Animals aren’t just smart—they’re genius when it comes to survival. While humans rely on technology and theories, some creatures cut straight to the chase and solve problems in ways that put us to shame.
They escape from locked enclosures, use tools with mind-blowing precision, and even outsmart scientists studying them. Whether it’s cracking puzzles, navigating impossible obstacles, or outwitting predators, these animals prove that intelligence isn’t exclusive to humans.
And let’s be honest—sometimes their solutions are way more practical than anything we’d come up with. No overthinking, no trial-and-error, just pure instinct and brilliance in action.
Ready to see nature’s problem-solvers in action? Here are the animals that make us question who the real masterminds are.
Pigeons Detecting Cancer
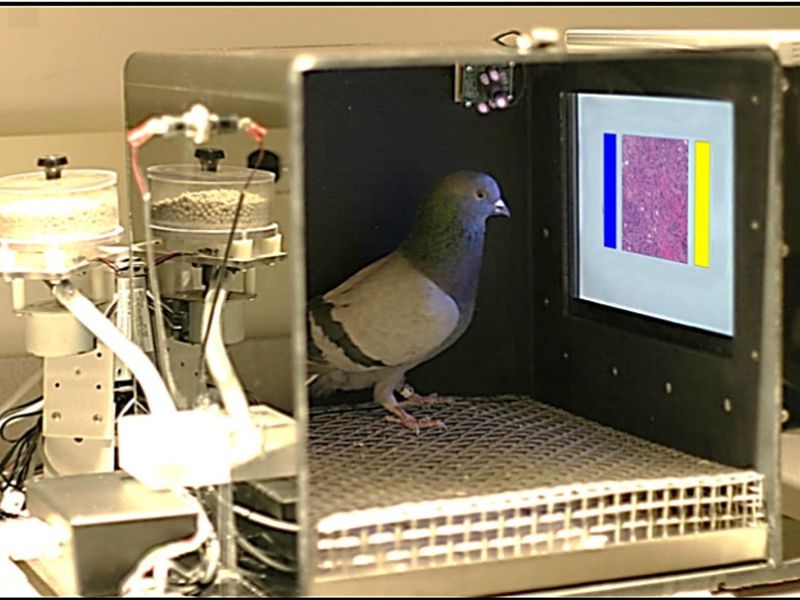
Pigeons have demonstrated an incredible ability to detect cancerous cells in human tissue samples. In controlled experiments, these birds accurately identified malignancy with surprising precision. Their keen eyesight and ability to distinguish between subtle variations in images make them unlikely but effective partners in medical diagnostics. This ability challenges traditional methods and highlights how leveraging nature’s capabilities can benefit human health. By training pigeons to recognize cancer, researchers have opened doors to new, cost-effective diagnostic techniques. This development could revolutionize early detection and make medical testing more accessible to underserved populations, showcasing a unique intersection between ornithology and oncology.
Beavers As Ecosystem Engineers
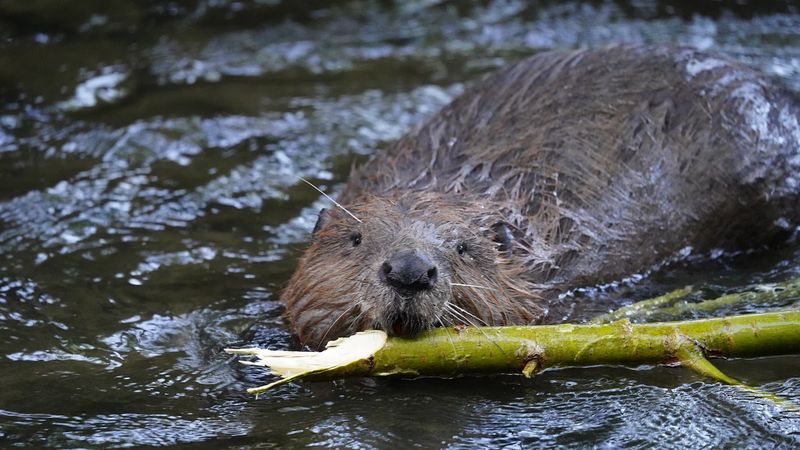

