Some animals are born survivors. Others? Not so much.
Whether through centuries of domestication, habitat destruction, or just bad luck in the wild, some species have become completely dependent on human care. Without us, they’d be helpless—struggling to find food, escape predators, or even reproduce.
From delicate creatures bred for beauty to once-wild animals now trapped in human-made environments, these species wouldn’t last long on their own. Some are too fragile, others too specialized, and a few have simply forgotten how to fend for themselves.
Here are 21 animals that owe their survival to human hands—and wouldn’t stand a chance without them.
Pandas
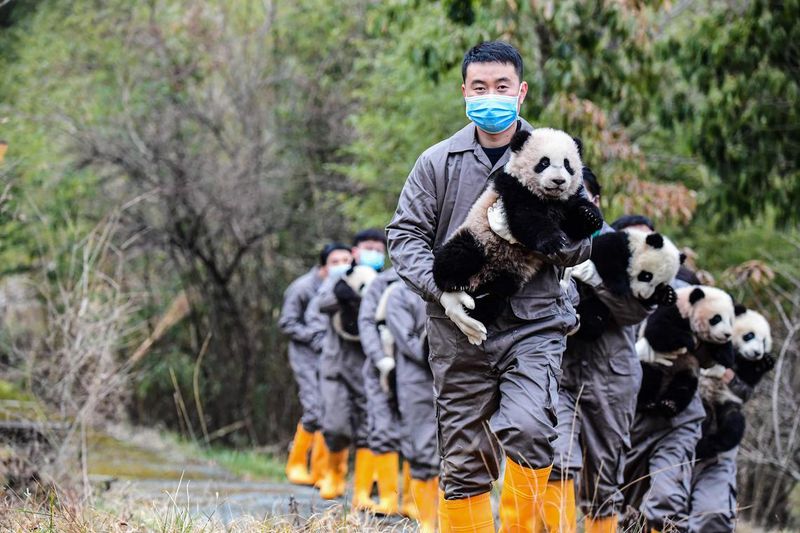

Pandas are iconic, yet their survival hinges on human intervention. Despite their strength, they lack efficient breeding habits, contributing to their vulnerability. Conservation areas in China play a critical role in their survival.
They rely heavily on bamboo, which is scarce in their natural habitat. Various conservation programs focus on breeding pandas in captivity and reintroducing them into the wild.
These efforts are vital as pandas face habitat destruction. Human care ensures they have a chance to thrive, making our role indispensable in their continued existence.
California Condors
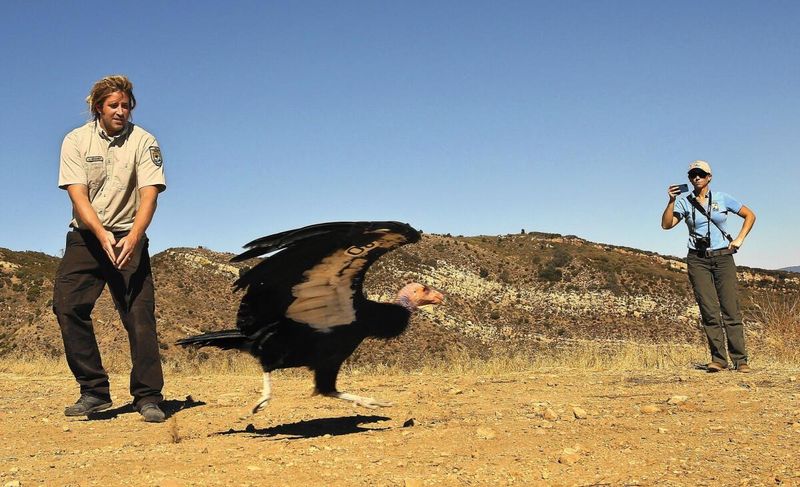

