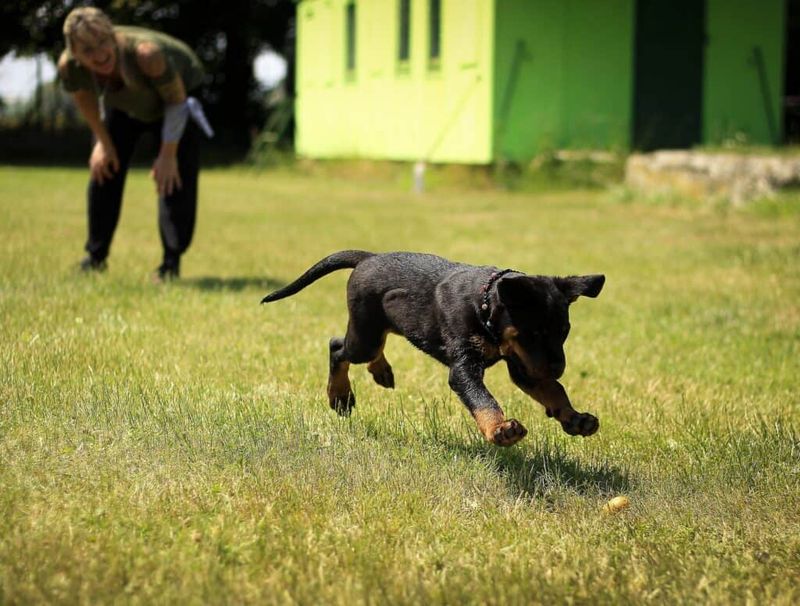

Obedience training establishes a foundation for a well-behaved pet. It enhances communication and builds trust between pets and owners. Training also aids in managing behavioral issues.
Enroll in a class or practice commands at home to instill good manners.
Tip: Positive reinforcement is key—the happier the experience, the more effective the training.