Beavers are often dubbed ‘nature’s engineers’ due to their dam-building prowess. By constructing these structures, beavers create wetlands that support diverse ecosystems. Their work helps to regulate water flow, prevent floods, and maintain water quality. This natural form of landscape management is something human engineers often attempt to replicate but seldom achieve with such ecological balance. Beavers’ activities demonstrate how animal instincts can lead to significant environmental benefits. Their industrious nature not only supports biodiversity but also provides essential services like water purification and habitat creation, which are crucial for many species’ survival.
Ants Teaching Route Efficiency
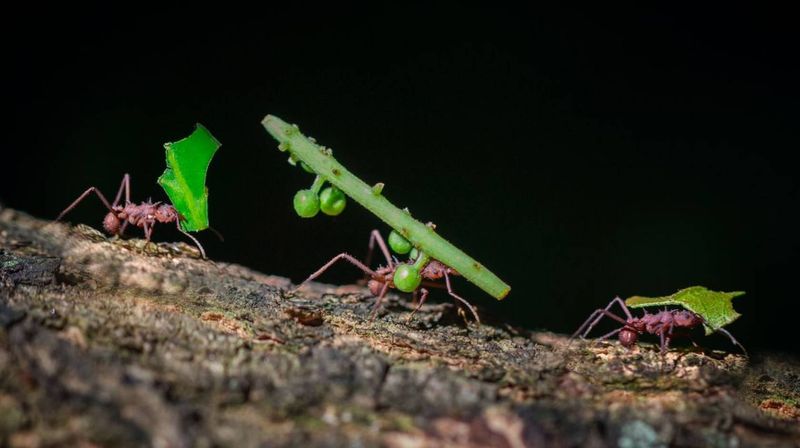

Ants are masters of efficiency, particularly when it comes to finding the shortest route to food sources. Through a process known as ‘ant colony optimization,’ ants use pheromones to communicate and optimize their paths. This concept has inspired algorithms that solve complex human logistical problems. Ants’ innate ability to streamline processes highlights how observing nature can lead to innovations in technology and transportation. These tiny creatures exemplify teamwork and efficiency, reminding us that solutions to human challenges can often be found in the natural world. Such insights influence everything from computer science to urban planning.
Dolphins Using Tools
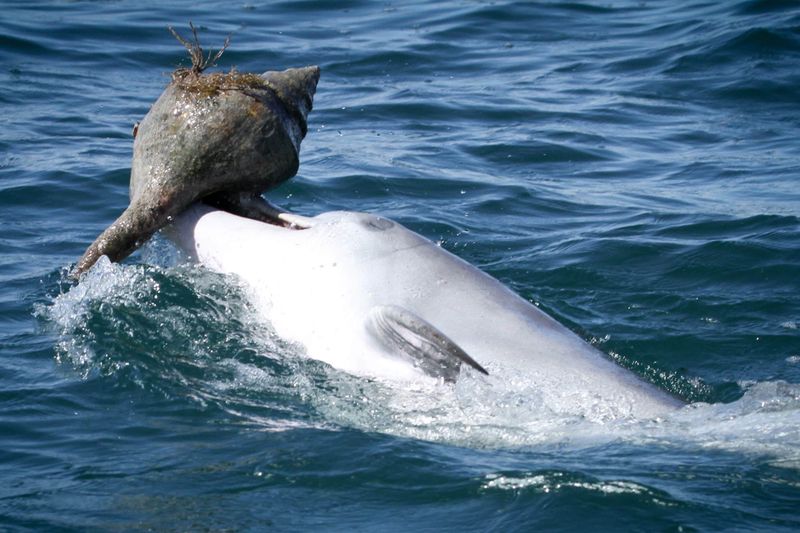

Dolphins are intelligent marine mammals known for their problem-solving abilities, including using tools. Some dolphins use marine sponges to protect their snouts while foraging on the ocean floor. This behavior is passed down through generations, showcasing cultural transmission akin to humans. By adapting their environment to solve challenges, dolphins illustrate the importance of cultural learning and innovation. Such intelligent behaviors emphasize the potential for cooperative tool use in solving ecological problems. This insight into dolphin behavior enhances our understanding of animal cognition and the ways we can learn from them to foster creativity and adaptability.
Octopuses Escaping Cages
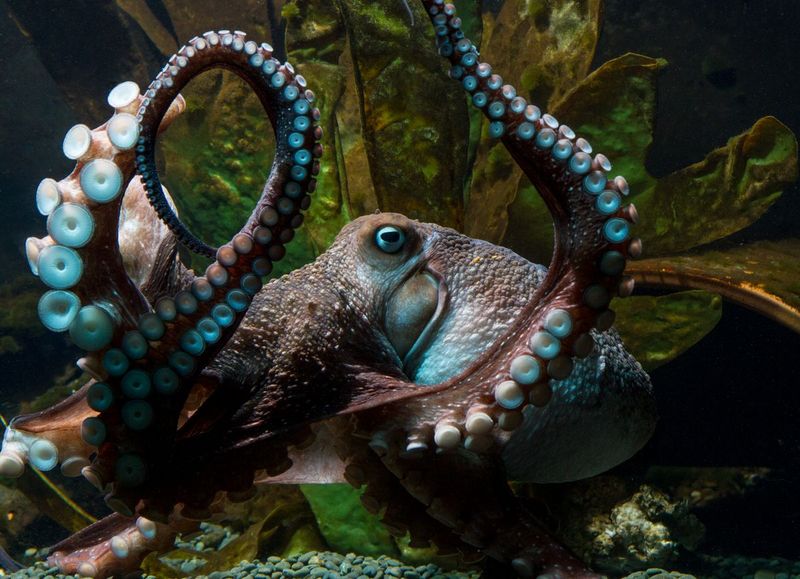