The majestic California condor once teetered on the brink of extinction. By the 1980s, numbers had dwindled alarmingly, prompting conservationists to take action. Captive breeding programs were established to save them.
These programs have been successful, allowing condors to be reintroduced into the wild. Their survival depends on continuous monitoring and protection from threats like lead poisoning.
Without human care, these magnificent birds would likely not exist today. The ongoing conservation efforts highlight the importance of our intervention in preserving such rare species.
Axolotls
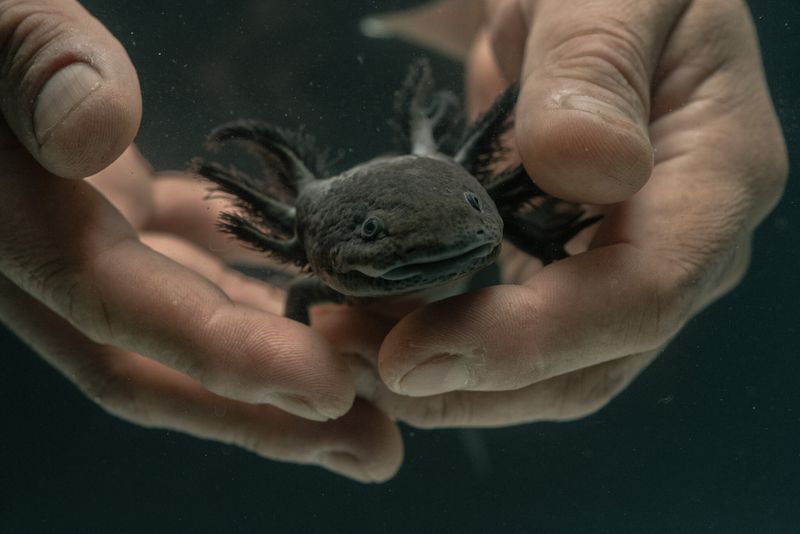

Axolotls are unique amphibians known for their regenerative abilities. Unfortunately, they are critically endangered in the wild due to habitat loss and pollution in their native Mexico City lakes.
Captive breeding programs help maintain their population, allowing scientists to study their fascinating biology. These programs also raise awareness about environmental conservation.
Without human intervention, axolotls would face extinction. Their survival underscores the importance of protecting natural habitats while supporting scientific research to understand and preserve such incredible creatures.
Tasmanian Devils
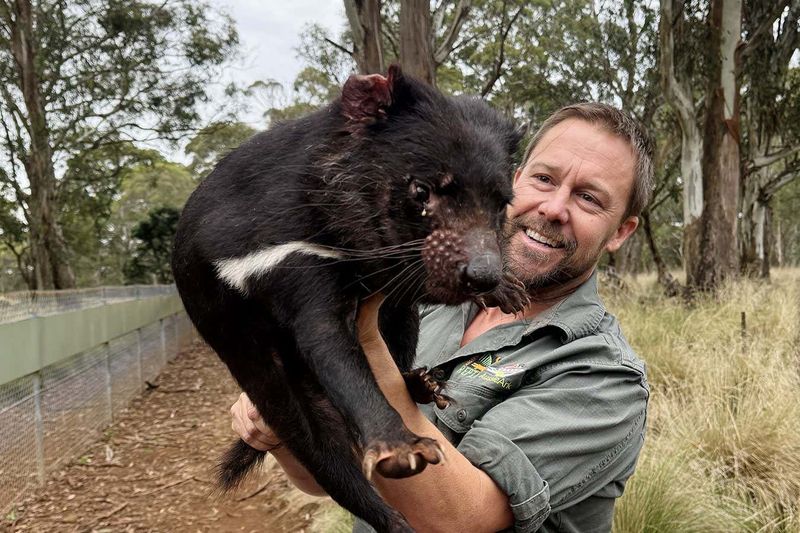

Tasmanian devils face significant threats from a contagious cancer called Devil Facial Tumour Disease (DFTD). This disease has decimated their populations, prompting conservationists to establish breeding and quarantine programs.
These programs aim to create a healthy population free from the disease. Human intervention is crucial for their survival, as natural recovery would be unlikely.
Through dedicated efforts, there is hope for the species’ recovery in the wild. The support of conservation projects is vital in ensuring that Tasmanian devils continue to thrive amid these challenges.
Coral Reefs
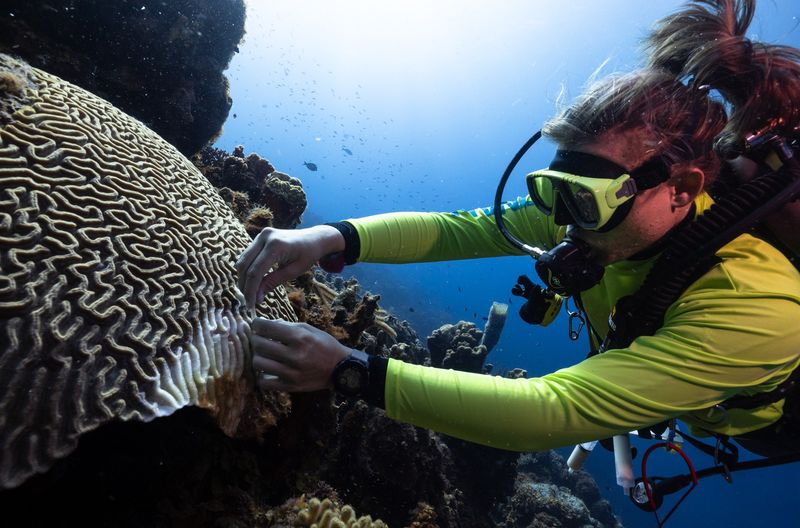