Octopuses are renowned for their escape artistry, often slipping out of enclosures that seem secure. Their ability to manipulate objects and navigate complex environments astounds scientists. This skill is not just a spectacle but demonstrates advanced problem-solving and intelligence. Octopuses’ capabilities prompt us to rethink how we understand animal intelligence and adaptability. By studying their behaviors, researchers gain insights into neurological plasticity and problem-solving skills. These remarkable cephalopods encourage innovative thinking in robotics and design, as their flexible movements and cognitive abilities inspire advancements in creating adaptive machines.
Crows Solving Puzzles
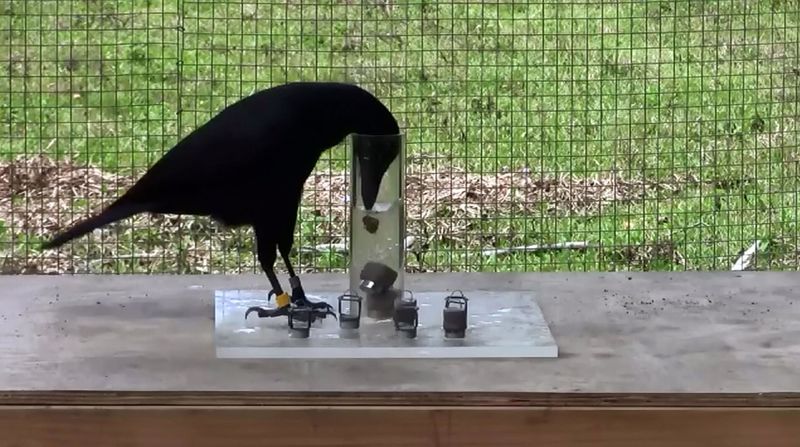

Crows are highly intelligent birds known for solving complex puzzles to access food. Researchers have documented instances where crows use tools like sticks to retrieve out-of-reach items. Their problem-solving skills mirror those of young children and offer insights into avian intelligence. Observing crows in action highlights their ability to plan and execute intricate tasks. These birds demonstrate cognitive processes similar to humans, challenging us to rethink the boundaries of animal intelligence. Their ingenuity inspires innovations in artificial intelligence and robotics, as understanding their problem-solving strategies can lead to breakthroughs in technology.
Elephants Using Self-Medication
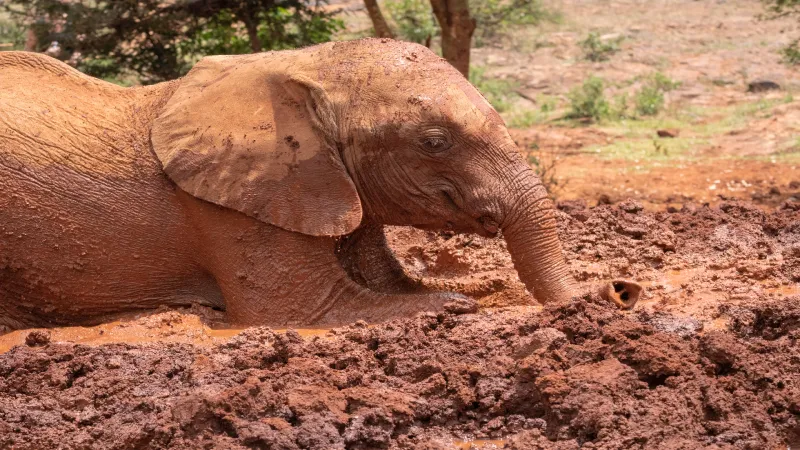

Elephants have been observed using plants for self-medication, a practice known as zoopharmacognosy. These animals consume specific plants to alleviate ailments such as digestive issues or parasitic infections. This behavior illustrates an intuitive understanding of herbal medicine. By observing elephants, scientists explore natural remedies and their potential applications in human medicine. This practice underscores the importance of biodiversity and the wisdom animals possess regarding their health. Elephants’ self-medication offers insights into the development of new pharmaceuticals, highlighting the interconnectedness of ecosystems and human health in discovering innovative treatments.
Parrots Mimicking Human Speech
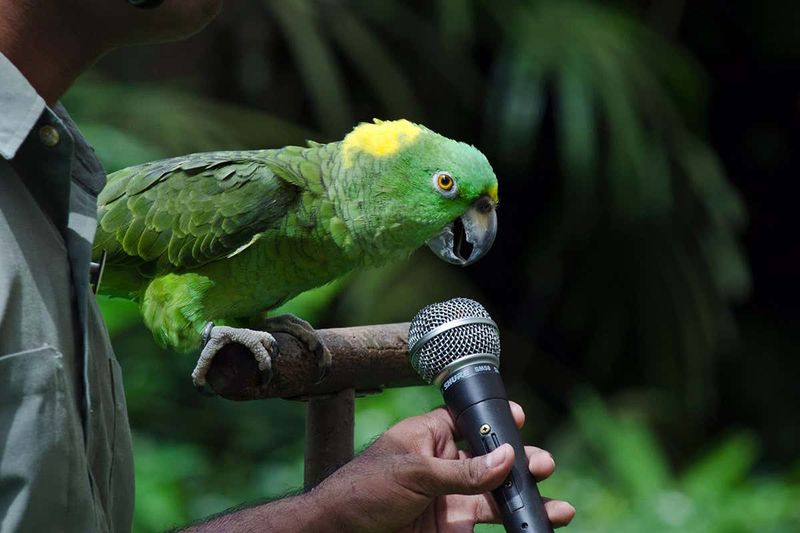

Parrots are famous for their ability to mimic human speech, a skill that requires complex vocal learning. This ability to replicate sounds is not just a party trick; it reflects their sophisticated brain functions. Parrots’ capability to understand and use language-like communication offers insights into the evolution of speech. Their vocal imitation helps researchers study language development and cognitive processes in animals. By examining parrots, scientists can better understand the foundations of human speech and language acquisition. This interaction between humans and parrots reveals the potential for cross-species communication, enriching both linguistic studies and wildlife conservation efforts.
Bats Navigating with Echolocation
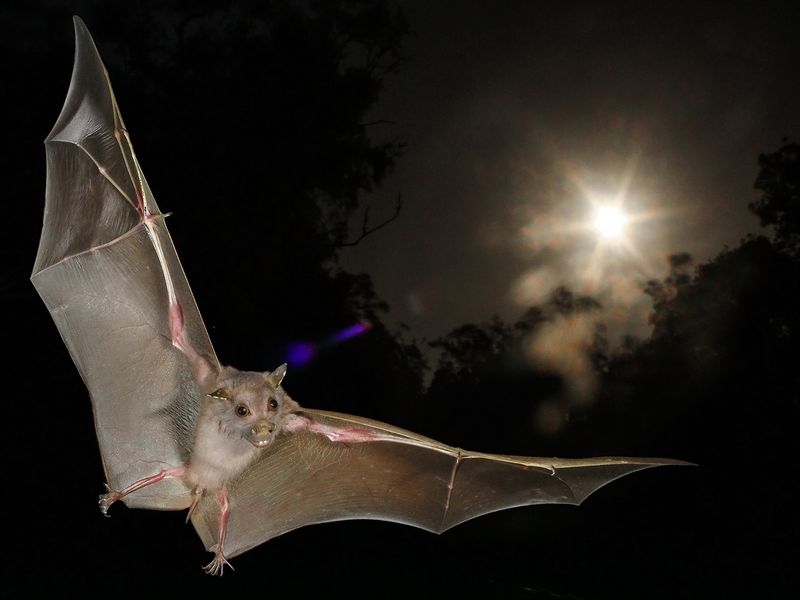

Bats are masters of echolocation, using sound waves to navigate and hunt in complete darkness. This unique ability allows them to detect obstacles and prey with remarkable precision. Bats’ echolocation has inspired technological advancements, particularly in sonar and navigation systems used by humans. Their natural sonar capabilities offer insights into improving human tools for exploration and mapping. By understanding bats’ echolocation, researchers enhance technologies like autonomous vehicle sensors and medical imaging devices. These nocturnal creatures remind us of the potential to learn from nature in developing innovative solutions to complex human challenges.
Honeybees Communicating Through Dance
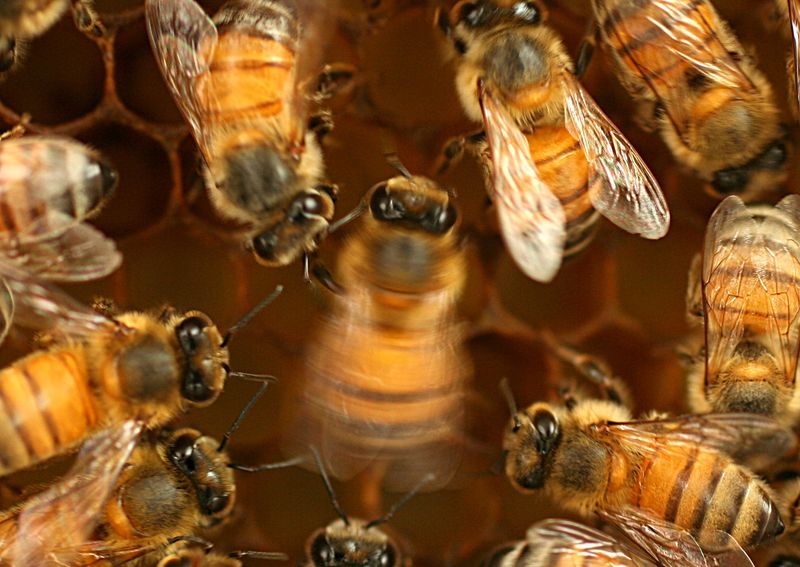