Coral reefs, though not animals in the traditional sense, are vital marine ecosystems. They face threats from climate change and ocean acidification, leading to widespread bleaching.
Conservation efforts focus on restoring damaged reefs and promoting sustainable fishing practices. Human intervention is crucial to mitigate these threats and aid recovery.
Without our help, the complex ecosystems within coral reefs would collapse, affecting countless marine species. Our role in their preservation is pivotal to maintaining biodiversity in our oceans.
Elephants
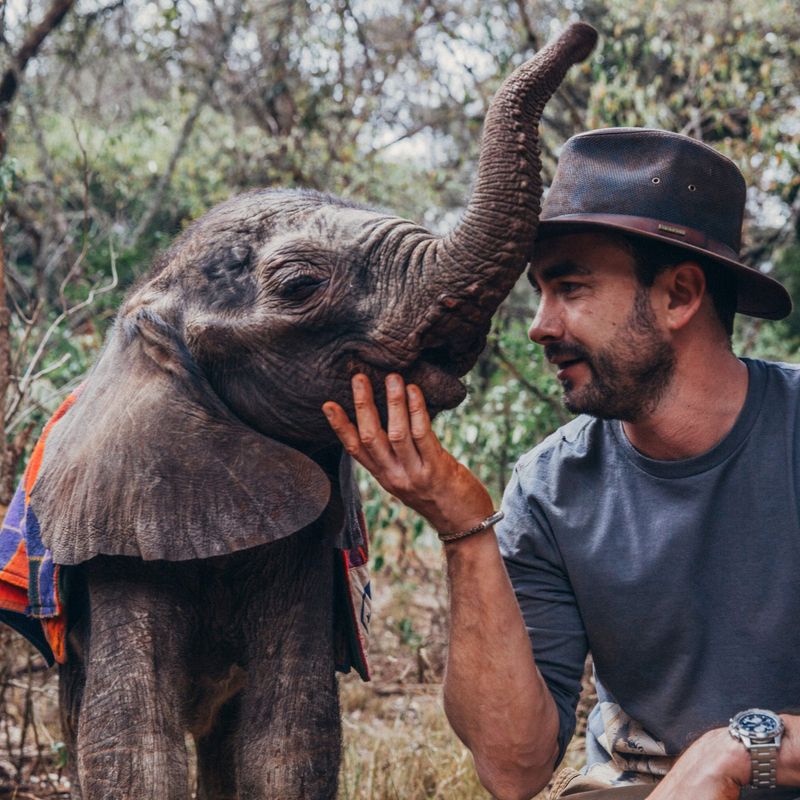

Elephants are magnificent creatures, but they face significant threats from poaching and habitat destruction. Conservation programs work tirelessly to protect them through anti-poaching efforts and habitat conservation.
Sanctuaries provide safe havens for elephants, ensuring they have space to roam and thrive. Human involvement is crucial to safeguard these gentle giants from extinction.
Through concerted global efforts, we can ensure that future generations witness the majesty of elephants in the wild, underscoring the necessity of our ongoing commitment to their preservation.
Amur Leopards
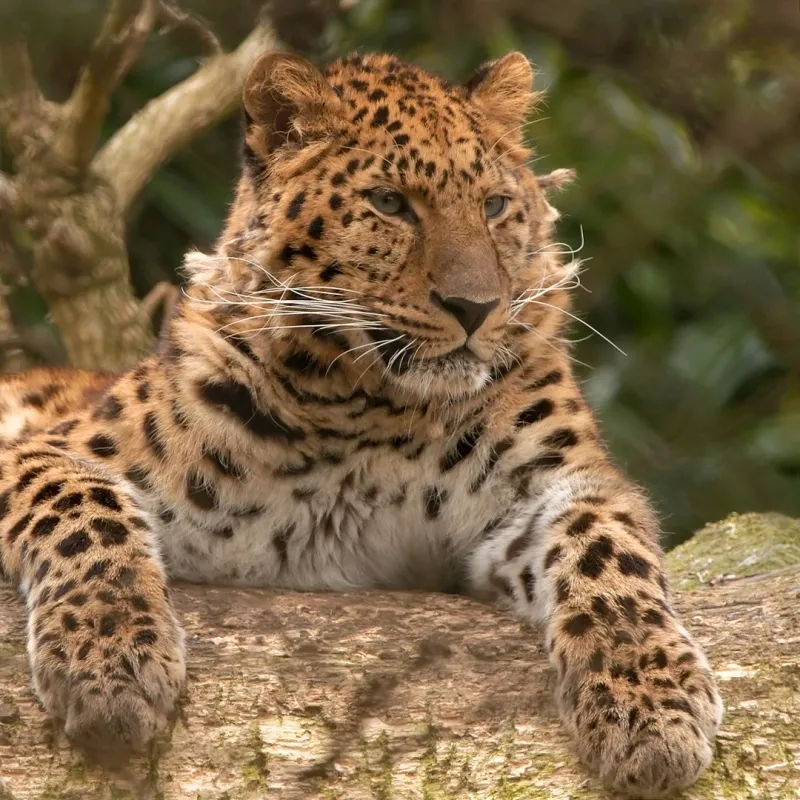