Honeybees communicate through a fascinating method known as the ‘waggle dance,’ which conveys information about the location of food sources. This dance involves specific movements that indicate direction and distance. Bees’ intricate communication methods have inspired studies in information exchange and navigation systems. By decoding their dances, researchers develop better ways to understand collective behavior and coordination. Honeybees’ communication strategies showcase the power of non-verbal information sharing, influencing fields from robotics to social science. Their dances not only ensure hive survival but also offer a window into improving human communication technologies and collaborative efforts.
Chimpanzees Using Sign Language
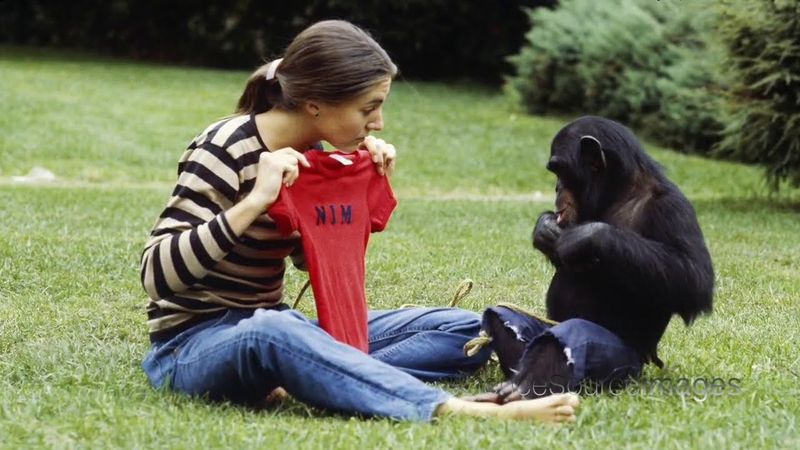

Chimpanzees have shown an ability to learn and use sign language to communicate with humans. This breakthrough highlights their cognitive abilities and parallels with human intelligence. By engaging in sign language, chimpanzees demonstrate complex thought processes and social interactions. This form of communication provides insights into the evolution of language and cognitive development. Observing chimpanzees in this context enriches our understanding of primate behavior and the potential for interspecies communication. Their use of sign language paves the way for new approaches in enhancing human-animal interactions and contributes to conservation efforts by fostering empathy and understanding.
Prairie Dogs Building Complex Burrows
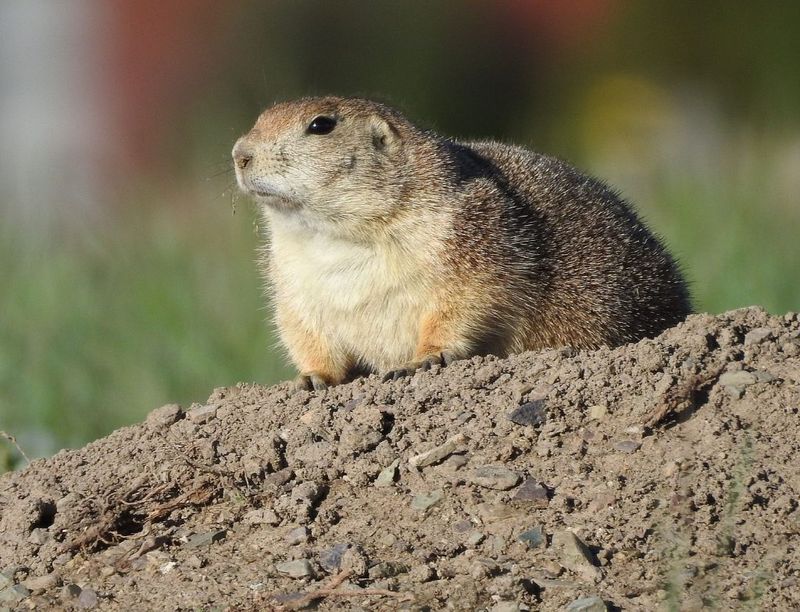

Prairie dogs are skilled architects, constructing complex burrow systems that include chambers and ventilation shafts. These structures provide shelter and regulate temperature, demonstrating remarkable engineering abilities. Prairie dogs’ burrows support entire ecosystems by providing habitats for various species. Their construction techniques inspire sustainable building practices and urban planning. By studying prairie dogs, architects and engineers can learn about efficient design and resource management. These small mammals remind us of the ecological impact of thoughtful construction and the lessons nature offers in creating sustainable living spaces for humans and other species alike.
Rats Learning and Sharing Solutions
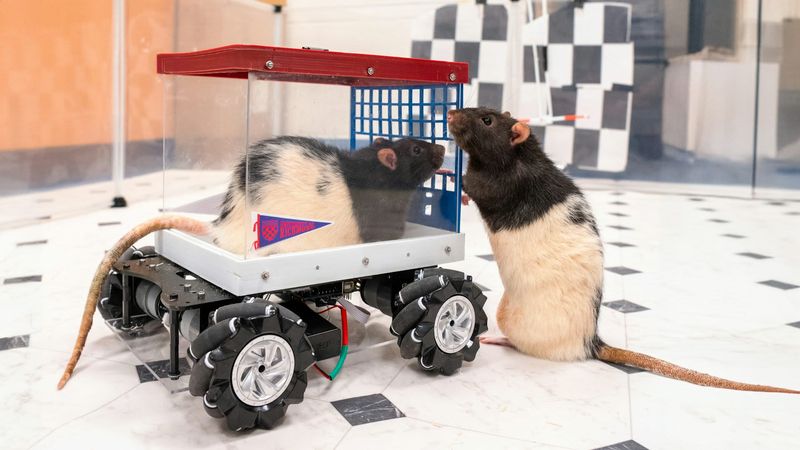

Rats are known for their intelligence and ability to learn from one another. In experiments, rats have shown they can teach peers how to solve complex puzzles, demonstrating social learning. This behavior emphasizes the value of collaboration and knowledge sharing in problem-solving. Observing rats offers insights into team dynamics and learning processes that can be applied to human education systems. Their capacity to work together and pass on knowledge mirrors human learning techniques, highlighting the importance of social interactions in overcoming challenges. Rats’ problem-solving skills continue to inspire research in neuroscience and educational methodologies.
Sea Otters Using Rocks as Tools
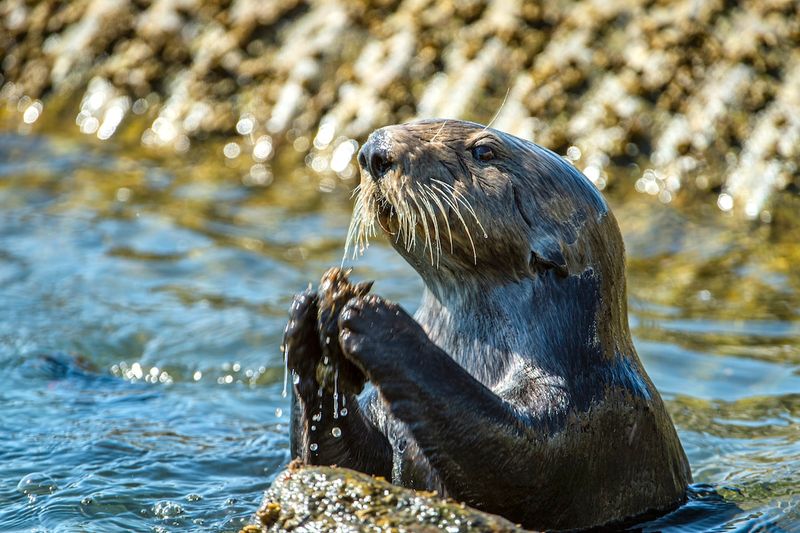

Sea otters are adept at using rocks as tools to crack open shellfish, displaying remarkable problem-solving skills. This behavior is a fascinating example of tool use in marine environments, highlighting their adaptability and intelligence. By watching sea otters, scientists gain insights into the evolution of tool use and its significance in survival. Their actions illustrate the importance of innovation and resourcefulness in overcoming environmental challenges. Sea otters’ tool use encourages further exploration into animal cognition and the parallels between human and animal problem-solving strategies, enriching our understanding of marine life and its complexities.
Orangutans Crafting Umbrellas
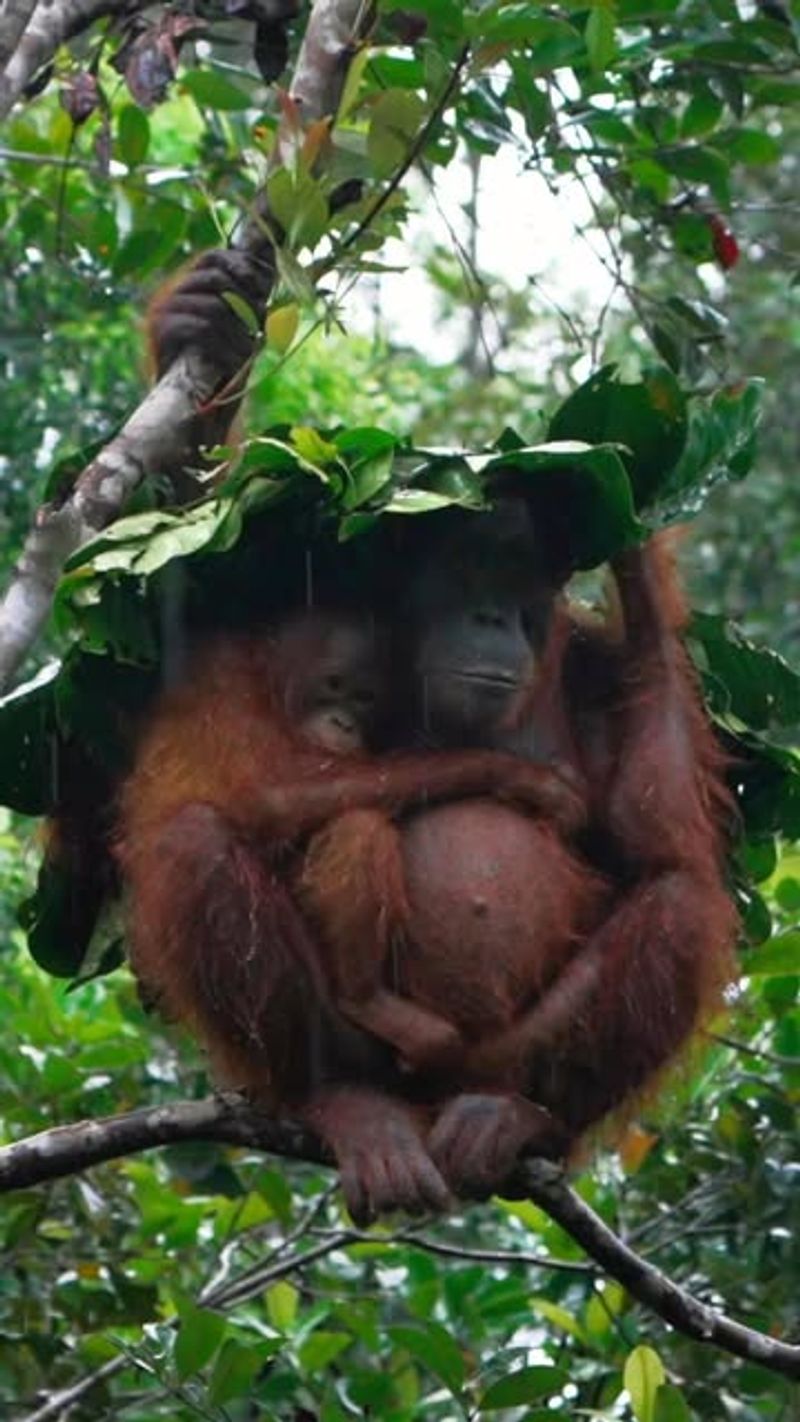