The critically endangered Amur leopard is one of the rarest cats in the world. Due to habitat loss and poaching, only a few individuals remain in the wild.
Conservation initiatives focus on habitat protection and anti-poaching measures. Breeding programs aim to increase their numbers, offering hope for their survival.
Human intervention is key to preventing the extinction of these beautiful creatures. By supporting conservation efforts, we can help secure a future for Amur leopards in their natural habitat.
Bald Eagles
Bald eagles, once endangered, have made a remarkable recovery thanks to conservation efforts. DDT, a harmful pesticide, led to their decline but was banned, allowing populations to rebound.
Protection of nesting sites and habitats remains crucial to their ongoing survival. Human intervention continues to play a vital role in monitoring eagle populations and ensuring their habitats are preserved.
Their resurgence is a testament to the positive impact of dedicated conservation work, serving as an inspiration for protecting other vulnerable species.
Black-footed Ferrets
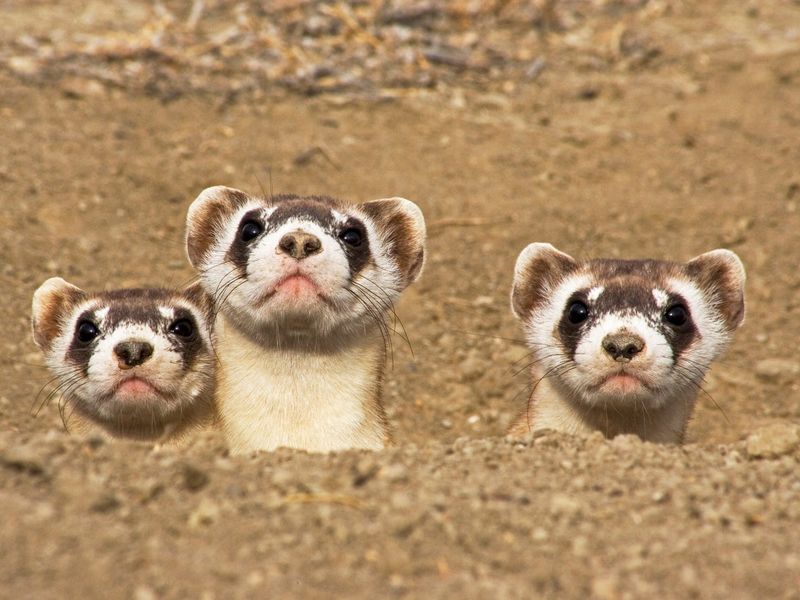

Black-footed ferrets were once thought extinct until a small population was discovered in 1981. Captive breeding programs have since revived their numbers, with reintroduction efforts ongoing.
Their survival hinges on the availability of prairie dog populations, their primary prey, which also requires protection. Human care is essential to maintain these delicate ecosystems.
Without intervention, black-footed ferrets would not have the chance to roam the prairies once more. Continued efforts are necessary to ensure their persistence in the wild.
Mountain Gorillas
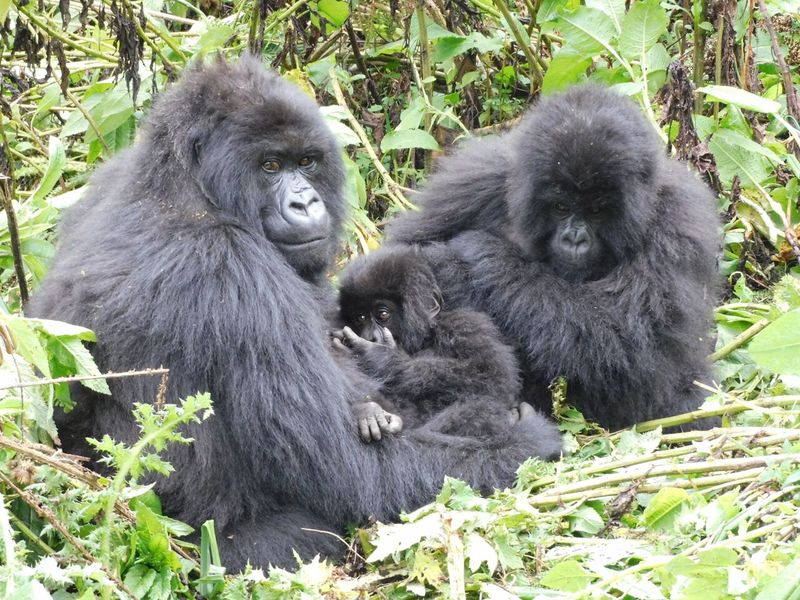

Mountain gorillas, living in the dense forests of Central Africa, face threats from poaching and habitat destruction. Conservation efforts focus on anti-poaching measures and habitat preservation.
Ecotourism provides funding for these initiatives, offering a sustainable way to support gorilla populations. Human intervention is crucial for their survival, as natural recovery is unlikely.
Through dedicated efforts, mountain gorillas have seen population increases, but continued vigilance is necessary to ensure their future in the wild.
Hawksbill Turtles
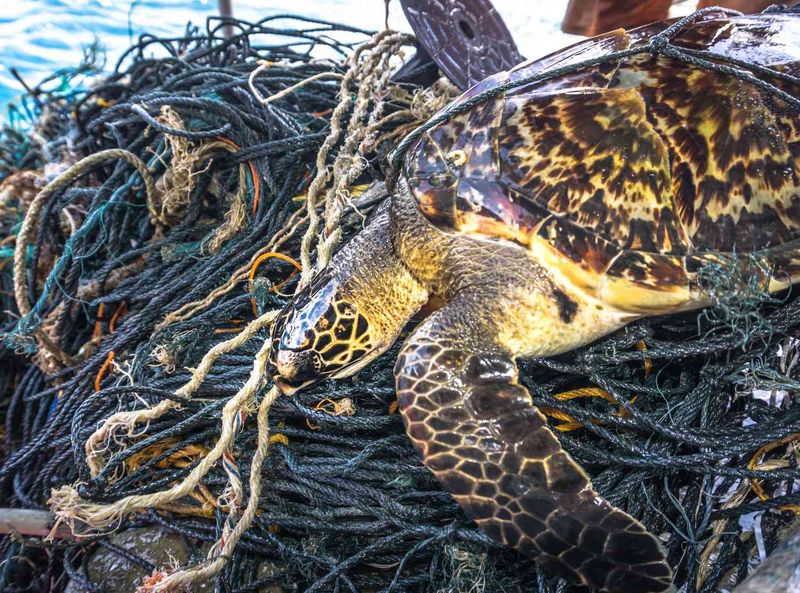

Hawksbill turtles, known for their beautiful shells, face numerous threats from poaching and habitat loss. Conservation programs focus on protecting nesting sites and reducing bycatch in fishing operations.
Human intervention has been instrumental in stabilizing their populations, but ongoing efforts are needed to address climate change impacts. Without our support, hawksbill turtles would struggle to survive in the wild.
By continuing conservation initiatives, we can help ensure that these ancient mariners navigate the oceans for generations to come.
Koalas
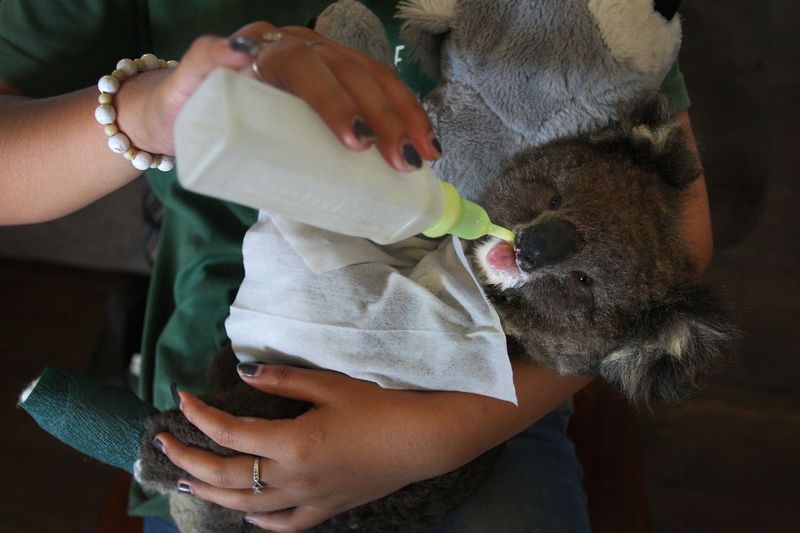