Orangutans have been observed using large leaves as makeshift umbrellas to shield themselves from rain. This behavior showcases their ability to adapt creatively to environmental challenges. By employing natural resources for protection, orangutans demonstrate problem-solving that parallels human ingenuity. This adaptability highlights their critical thinking and resource use, offering insights into primate intelligence. Such behaviors emphasize the importance of understanding animal cognition in conservation efforts. Observing orangutans’ innovative use of tools inspires researchers to explore further into how animals interact with their environment, leading to discoveries that benefit both wildlife and human societies.
Elephants Detecting Water Sources
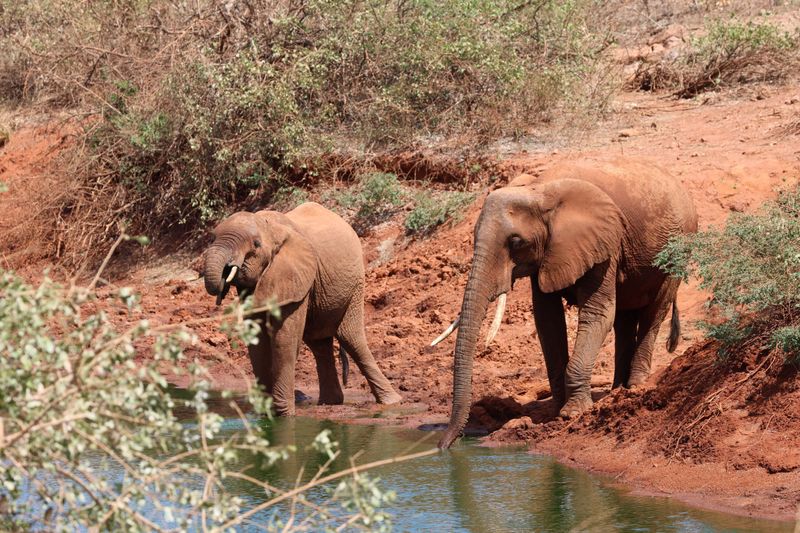