Koalas, native to Australia, face challenges from habitat destruction and disease. Conservation programs work to preserve eucalyptus forests and treat sick koalas.
Human care is crucial for their survival, as natural habitats continue to shrink. Efforts to rehabilitate and release healthy individuals are vital to maintaining populations.
Through dedicated conservation work, we can ensure koalas continue to thrive in Australia’s unique landscapes, highlighting the importance of protecting both the animals and their habitats.
Northern White Rhinos
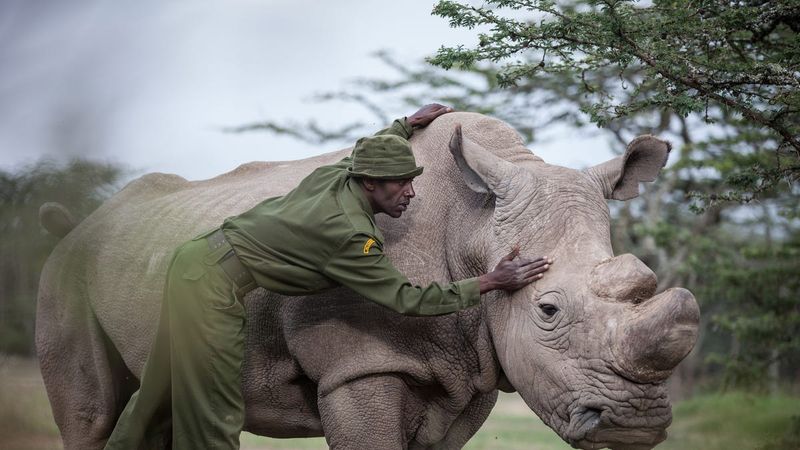

The northern white rhino is on the brink of extinction, with only two known individuals remaining, both female. Conservationists are racing to save the species through advanced reproductive technologies.
Without human intervention, these majestic creatures would vanish forever. Efforts include creating viable embryos for potential future surrogates.
The plight of the northern white rhino highlights the urgent need for conservation and innovative approaches to save endangered species from extinction.
Snow Leopards

Snow leopards are elusive big cats living in Central Asia’s cold, rugged mountains. They face threats from poaching and habitat fragmentation.
Human intervention focuses on community engagement and anti-poaching initiatives. Conservationists work to create a harmonious coexistence between locals and these majestic predators.
Without our efforts, snow leopards would struggle to survive. Supporting conservation programs helps protect these elusive creatures and ensures their continued presence in the wild.
Vaquitas
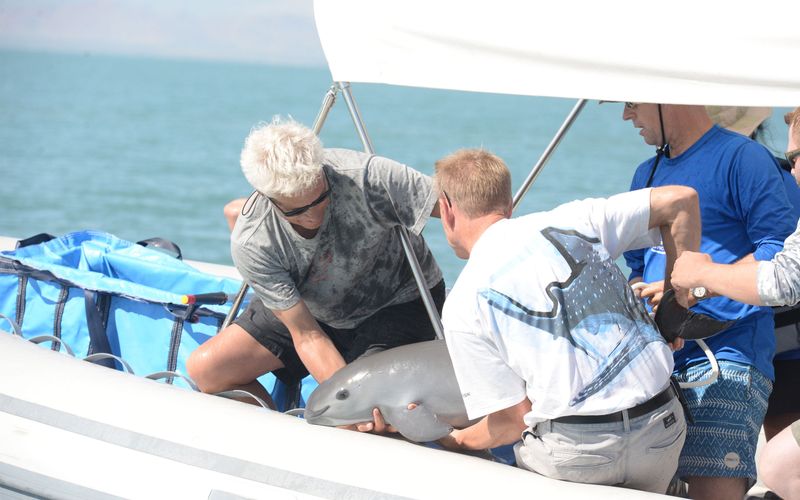

The vaquita, a small porpoise, is critically endangered, with only a few individuals left in the wild. Bycatch in illegal fishing nets is a major threat to their existence.
Conservationists are working to remove these nets and raise awareness about the vaquita’s plight. Without immediate action, they face imminent extinction.
Human intervention is crucial to save the vaquita from disappearing entirely. Supporting conservation efforts can help protect these rare marine mammals and secure their future.
Orangutans
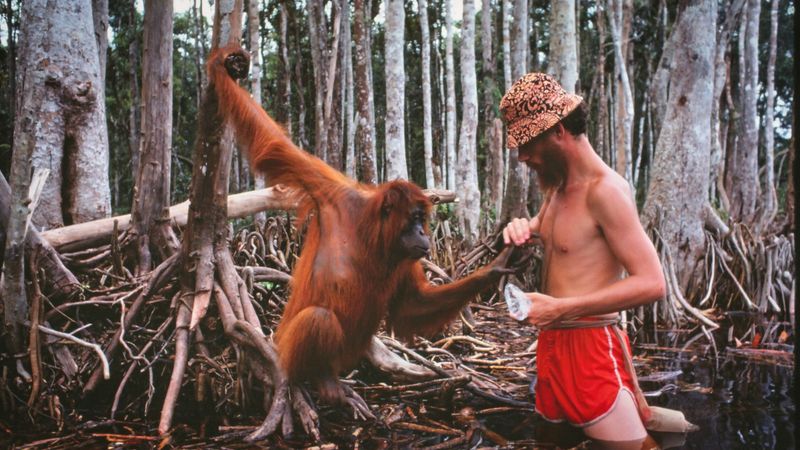

Orangutans, native to Borneo and Sumatra, are threatened by deforestation and illegal wildlife trade. Conservation programs focus on habitat protection and rehabilitation of rescued individuals.
Human support is vital to prevent their extinction, as natural habitats continue to dwindle. Ecotourism provides funding for conservation efforts, creating awareness about their plight.
By preserving forests and fostering community involvement, orangutans have a fighting chance to thrive in their natural environment.
Blue Whales
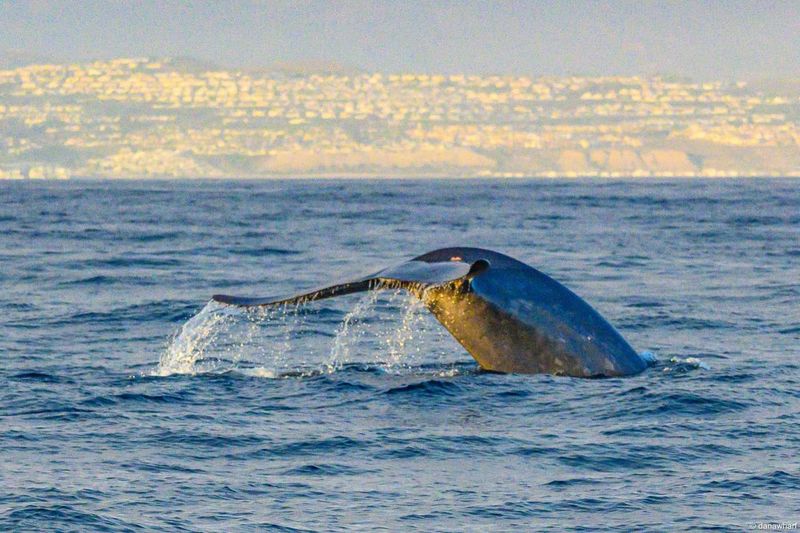

Blue whales, the largest animals on Earth, were once hunted to near extinction. Conservation efforts, including international whaling bans, have aided their recovery.
Human intervention remains important to monitor populations and protect them from threats like ship strikes and ocean noise. Continued vigilance is necessary to ensure their survival.
The recovery of blue whales highlights the power of global cooperation in conserving marine life, but ongoing efforts are essential to secure their future.
Iberian Lynxes
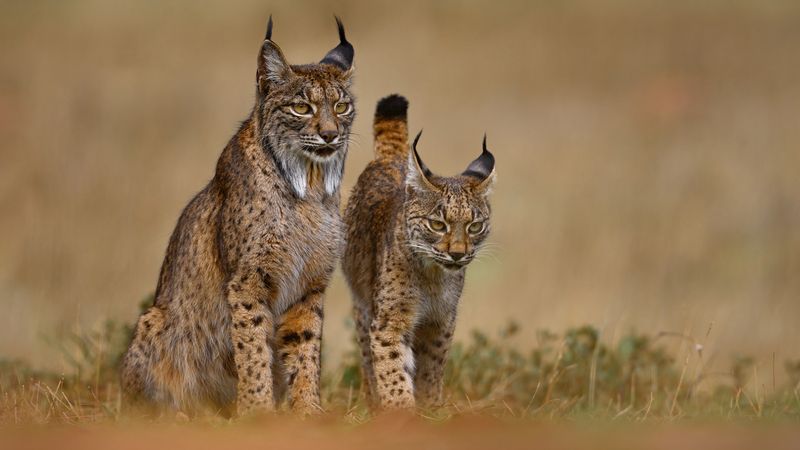