Elephants possess an extraordinary ability to detect underground water sources using their keen sense of smell. This skill is vital for survival in arid environments and has fascinated scientists studying animal sensory capabilities. By understanding elephants’ methods, researchers hope to develop new technologies for water detection in drought-prone areas. This remarkable skill underscores the importance of preserving wildlife and their habitats. Elephants’ natural water-finding abilities inspire innovations that address human challenges, such as resource management and environmental sustainability, showcasing how learning from nature can lead to advancements in technology and conservation.
Cats Sensing Earthquakes
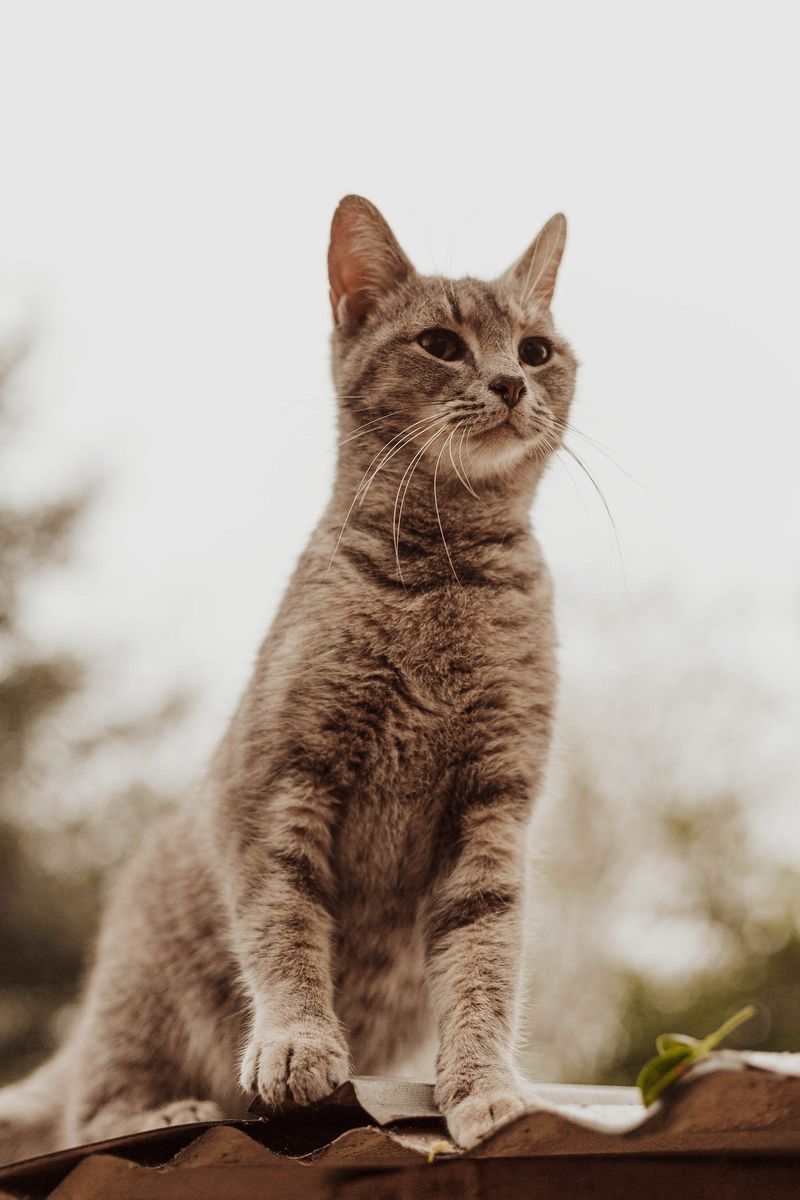

Cats have long been rumored to sense earthquakes before they occur, exhibiting unusual behavior in advance of seismic activity. This phenomenon suggests that cats may detect subtle environmental changes that humans cannot perceive. Their heightened senses provide potential for early warning systems in earthquake-prone regions. Studying cats’ reactions to seismic precursors could lead to breakthroughs in disaster preparedness and safety. These feline behaviors remind us of the untapped potential in understanding animal senses. By observing cats, researchers aim to improve early detection methods, enhancing public safety through insights gleaned from our four-legged companions.
Dogs Detecting Human Emotions
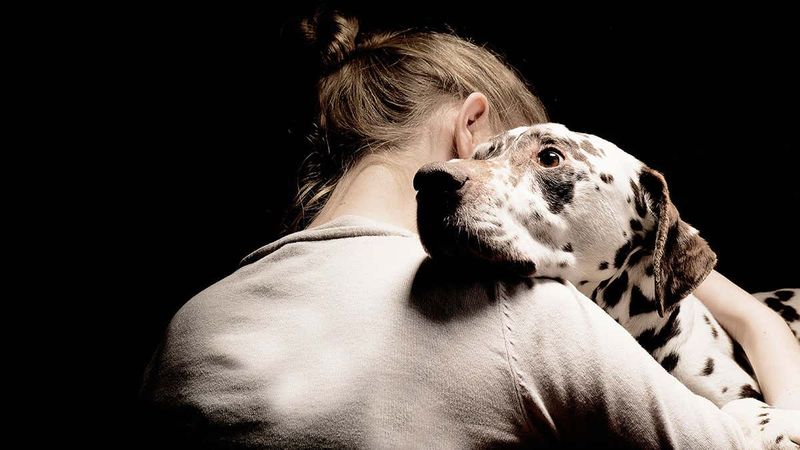

Dogs are known for their exceptional ability to read and respond to human emotions, offering companionship and comfort. This empathetic nature is not only heartwarming but also provides therapeutic benefits. Dogs’ keen sensitivity to emotional cues inspires research into animal-assisted therapy and emotional intelligence. By studying dogs, scientists explore the depth of interspecies relationships and the potential for improving mental health support. Their ability to connect with humans on an emotional level highlights the importance of empathy in both animal and human interactions, fostering a greater understanding of emotional wellness in therapeutic settings.