The Iberian lynx, one of the world’s most endangered felines, has seen population increases due to dedicated conservation efforts. Habitat destruction and prey scarcity threatened their survival.
Breeding programs and habitat restoration have been instrumental in their recovery. Human intervention is crucial to maintain these gains and ensure their future.
Supporting conservation initiatives helps protect the Iberian lynx and preserve the biodiversity of their natural habitats.
Gharials
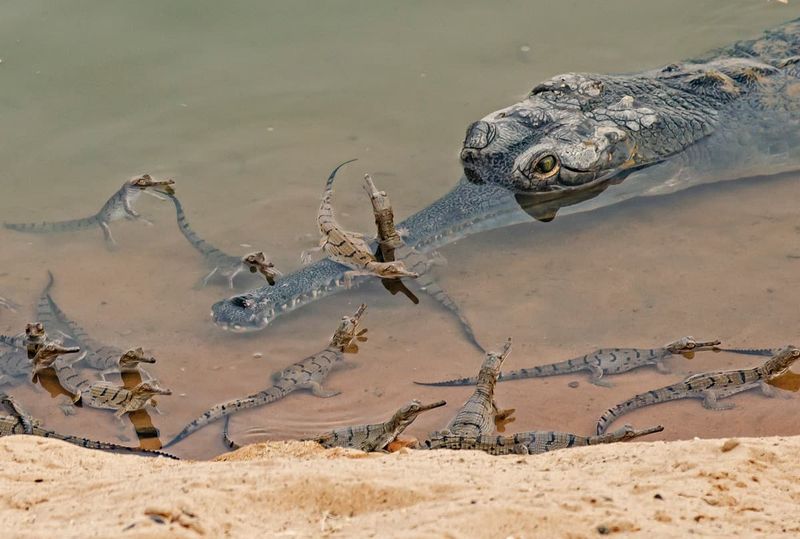

Gharials, fish-eating crocodilians, are critically endangered due to habitat loss and fishing net entanglement. Conservation programs focus on protecting nesting sites and monitoring populations.
Human intervention is crucial for their survival, as natural habitats continue to deteriorate. Breeding programs aim to bolster wild populations.
Without ongoing conservation efforts, gharials would face extinction. Our role is pivotal in ensuring these unique reptiles continue to inhabit their riverine environments.
Sumatran Tigers
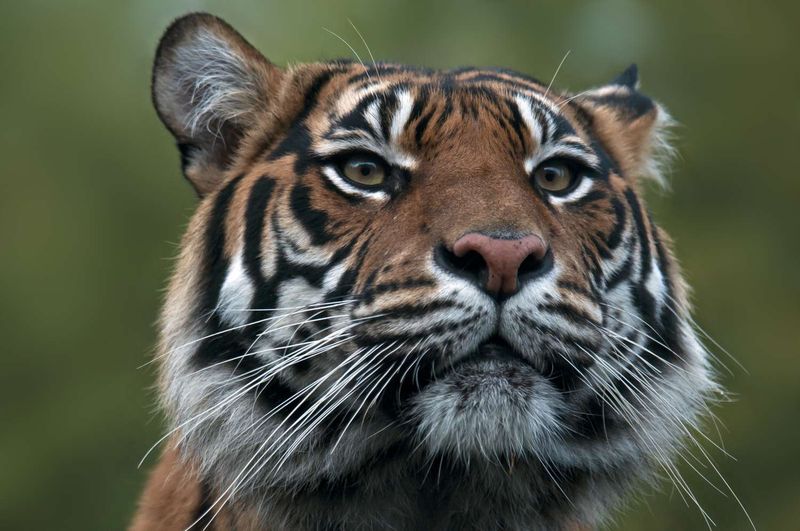

Sumatran tigers are critically endangered, with habitat loss and poaching posing significant threats. Conservation efforts focus on habitat protection and anti-poaching measures.
Human care is essential to safeguard these magnificent cats, as their natural environment continues to dwindle. Successful breeding programs offer hope for their survival.
The plight of Sumatran tigers underscores the need for ongoing conservation work to ensure these majestic predators continue to roam the forests of Sumatra.
Saiga Antelope

The Saiga Antelope, an odd-looking creature with a bulbous nose, resides primarily in the vast steppes of Central Asia. Human intervention has become vital for its survival due to habitat loss and poaching. Conservationists have been relentless in efforts to protect these unique antelopes, ensuring their grassy plains remain a safe haven.
Their unusual appearance, with a flexible nose adapted to filter dust, sets them apart. Yet, without human care, their existence would be precarious. By maintaining protected areas and implementing anti-poaching measures, humans play a crucial role in safeguarding these enchanting creatures.

